Direct Memory Access (DMA)
Quick Navigation:
- Direct Memory Access (DMA) Definition
- Direct Memory Access (DMA) Explained Easy
- Direct Memory Access (DMA) Origin
- Direct Memory Access (DMA) Etymology
- Direct Memory Access (DMA) Usage Trends
- Direct Memory Access (DMA) Usage
- Direct Memory Access (DMA) Examples in Context
- Direct Memory Access (DMA) FAQ
- Direct Memory Access (DMA) Related Words
Direct Memory Access (DMA) Definition
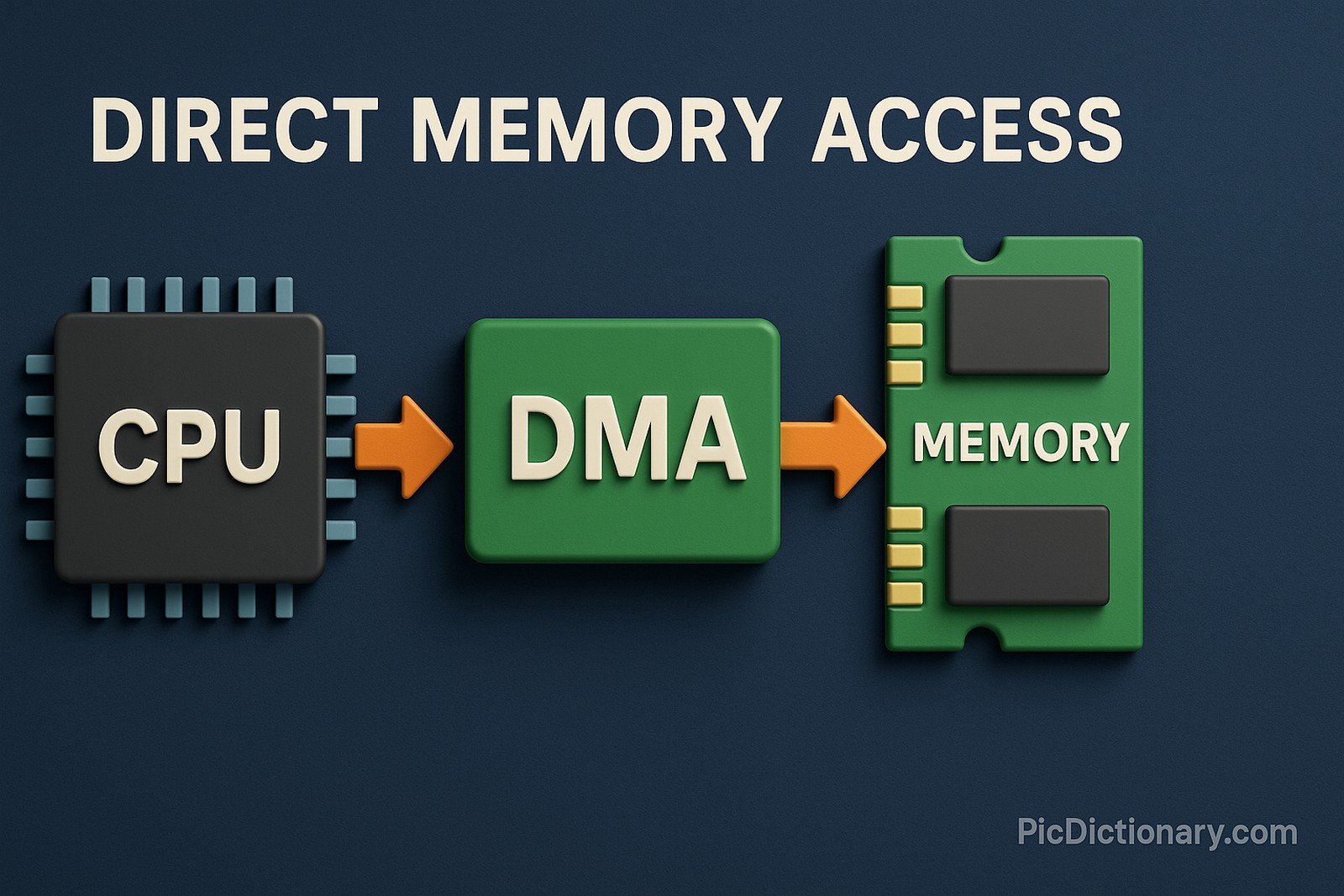
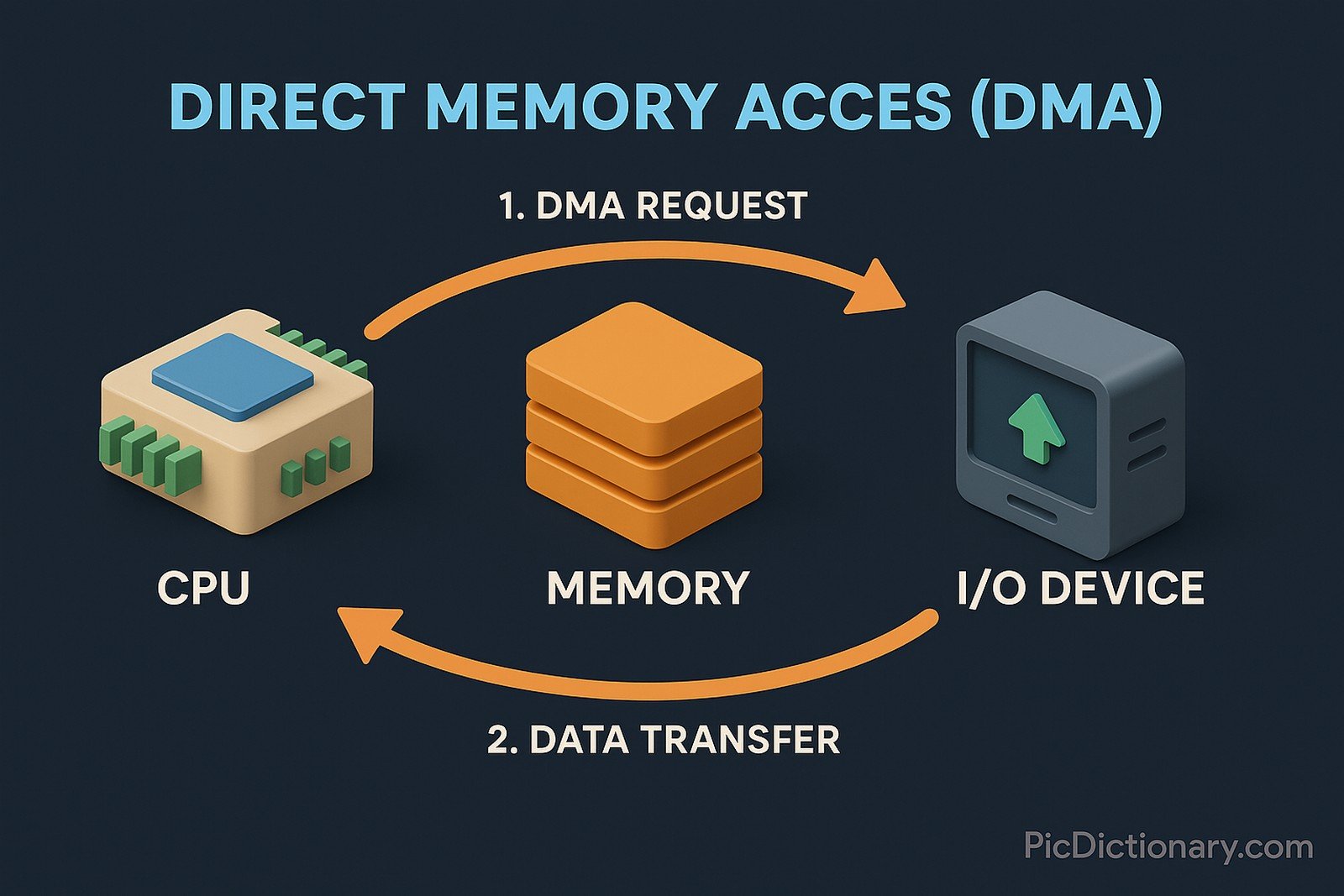
Direct Memory Access (DMA) is a feature in computer systems that allows certain hardware components to access the system’s main memory directly, without the continuous involvement of the central processing unit (CPU). This capability improves system performance by freeing up the CPU for other tasks, enabling faster data transfer between memory and peripherals like hard drives, graphics cards, and sound cards. DMA controllers handle the data movement and ensure data integrity and synchronization during these operations. It's a crucial part of efficient computer architecture, particularly in data-intensive applications.
Direct Memory Access (DMA) Explained Easy
Imagine if every time you needed something from the kitchen, you had to ask your parent to get it for you. It would slow everything down! DMA is like being allowed to go to the kitchen yourself without asking. In computers, this means devices can talk to memory directly without always asking the CPU to help, making things run much faster.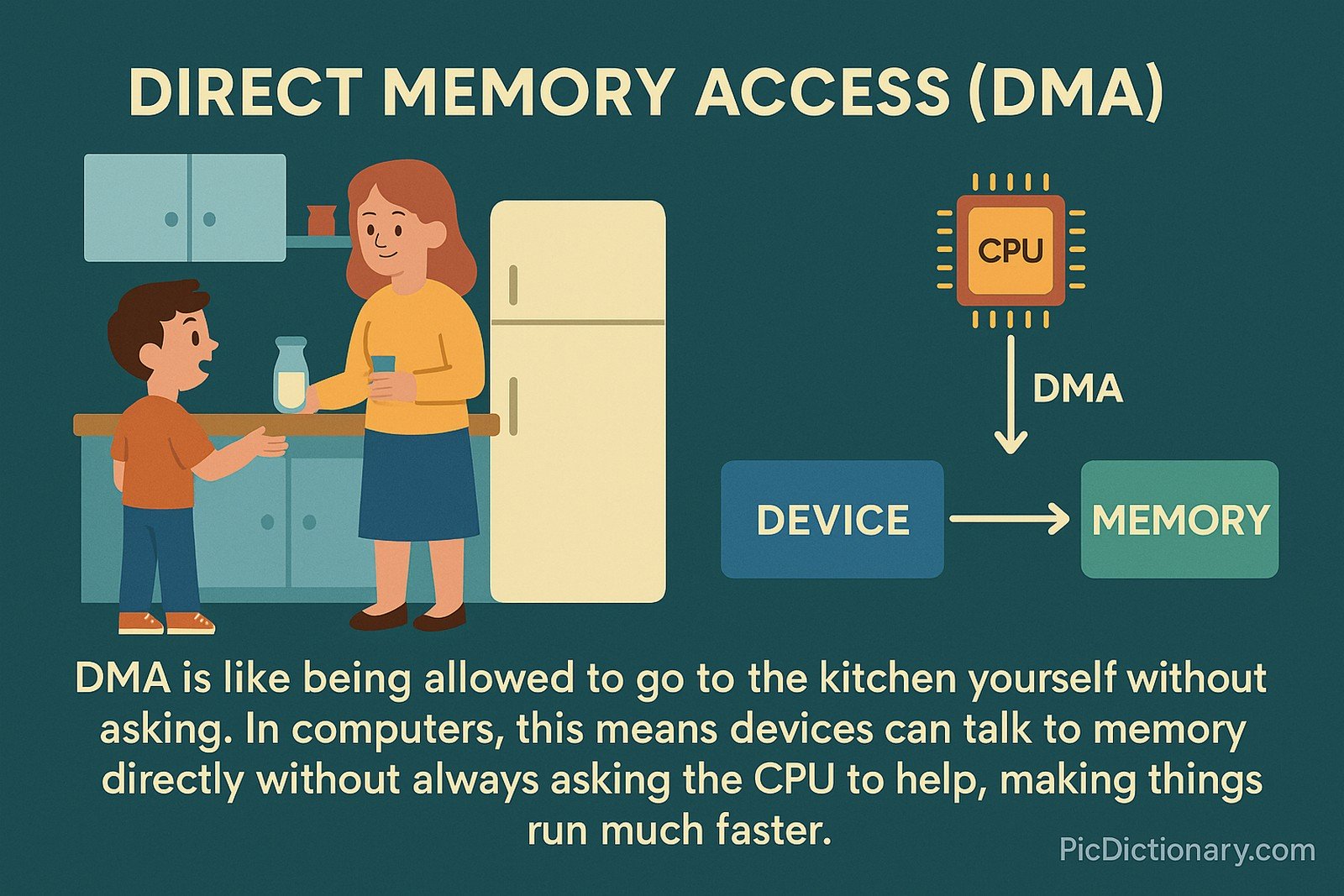
Direct Memory Access (DMA) Origin
DMA was introduced in the early days of computer development to overcome bottlenecks caused by CPUs handling every data transfer task. As systems and peripherals became more advanced in the 1960s and 1970s, DMA became an essential part of computer architecture, particularly in mainframe and early minicomputers.
Direct Memory Access (DMA) Etymology
The term "direct memory access" comes from the system's ability to directly access memory resources, bypassing intermediary control by the processor.
Direct Memory Access (DMA) Usage Trends
DMA has remained consistently important in computer systems. With the growth of high-speed peripherals and real-time applications, the use of DMA has expanded in areas like graphics processing, embedded systems, and networking. Its relevance is continuously reinforced by developments in high-performance computing and consumer electronics.
Direct Memory Access (DMA) Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Computer Architecture
- Data Transfer
- Embedded Systems - Typical Collocations:
- "DMA controller"
- "DMA transfer"
- "DMA channel"
- "high-speed DMA"
- "direct memory access operations"
Direct Memory Access (DMA) Examples in Context
- A graphics card uses DMA to transfer image data directly to system memory without CPU intervention.
- Modern audio interfaces rely on DMA to stream audio data efficiently between storage and the processor.
- In network cards, DMA facilitates fast packet handling by moving data directly into memory buffers.
Direct Memory Access (DMA) FAQ
- What is Direct Memory Access (DMA)?
DMA allows devices to read from or write to the system's main memory without involving the CPU. - Why is DMA used in computers?
It enhances performance by freeing the CPU from data transfer tasks, speeding up operations. - Which devices typically use DMA?
Devices like disk drives, network cards, graphics cards, and sound cards use DMA. - What is a DMA controller?
It’s a dedicated hardware unit that manages and controls DMA operations. - Can DMA transfers occur without CPU involvement?
Yes, though the CPU initiates the request, the transfer itself happens independently. - Does DMA improve gaming performance?
Yes, DMA allows faster data handling, which benefits graphics and audio processing. - How does DMA relate to embedded systems?
DMA in embedded systems helps efficiently manage data between memory and sensors or other interfaces. - Are there different types of DMA?
Yes, including burst mode, cycle stealing, and block transfer. - What are DMA channels?
They are specific pathways used for handling multiple DMA operations simultaneously. - Does DMA have security risks?
Improperly managed DMA can be exploited for unauthorized memory access, so secure system design is essential.
Direct Memory Access (DMA) Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Computer Architecture
- Data Transfer Methods
- Peripheral Communication
Did you know?
DMA technology is critical in spacecraft systems, where data from numerous sensors must be processed and transferred efficiently without overloading the central onboard computer.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment