CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing)
Quick Navigation:
- CIDR Definition
- CIDR Explained Easy
- CIDR Origin
- CIDR Etymology
- CIDR Usage Trends
- CIDR Usage
- CIDR Examples in Context
- CIDR FAQ
- CIDR Related Words
CIDR Definition
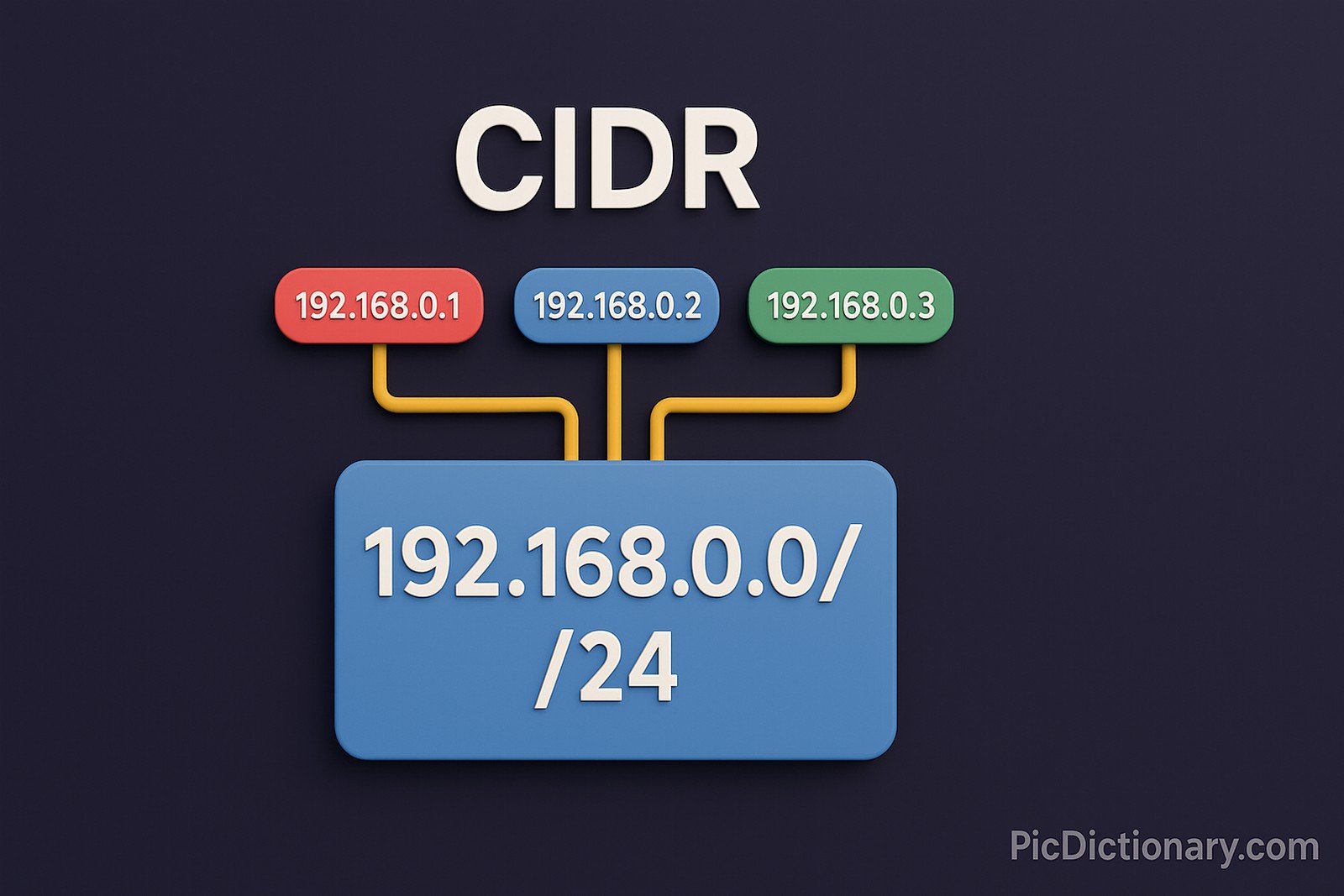
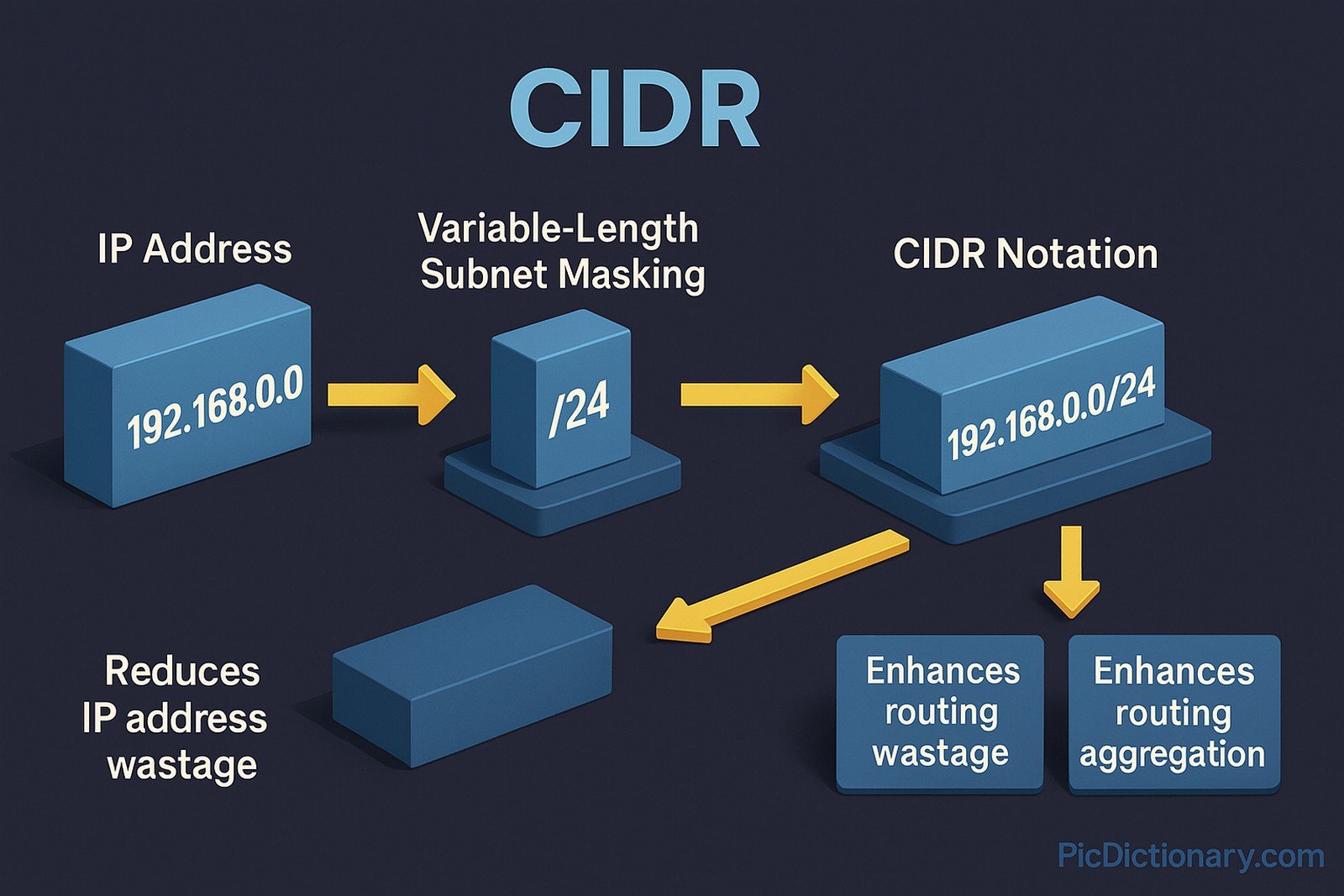
CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) is a method for allocating IP addresses and IP routing that replaced the older system of class-based IP addressing. It allows for more efficient use of IP address space by enabling variable-length subnet masking (VLSM). Through CIDR, IP addresses are written with a suffix indicating the length of the network prefix, such as 192.168.0.0/24. This flexibility significantly reduces IP address wastage and enhances routing aggregation, making the internet more scalable and efficient.
CIDR Explained Easy
Imagine you have a big box of crayons, and you need to share them with friends. Instead of giving each friend a fixed number of crayons whether they need them or not, you give each friend exactly how many crayons they need. That way, no crayons go to waste. CIDR works like that for IP addresses — it lets networks use exactly the number of addresses they need, saving space.
CIDR Origin
CIDR was introduced in 1993 by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) to address the growing problem of IP address exhaustion. It replaced the older system of class-based networking, allowing ISPs and organizations to allocate IP addresses more efficiently and aggregate routing tables to reduce network complexity.
CIDR Etymology
The term "CIDR" combines "classless" to denote its departure from rigid class-based addressing, and "inter-domain routing," indicating its usage in routing between different networks or domains.
CIDR Usage Trends
Since its introduction, CIDR has become the backbone of modern IP address allocation and routing. It is widely used in both IPv4 and IPv6 addressing. The trend of expanding global networks and the exhaustion of IPv4 addresses has kept CIDR highly relevant, with routing tables in large ISPs and data centers relying heavily on CIDR-based aggregation.
CIDR Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- IP Addressing
- Networking
- Routing Protocols - Typical Collocations:
- "CIDR block"
- "CIDR notation"
- "CIDR aggregation"
- "routing with CIDR"
CIDR Examples in Context
- An ISP assigns a business a CIDR block of 192.168.10.0/26 to efficiently use addresses.
- Network administrators use CIDR notation to define subnet sizes in configuration files.
- Large data centers rely on CIDR aggregation to manage complex routing tables.
CIDR FAQ
- What is CIDR?
CIDR is a system for IP address allocation and routing using variable-length subnet masking. - Why was CIDR introduced?
It was introduced to solve the problem of IP address exhaustion and to simplify routing. - What does CIDR notation mean?
CIDR notation includes an IP address followed by a slash and a number indicating the network prefix length. - Is CIDR used in IPv6?
Yes, CIDR principles are also used in IPv6 addressing. - What are the advantages of CIDR?
Efficient address allocation, smaller routing tables, and better scalability. - What is a CIDR block?
A CIDR block is a group of IP addresses defined using CIDR notation. - How does CIDR reduce routing table size?
By allowing route aggregation, multiple networks can be represented with one route entry. - Can CIDR be used in private networks?
Yes, CIDR is commonly used in both private and public networks. - What’s the difference between subnetting and CIDR?
Subnetting divides a larger network into smaller ones; CIDR allows defining variable-size networks outside of traditional class boundaries. - Do I need to understand CIDR to manage a network?
Yes, understanding CIDR is crucial for efficient IP address management and routing.
CIDR Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- IP Addressing
- Subnetting
- Routing
- Internet Infrastructure
Did you know?
CIDR played a vital role in delaying the exhaustion of IPv4 addresses and has been critical to the functioning of the internet, allowing service providers to handle billions of devices with efficient address aggregation.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment