Datagram Congestion Control Protocol (DCCP)

Quick Navigation:
- Datagram Congestion Control Protocol (DCCP) Definition
- Datagram Congestion Control Protocol (DCCP) Explained Easy
- Datagram Congestion Control Protocol (DCCP) Origin
- Datagram Congestion Control Protocol (DCCP) Etymology
- Datagram Congestion Control Protocol (DCCP) Usage Trends
- Datagram Congestion Control Protocol (DCCP) Usage
- Datagram Congestion Control Protocol (DCCP) Examples in Context
- Datagram Congestion Control Protocol (DCCP) FAQ
- Datagram Congestion Control Protocol (DCCP) Related Words
Datagram Congestion Control Protocol (DCCP) Definition
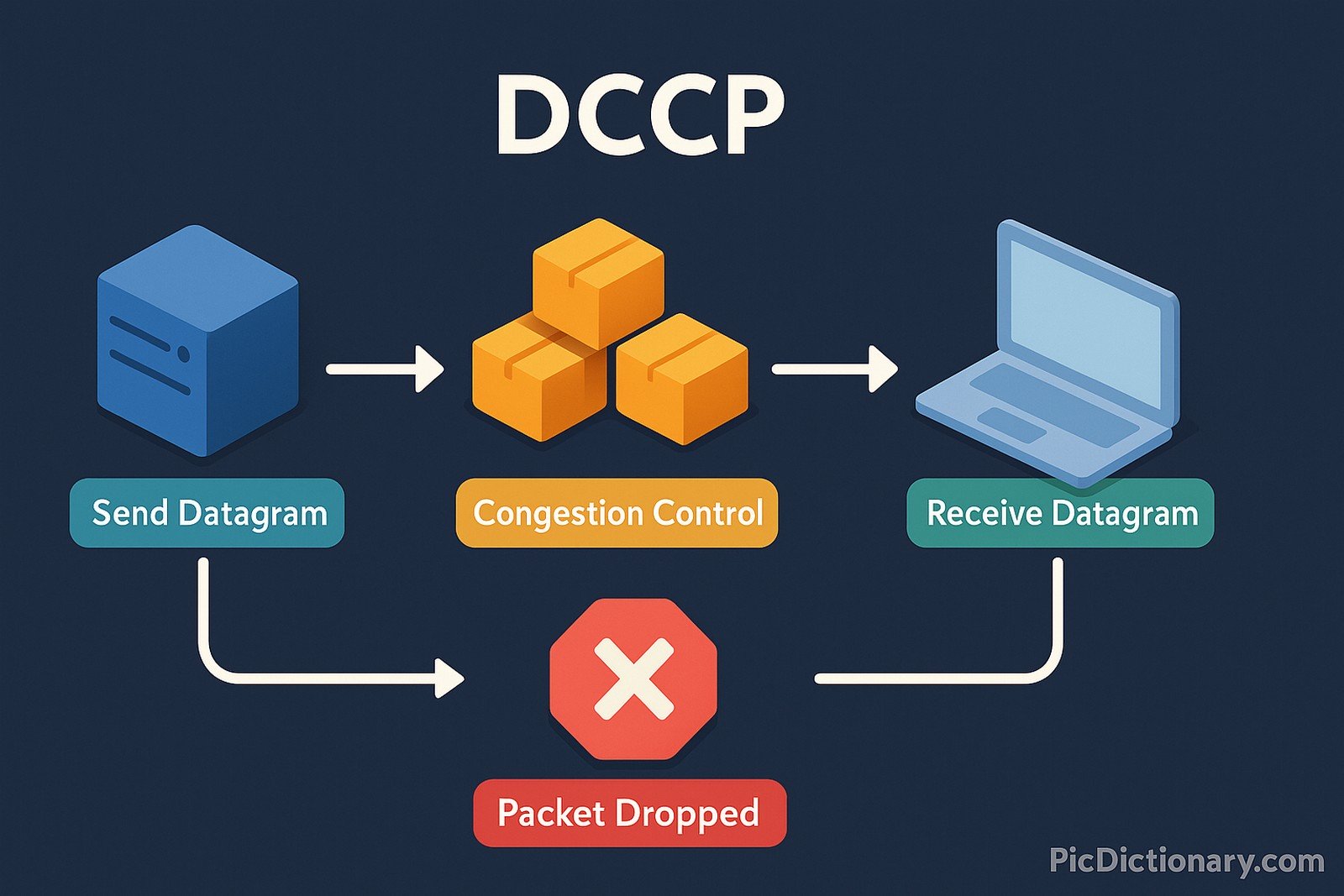
Datagram Congestion Control Protocol (DCCP) is a transport-layer protocol that enables the delivery of datagrams with congestion control mechanisms. Unlike TCP, which ensures reliable, ordered delivery, or UDP, which offers fast but unreliable transmission, DCCP provides a balance by implementing congestion control without guaranteeing packet delivery. This makes it suitable for real-time applications like streaming, online gaming, and VoIP, where timely delivery is more important than retransmission.
Datagram Congestion Control Protocol (DCCP) Explained Easy
Imagine you're on a highway with speed limits that change based on traffic. If there’s congestion, cars slow down to avoid accidents. If the road is clear, they speed up. DCCP works the same way—it controls data flow in a way that avoids congestion but doesn’t guarantee that every piece of information reaches its destination. This makes it perfect for video calls or games, where keeping things moving is more important than making sure every single packet arrives.
Datagram Congestion Control Protocol (DCCP) Origin
DCCP was introduced in 2000 as part of research efforts to enhance transport-layer communication. It was standardized in RFC 4340 by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) in 2006. The goal was to provide a protocol that handled congestion control efficiently while catering to applications needing fast, real-time communication without TCP’s overhead.
Datagram Congestion Control Protocol (DCCP) Etymology
The term "Datagram Congestion Control Protocol" breaks down as follows:
- Datagram: A self-contained, independent packet of data.
- Congestion Control: The mechanism for managing network traffic to prevent overload.
- Protocol: A set of rules governing communication.
Datagram Congestion Control Protocol (DCCP) Usage Trends
DCCP adoption has been limited, with most applications preferring TCP or UDP. However, it has gained recognition in niche areas such as multimedia streaming, gaming, and teleconferencing, where packet loss is tolerable but congestion control is necessary. Some operating systems support DCCP, though widespread adoption remains limited due to the dominance of existing protocols.
Datagram Congestion Control Protocol (DCCP) Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Transport Layer Protocol
- Congestion Control
- Multimedia Streaming - Typical Collocations:
- "DCCP for real-time streaming"
- "DCCP congestion management"
- "DCCP vs. TCP vs. UDP"
- "DCCP for VoIP applications"
Datagram Congestion Control Protocol (DCCP) Examples in Context
- A gaming company optimizes its network stack using DCCP to reduce lag while preventing congestion.
- A VoIP provider experiments with DCCP to improve call quality while avoiding excessive retransmissions.
- A multimedia streaming service explores DCCP as an alternative to UDP to manage fluctuating bandwidth conditions.
Datagram Congestion Control Protocol (DCCP) FAQ
- What is DCCP used for?
DCCP is used in applications where real-time communication is essential, such as streaming, gaming, and VoIP. - How does DCCP differ from TCP and UDP?
Unlike TCP, DCCP does not guarantee reliable delivery but includes congestion control, unlike UDP, which has neither. - Why is DCCP not widely used?
Many applications already rely on TCP or UDP, and DCCP's implementation complexity has slowed its adoption. - Does DCCP ensure data reliability?
No, DCCP focuses on congestion control rather than ensuring every packet is delivered. - Is DCCP supported on all operating systems?
Some Linux distributions support DCCP, but it is not universally implemented. - Can DCCP replace TCP for streaming?
In some cases, yes, but it depends on the application's tolerance for packet loss. - Is DCCP used for secure communication?
DCCP itself does not provide encryption, but it can work with security protocols like DTLS. - How does DCCP affect network congestion?
It dynamically adjusts transmission rates to prevent excessive congestion. - What industries benefit from DCCP?
Media streaming, online gaming, and real-time voice and video applications benefit the most. - Can DCCP be used for file transfers?
Not effectively, as it does not guarantee packet delivery like TCP.
Datagram Congestion Control Protocol (DCCP) Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Network Protocols
- Transport Layer Communication
- Real-time Data Transmission
Did you know?
In 2018, researchers proposed using DCCP for adaptive video streaming services, aiming to optimize quality while reducing buffering. However, the idea struggled to gain traction against well-established protocols like QUIC and TCP-based solutions.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment