RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks)

Quick Navigation:
- RAID Definition
- RAID Explained Easy
- RAID Origin
- RAID Etymology
- RAID Usage Trends
- RAID Usage
- RAID Examples in Context
- RAID FAQ
- RAID Related Words
RAID Definition
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a data storage technology that combines multiple physical disk drives into one logical unit to improve data redundancy, performance, or both. Different RAID levels, such as RAID 0, 1, 5, and 10, offer varying degrees of fault tolerance and speed. RAID uses techniques like striping (splitting data across disks), mirroring (copying identical data to multiple disks), and parity (error checking and correction) to protect against drive failures and optimize read/write operations in critical systems like servers, NAS devices, and enterprise storage solutions.
RAID Explained Easy
Imagine you have a big Lego set. Instead of building one tower with all your bricks, you build several smaller towers. If one tower falls, you still have others that hold pieces of the structure. RAID is like that — it spreads your data across multiple hard drives so even if one fails, your data is safe and your computer keeps running.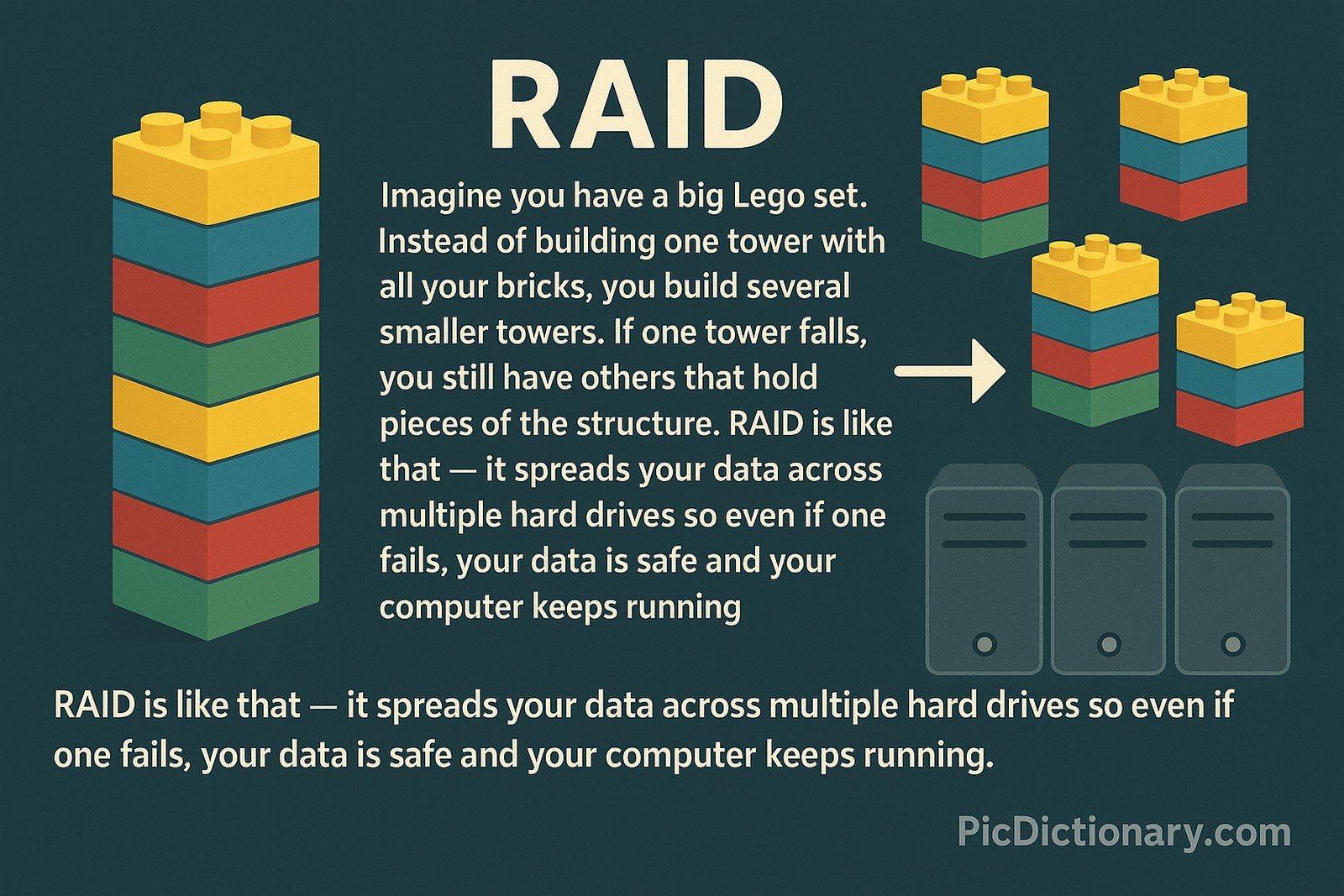
RAID Origin
RAID was first introduced in 1987 by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley. Their influential paper titled "A Case for Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks" proposed using multiple low-cost disks to achieve better performance and reliability than single expensive disk drives, paving the way for modern data storage systems.
RAID Etymology
The word "RAID" was coined by David Patterson, Garth A. Gibson, and Randy H. Katz in their landmark 1987 research paper.
RAID Usage Trends
RAID has evolved from enterprise-level servers to small business and personal use, particularly with the growth of large-scale data storage and cloud systems. Usage trends show RAID remains crucial for database systems, high-availability servers, and media production workflows. Newer RAID variations and software-based solutions continue to enhance storage performance, though some environments now combine RAID with cloud backup solutions.
RAID Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Data Storage
- Fault Tolerance
- Disk Management - Typical Collocations:
- "RAID array"
- "RAID controller"
- "RAID configuration"
- "RAID setup"
- "RAID levels"
RAID Examples in Context
- Many businesses use RAID 1 for critical financial data, ensuring mirrored backups.
- Video editors often use RAID 0 for faster read/write speeds when handling large media files.
- Data centers rely on RAID 5 or RAID 6 to protect against drive failures while maintaining capacity and speed.
RAID FAQ
- What is RAID?
RAID is a data storage method that uses multiple disks to increase performance, reliability, or both. - Why do I need RAID?
RAID helps protect your data from drive failures and improves disk performance. - Which RAID level is best for performance?
RAID 0 offers the best performance but no fault tolerance. - Which RAID level is best for redundancy?
RAID 1 provides full data mirroring, offering the best redundancy. - Can RAID protect against all data loss?
No, RAID can’t protect against accidental deletion or catastrophic events; backups are still essential. - Is RAID used in personal computers?
Yes, enthusiasts and professionals use RAID in personal setups for speed and data safety. - Does RAID replace backups?
No, RAID is not a substitute for backups; it helps with redundancy but not comprehensive data protection. - How do I know if my computer supports RAID?
Check your motherboard specifications or BIOS for RAID support settings. - What is a RAID controller?
A RAID controller is hardware or software that manages RAID configurations and data flow between disks. - Can I build a RAID array with different disk sizes?
It's possible, but the total usable space will be limited by the smallest disk size in the array.
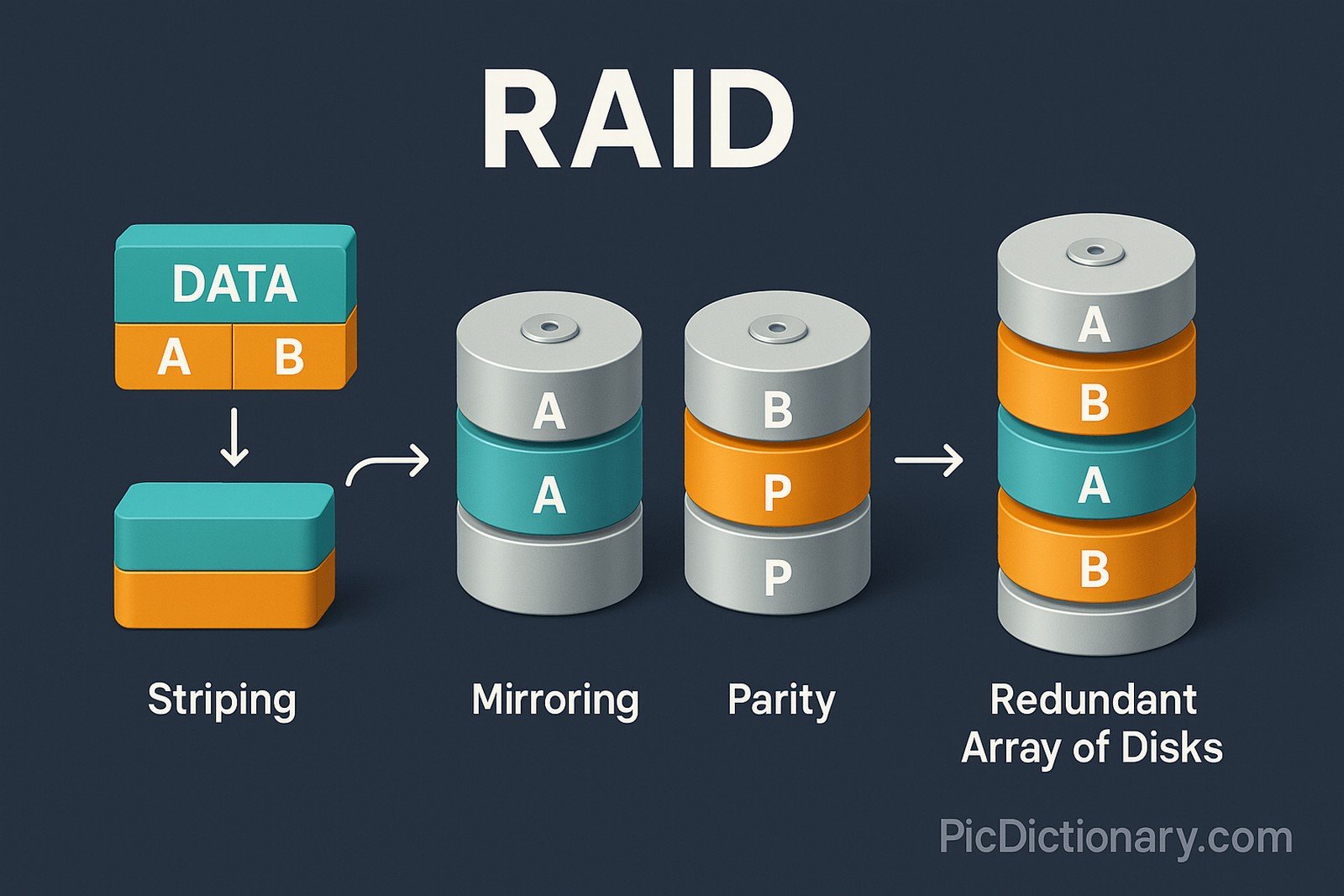
RAID Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Data Storage
- Backup Solutions
- Disk Management
- Enterprise IT
Did you know?
NASA’s Mars rovers use concepts similar to RAID to ensure data redundancy. Due to the critical nature of their missions, onboard systems split and mirror data across multiple storage units to safeguard information even in case of partial system failure.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment