Logical Volume Manager (LVM)
 (Representational Image | Source: Dall-E)
(Representational Image | Source: Dall-E)
Quick Navigation:
- LVM Definition
- LVM Explained Easy
- LVM Origin
- LVM Etymology
- LVM Usage Trends
- LVM Usage
- LVM Examples in Context
- LVM FAQ
- LVM Related Words
LVM Definition
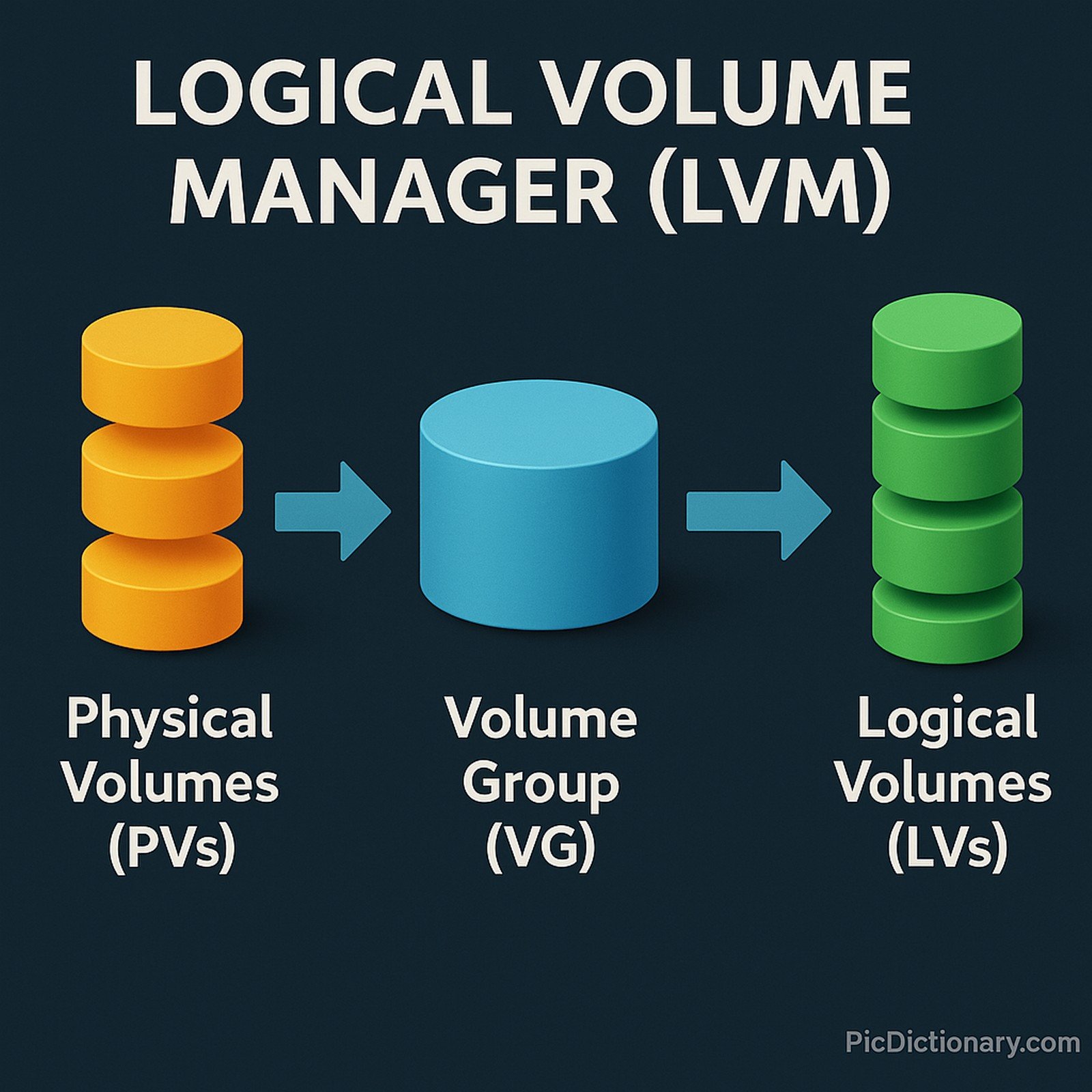
Logical Volume Manager (LVM) is a storage management system that allows for flexible disk partitioning in Linux-based operating systems. It enables users to dynamically allocate, resize, and manage disk space without disrupting the system. LVM abstracts physical storage devices into logical volumes, providing better scalability, snapshotting capabilities, and improved storage utilization. It consists of three layers: Physical Volumes (PVs), Volume Groups (VGs), and Logical Volumes (LVs). This abstraction simplifies storage management and is widely used in enterprise environments.
LVM Explained Easy
Imagine you have a bookshelf with different sections, and each section can expand or shrink as needed. Instead of being stuck with fixed shelves, you can reorganize them freely without buying a new bookshelf. LVM works the same way—it lets your computer manage storage flexibly, so you can resize and move space as required, without being locked into a fixed structure.
LVM Origin
LVM was first introduced in Linux as a response to the need for dynamic storage management. Its design was inspired by the Logical Volume Manager in IBM’s AIX operating system, which was one of the earliest implementations. Over time, LVM evolved with added features like snapshots, RAID support, and thin provisioning, making it a powerful tool for modern storage solutions.
LVM Etymology
The term "Logical Volume Manager" comes from its function—"logical" refers to how storage is structured abstractly rather than physically, and "volume manager" denotes its role in handling disk partitions efficiently.
LVM Usage Trends
LVM has become an essential component of Linux-based servers and virtualization environments. Its ability to dynamically manage storage without downtime makes it highly valuable in cloud computing, high-availability systems, and enterprise data centers. With growing data demands, LVM continues to be a preferred choice for scalable and efficient storage management.
LVM Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Storage Management
- Linux Administration
- Virtualization
- RAID & Snapshots - Typical Collocations:
- "LVM partitioning"
- "LVM snapshot backup"
- "LVM volume resizing"
- "LVM disk management"
LVM Examples in Context
- A system administrator uses LVM to resize a database partition without downtime.
- Cloud service providers use LVM to create logical partitions for virtual machines.
- A Linux user takes an LVM snapshot before upgrading the operating system to ensure rollback capability.
LVM FAQ
- What is LVM used for?
LVM is used for flexible storage management, allowing resizing and efficient partitioning of disk space. - What are the main components of LVM?
LVM consists of Physical Volumes (PVs), Volume Groups (VGs), and Logical Volumes (LVs). - How does LVM differ from traditional partitioning?
Unlike fixed partitions, LVM allows dynamic resizing and reallocation of storage without requiring reformatting. - Can LVM improve performance?
Yes, by distributing data across multiple physical disks, LVM can enhance performance, especially when used with RAID. - Is LVM only available on Linux?
While primarily used in Linux, similar volume management systems exist in other OSes, like Windows Storage Spaces. - What is an LVM snapshot?
An LVM snapshot is a point-in-time copy of a volume, useful for backups and testing. - Can I convert an existing partition to LVM?
Yes, but it requires careful data migration since LVM uses a different partition structure. - Does LVM support encryption?
Yes, LVM can be combined with LUKS (Linux Unified Key Setup) for encrypted storage. - What are the risks of using LVM?
Improper configuration or disk failures can lead to data loss, so backups are essential. - Is LVM beneficial for home users?
Yes, especially for users who frequently manage partitions or require snapshot functionality.
LVM Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Linux Storage
- File Systems
- System Administration
Did you know?
LVM played a critical role in the early days of virtualization. Before modern cloud computing, system administrators used LVM snapshots to create rapid backups and clones of entire systems, minimizing downtime and improving disaster recovery strategies. Even today, LVM remains a fundamental tool in managing virtualized environments.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment