System Bus
 (Representational Image | Source: Dall-E)
(Representational Image | Source: Dall-E)
Quick Navigation:
- System Bus Definition
- System Bus Explained Easy
- System Bus Origin
- System Bus Etymology
- System Bus Usage Trends
- System Bus Usage
- System Bus Examples in Context
- System Bus FAQ
- System Bus Related Words
System Bus Definition
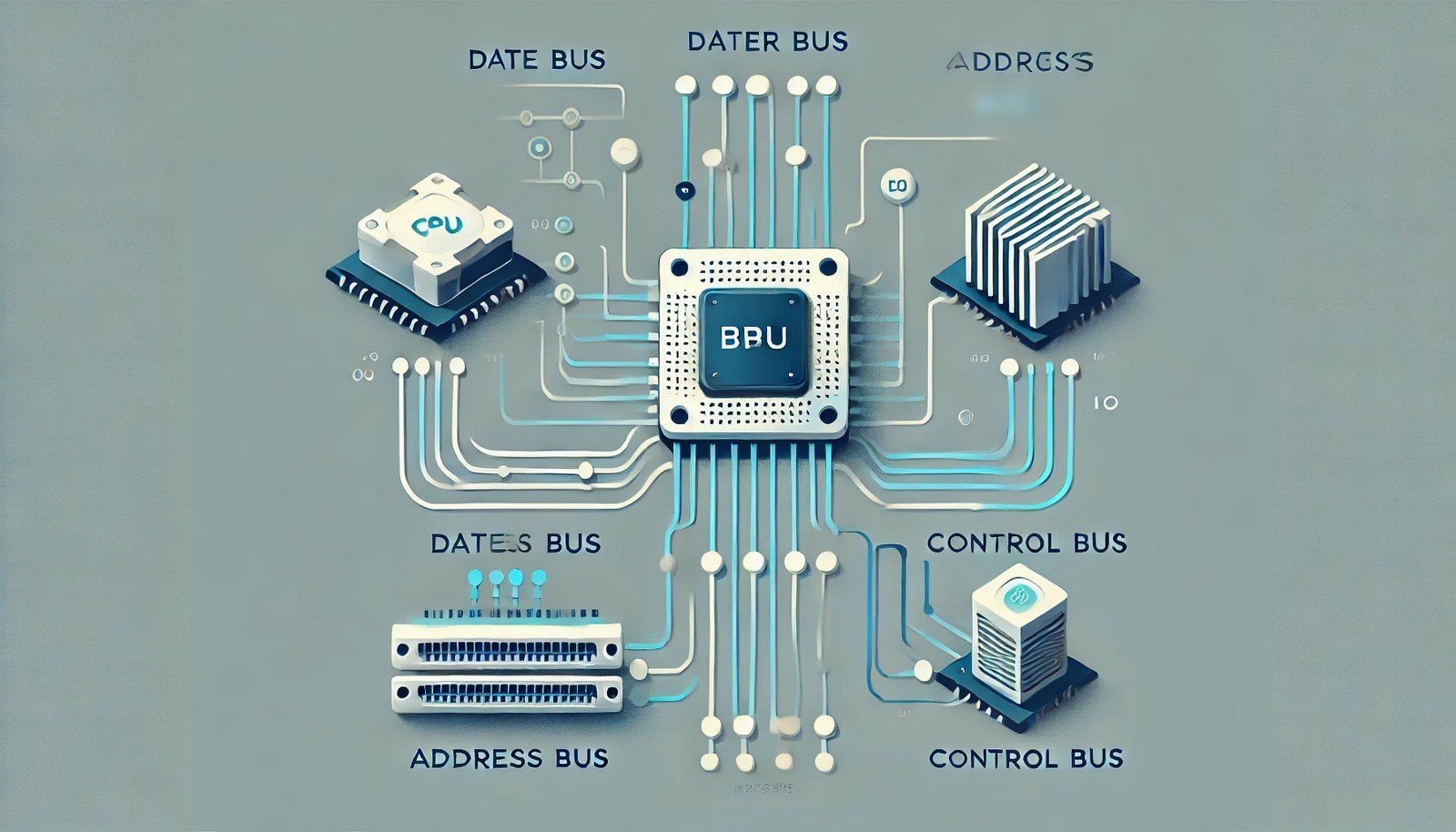
A system bus is a communication pathway used within a computer system to transfer data between components, including the central processing unit (CPU), memory, and input/output (I/O) devices. It consists of three main types: the data bus, which carries actual data; the address bus, which specifies memory locations; and the control bus, which manages commands and responses. The efficiency and speed of a system bus impact overall system performance, influencing how quickly data can move within the architecture.
System Bus Explained Easy
Imagine a city with roads that connect homes, offices, and stores. The system bus is like these roads, helping information travel between parts of a computer. Just like roads have lanes for different types of traffic, the system bus has separate paths for carrying data, addresses, and control signals to keep everything organized.
System Bus Origin
The concept of a system bus emerged in the early days of computing, particularly during the development of microprocessors in the 1970s. It evolved as computing systems required a more efficient way to interconnect components without excessive wiring, leading to the structured bus architectures seen in modern computers.
System Bus Etymology
The term “bus” originates from the Latin word omnibus, meaning "for all." In computing, it refers to a shared communication pathway accessible by multiple components.
System Bus Usage Trends
System buses have evolved significantly over the years. Early computers used a single system bus for all communications, but as processing speeds increased, dedicated buses like PCI Express (PCIe) and direct memory interfaces have become common. High-speed serial buses have largely replaced parallel buses to support modern computing demands, ensuring higher bandwidth and efficiency.
System Bus Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Computer Architecture
- Hardware Communication
- Data Transmission
- Typical Collocations:
- "system bus speed"
- "data bus width"
- "address bus range"
- "control bus signals"
System Bus Examples in Context
- The system bus of a modern gaming PC operates at high speeds to facilitate seamless communication between the processor and graphics card.
- Older computer architectures relied on a single system bus, which often became a bottleneck in performance.
- The efficiency of a system bus determines how quickly a computer can process instructions and respond to user inputs.
System Bus FAQ
- What is a system bus?
A system bus is a communication link that connects the CPU, memory, and I/O devices in a computer. - What are the types of system buses?
The three main types are the data bus, address bus, and control bus, each serving a distinct role in communication. - Why is the system bus important?
It determines how efficiently data is transferred between components, directly affecting system performance. - How does system bus speed impact a computer?
Faster bus speeds enable quicker data exchanges, improving overall computing efficiency. - What is the difference between a parallel and a serial bus?
A parallel bus transfers multiple bits simultaneously, while a serial bus sends data one bit at a time, often at higher speeds. - How has the system bus evolved over time?
Early computers had a single system bus, but modern architectures use separate buses for optimized performance. - What are some examples of modern system buses?
PCIe, USB, and HyperTransport are examples of high-speed bus technologies in use today.
System Bus Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Computer Architecture
- Data Communication
- Bus Protocols
Did you know?
In early computing, system buses were much slower, limiting overall computer performance. The introduction of direct memory access (DMA) allowed devices to communicate directly with memory, bypassing the CPU for efficiency. This innovation dramatically improved data transfer speeds and reduced processing overhead.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment