USB (Universal Serial Bus)

Quick Navigation:
- USB Definition
- USB Explained Easy
- USB Origin
- USB Etymology
- USB Usage Trends
- USB Usage
- USB Examples in Context
- USB FAQ
- USB Related Words
USB Definition
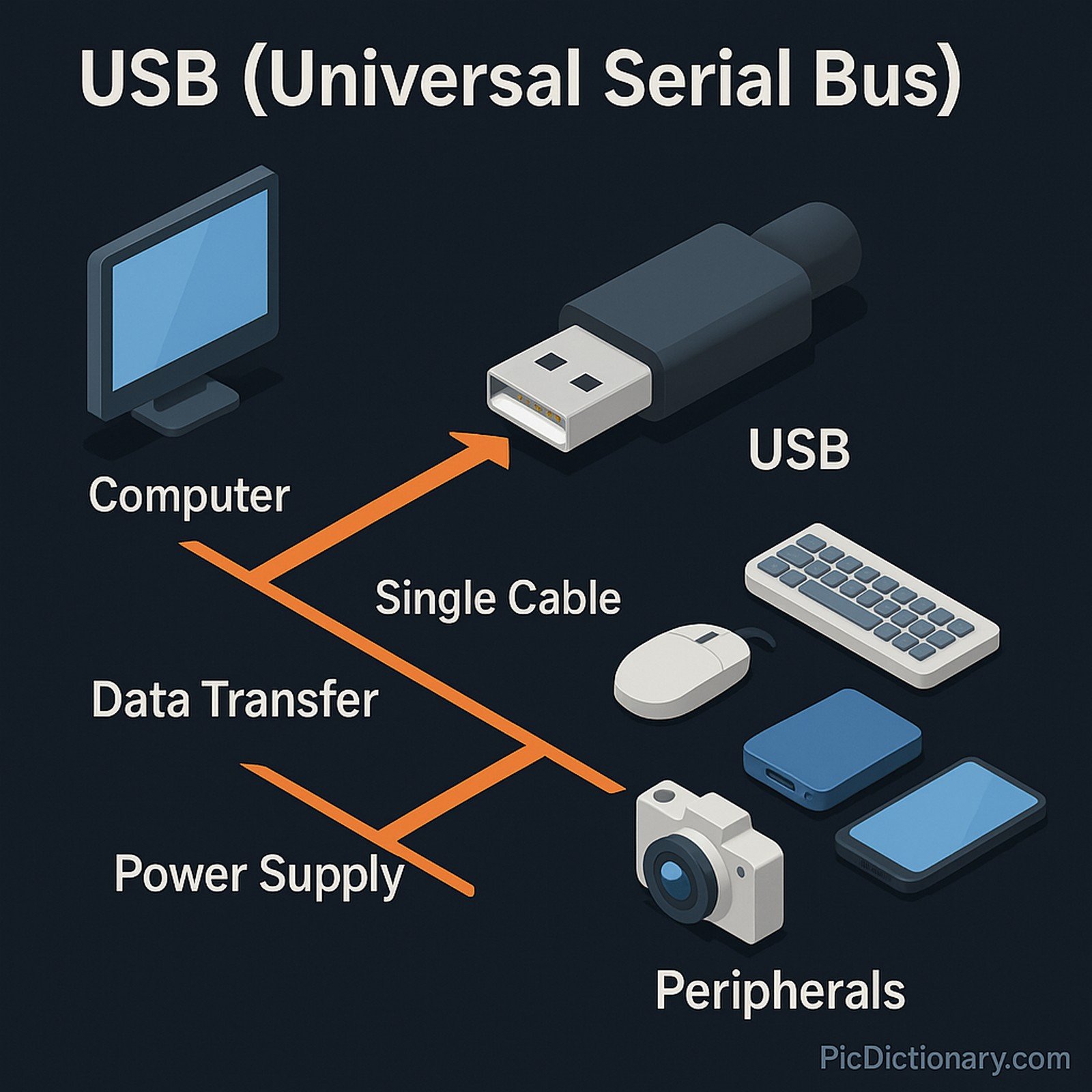
USB (Universal Serial Bus) is an industry-standard technology for connecting peripherals to computers and other devices. It supports data transfer and power supply over a single cable, with multiple versions such as USB 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, and USB-C. USB technology simplifies hardware communication, enabling plug-and-play capability across devices like keyboards, mice, storage drives, cameras, and smartphones. It also supports hot-swapping, allowing devices to be connected and disconnected without shutting.
USB Explained Easy
Imagine a magic cable that connects your computer to many devices like a mouse, keyboard, or even your phone, making them talk to each other. You don’t need to worry about plugging it in perfectly or restarting your computer. That magic cable is called USB, and it helps devices share information and power easily.
USB Origin
USB was developed in the mid-1990s by a group of companies including Intel, Microsoft, IBM, and Compaq. It was created to simplify computer connections by replacing the variety of ports with a single standard.
USB Etymology
The term "USB" refers to a standardized communication method designed for universal compatibility and serial data transmission.
USB Usage Trends
USB technology has evolved from simple data transfers to handling high-speed data, video, and power delivery. Modern trends show an increase in USB-C adoption due to its reversible design and ability to support power, data, and video simultaneously. With advancements in device connectivity and charging requirements, USB continues to dominate both consumer electronics and enterprise setups.
USB Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Computer Hardware
- Connectivity
- Data Transfer Standards - Typical Collocations:
- "USB port"
- "USB cable"
- "USB flash drive"
- "USB hub"
- "USB-C charger"
USB Examples in Context
- Many smartphones now use USB-C for both charging and data transfer.
- USB flash drives allow users to carry large amounts of data in their pockets.
- External hard drives connect to computers through USB ports for backup purposes.
USB FAQ
- What does USB stand for?
USB stands for Universal Serial Bus. - Can USB transfer both power and data?
Yes, USB can transfer both power and data over a single cable. - What is the difference between USB 2.0 and USB 3.0?
USB 3.0 offers faster data transfer rates and improved power management compared to USB 2.0. - What is USB-C?
USB-C is a newer type of USB connector that is reversible and supports fast charging, high-speed data transfer, and video output. - Is USB backward compatible?
Yes, most USB versions are designed to be backward compatible with older devices. - Why is USB important?
USB provides a universal standard for connecting and powering a wide range of devices easily. - Can USB be used for video output?
Yes, with protocols like DisplayPort over USB-C, video output is supported. - What is a USB hub?
A USB hub allows multiple USB devices to connect to a single USB port. - Is USB secure for data transfer?
While USB is convenient, security depends on user practices and device safeguards. - What are common devices that use USB?
Common devices include flash drives, external hard drives, printers, cameras, keyboards, and smartphones.
USB Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Computer Hardware
- Data Transfer
- Device Connectivity
- Charging Technology
Did you know?
The first USB standard was released in 1996, and the introduction of USB-C in 2014 revolutionized device connections with its reversible design and multifunctionality. Today, USB-C is used in laptops, phones, monitors, and more, aiming to replace most other cable types.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment