Memory Mapping Unit (MMU)
Quick Navigation:
- Memory Mapping Unit (MMU) Definition
- Memory Mapping Unit (MMU) Explained Easy
- Memory Mapping Unit (MMU) Origin
- Memory Mapping Unit (MMU) Etymology
- Memory Mapping Unit (MMU) Usage Trends
- Memory Mapping Unit (MMU) Usage
- Memory Mapping Unit (MMU) Examples in Context
- Memory Mapping Unit (MMU) FAQ
- Memory Mapping Unit (MMU) Related Words
Memory Mapping Unit (MMU) Definition
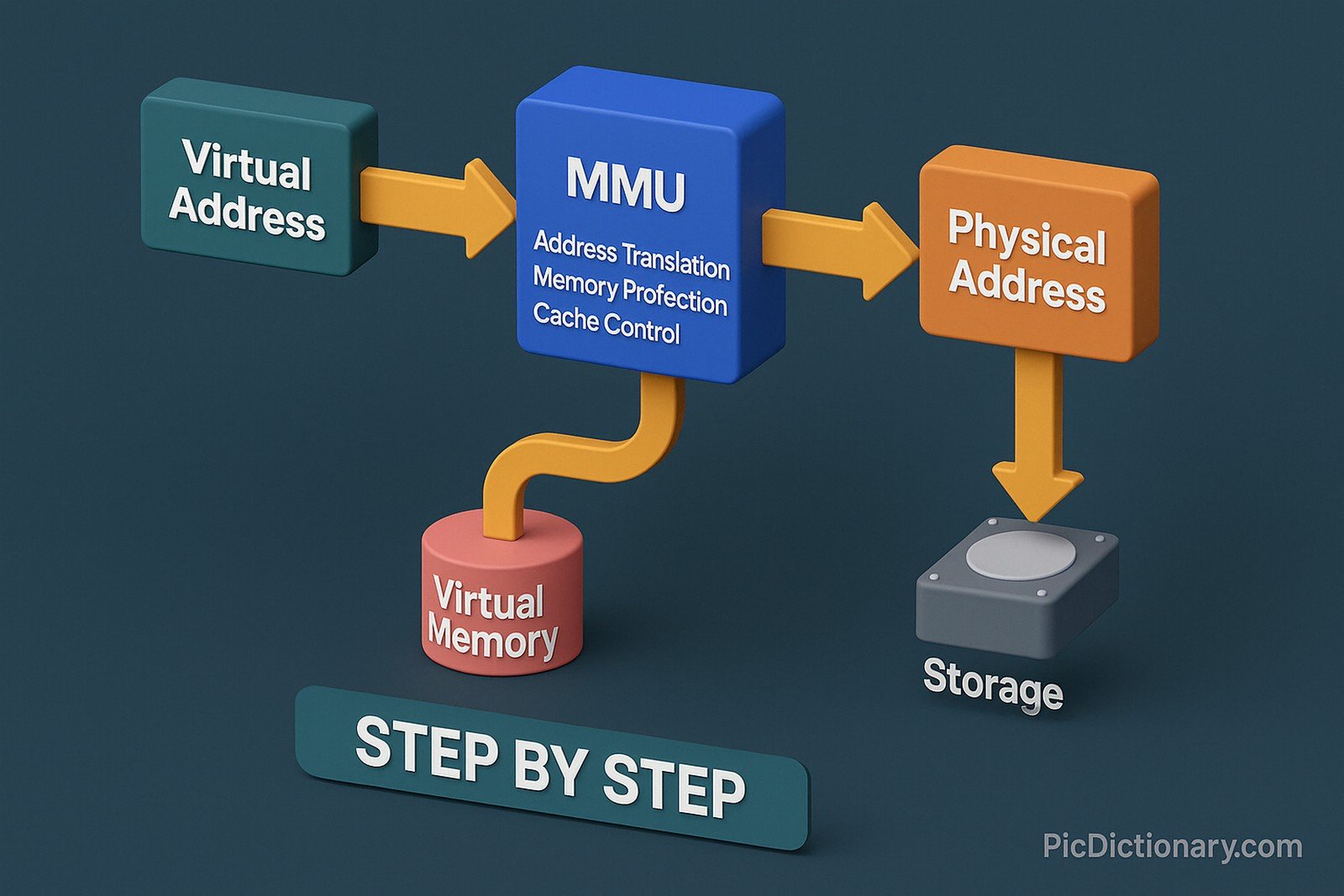
A Memory Mapping Unit (MMU) is a specialized hardware component responsible for translating virtual addresses to physical addresses in a computer's memory system. It allows different programs to access memory without interfering with each other, enabling multitasking and memory protection. The MMU also facilitates virtual memory, allowing the system to use storage devices as temporary RAM. It includes functions like address translation, memory protection, cache control, and bus arbitration, playing a vital role in modern computer architectures.
Memory Mapping Unit (MMU) Explained Easy
Think of your computer as a big building with many rooms, and each room has a different purpose. The MMU is like a security guard who tells you which rooms you can enter and helps you find the right ones without getting lost. It keeps everything organized and safe, making sure you only go where you're allowed.
Memory Mapping Unit (MMU) Origin
The concept of memory mapping dates back to the 1960s when early computer systems began requiring more complex memory management to handle multiple processes and larger programs. The development of the MMU became more significant with the rise of multitasking operating systems.
Memory Mapping Unit (MMU) Etymology
The term comes from the process of "mapping" virtual addresses to physical memory locations, with "unit" signifying its role as a standalone functional block in computer hardware.
Memory Mapping Unit (MMU) Usage Trends
MMUs have become increasingly important with the growth of complex operating systems, embedded devices, and smartphones. Demand for virtualization and secure memory handling has made MMUs critical in both consumer and enterprise computing devices. From microcontrollers in IoT devices to servers in data centers, MMUs are present in nearly all advanced architectures.
Memory Mapping Unit (MMU) Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Hardware Architecture
- Virtual Memory
- Operating Systems - Typical Collocations:
- "memory mapping unit design"
- "MMU configuration"
- "address translation by MMU"
- "MMU-based protection"
Memory Mapping Unit (MMU) Examples in Context
- The processor uses the MMU to translate virtual addresses when accessing memory.
- In smartphones, the MMU helps manage app memory securely and efficiently.
- Embedded systems often rely on an MMU to provide isolation between critical tasks.
Memory Mapping Unit (MMU) FAQ
- What does a Memory Mapping Unit (MMU) do?
It translates virtual addresses to physical addresses and manages memory access and protection. - Why is an MMU important?
It allows safe multitasking, virtual memory usage, and protects memory from unauthorized access. - Where is an MMU used?
In CPUs, embedded systems, servers, and mobile devices. - Can a system function without an MMU?
Some simple microcontrollers can, but complex operating systems generally require an MMU. - How does the MMU improve security?
By isolating processes and controlling access to memory areas. - Does every computer have an MMU?
Most modern computers and devices have one, but ultra-simple microcontrollers might not. - What are common MMU features?
Address translation, access control, cache management, and interrupt handling. - Is MMU part of the CPU?
It can be integrated into the CPU or exist as a separate chip. - How does the MMU affect performance?
It improves system efficiency by optimizing memory usage and providing fast address translation. - Can MMU faults occur?
Yes, faults like page faults happen when addresses are not mapped or permissions are violated.
Memory Mapping Unit (MMU) Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Computer Architecture
- Virtual Memory
- Microprocessor Design
- Embedded Systems
Did you know?
In some advanced processors, the MMU not only handles address translation but also enforces security domains, allowing confidential operations (like cryptographic key management) to occur without risk of leaks or tampering.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment