Transport Layer Security (TLS)
 (Representational Image | Source: Dall-E)
(Representational Image | Source: Dall-E)
Quick Navigation:
- TLS Definition
- TLS Explained Easy
- TLS Origin
- TLS Etymology
- TLS Usage Trends
- TLS Usage
- TLS Examples in Context
- TLS FAQ
- TLS Related Words
TLS Definition
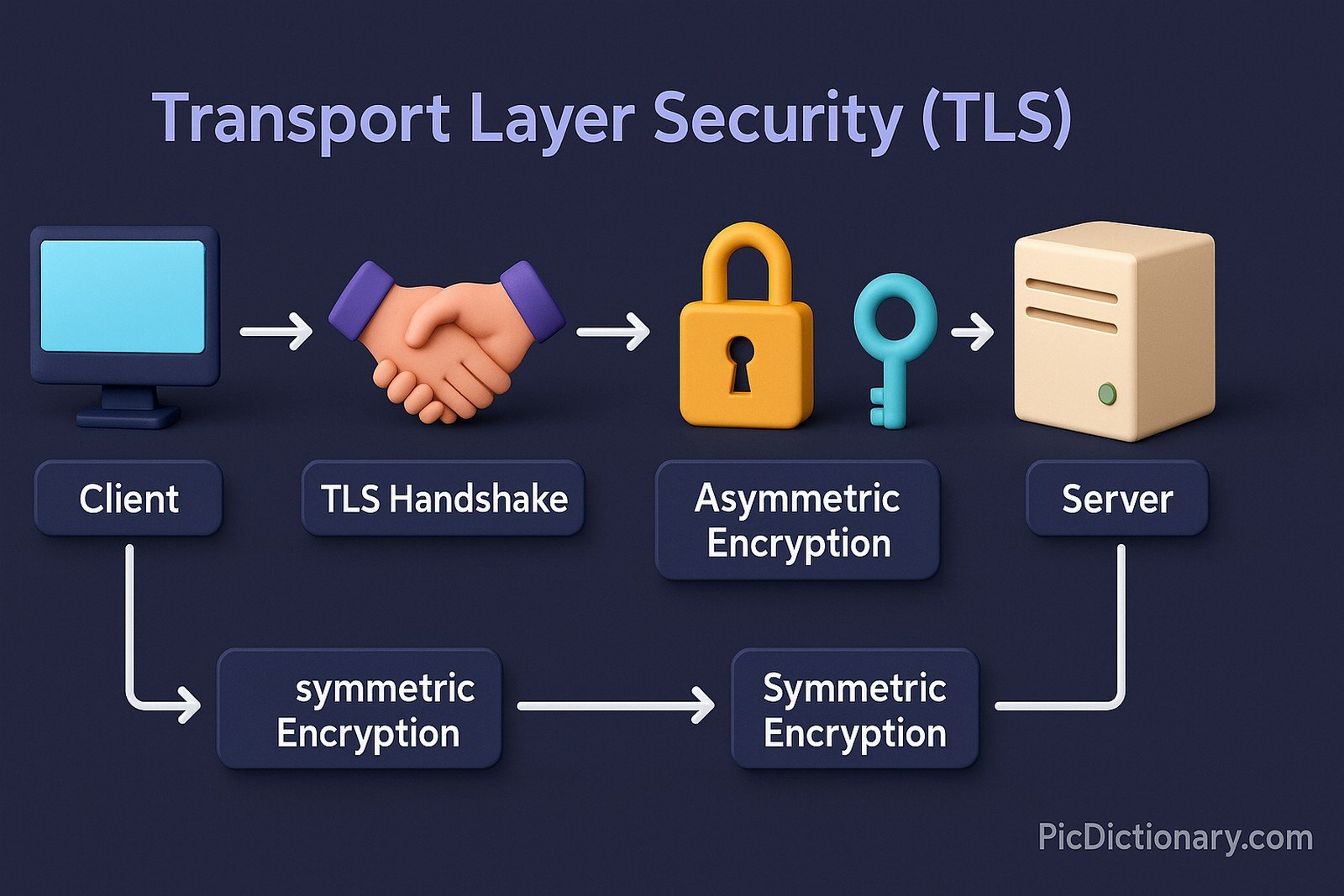
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is a cryptographic protocol designed to provide secure communication over a computer network. It ensures data integrity, confidentiality, and authentication between communicating parties, primarily used in web browsing, email, instant messaging, and VoIP. TLS replaces the older Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol and provides stronger encryption and authentication mechanisms. It operates through a handshake process where two parties establish a secure connection using asymmetric encryption before switching to symmetric encryption for data exchange.
TLS Explained Easy
Imagine you are sending a secret letter to a friend. Before sending it, you lock it in a special box that only your friend has the key to open. Even if someone intercepts the box, they can’t read the letter inside. TLS works like that but for websites and online communication, keeping data safe from hackers.
TLS Origin
TLS was developed as an improved and more secure version of SSL. The first version, TLS 1.0, was published in 1999 by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) as RFC 2246. It was created in response to vulnerabilities in SSL, strengthening encryption standards and security features. Over time, newer versions, such as TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.3, have replaced older ones to adapt to evolving cybersecurity threats.
TLS Etymology
The term “Transport Layer Security” signifies its function: securing data transmissions (transport) at the transport layer of the network model.
TLS Usage Trends
TLS usage has grown significantly due to increasing cybersecurity concerns. Most modern web browsers enforce TLS encryption by default, and search engines favor websites with HTTPS (secured via TLS). With cyber threats evolving, many organizations mandate TLS 1.2 or 1.3 for compliance with security standards like PCI-DSS and GDPR.
TLS Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Network Security
- Data Encryption
- Secure Communication - Typical Collocations:
- "TLS handshake"
- "TLS certificate"
- "TLS encryption protocol"
- "TLS vs. SSL"
TLS Examples in Context
- A website using HTTPS ensures user data is encrypted using TLS.
- Email providers secure messages with TLS to prevent unauthorized access.
- TLS is used in VPN connections to encrypt data between users and servers.
TLS FAQ
- What is TLS used for?
TLS secures communication over networks, including websites, emails, and messaging services. - How does TLS work?
TLS encrypts data transmission between two parties, preventing interception or tampering. - Is TLS the same as SSL?
No, TLS is the successor to SSL, offering improved security and encryption. - Why is TLS important?
It protects sensitive information, such as passwords and payment details, from cyberattacks. - Which TLS version is the latest?
TLS 1.3 is the most recent version, offering better security and performance. - How can I check if a website uses TLS?
Look for "HTTPS" in the URL and a padlock symbol in the browser’s address bar. - What happens if a website doesn’t use TLS?
Data is transmitted in plaintext, making it vulnerable to interception and attacks. - Do all websites use TLS?
Not all, but most reputable sites enforce TLS encryption for security. - Can TLS be hacked?
While TLS itself is highly secure, outdated versions or weak implementations can be exploited. - How can I enable TLS on my website?
Obtain an SSL/TLS certificate from a trusted certificate authority (CA) and configure your server accordingly.
TLS Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Network Security
- Cryptography
- Secure Web Browsing
Did you know?
TLS is the backbone of HTTPS, which is now a ranking factor for Google search results. Websites that don’t use TLS encryption risk losing traffic and credibility.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment