Storage Tiers
 (Representational Image | Source: Dall-E)
(Representational Image | Source: Dall-E)
Quick Navigation:
- Storage Tiers Definition
- Storage Tiers Explained Easy
- Storage Tiers Origin
- Storage Tiers Etymology
- Storage Tiers Usage Trends
- Storage Tiers Usage
- Storage Tiers Examples in Context
- Storage Tiers FAQ
- Storage Tiers Related Words
Storage Tiers Definition
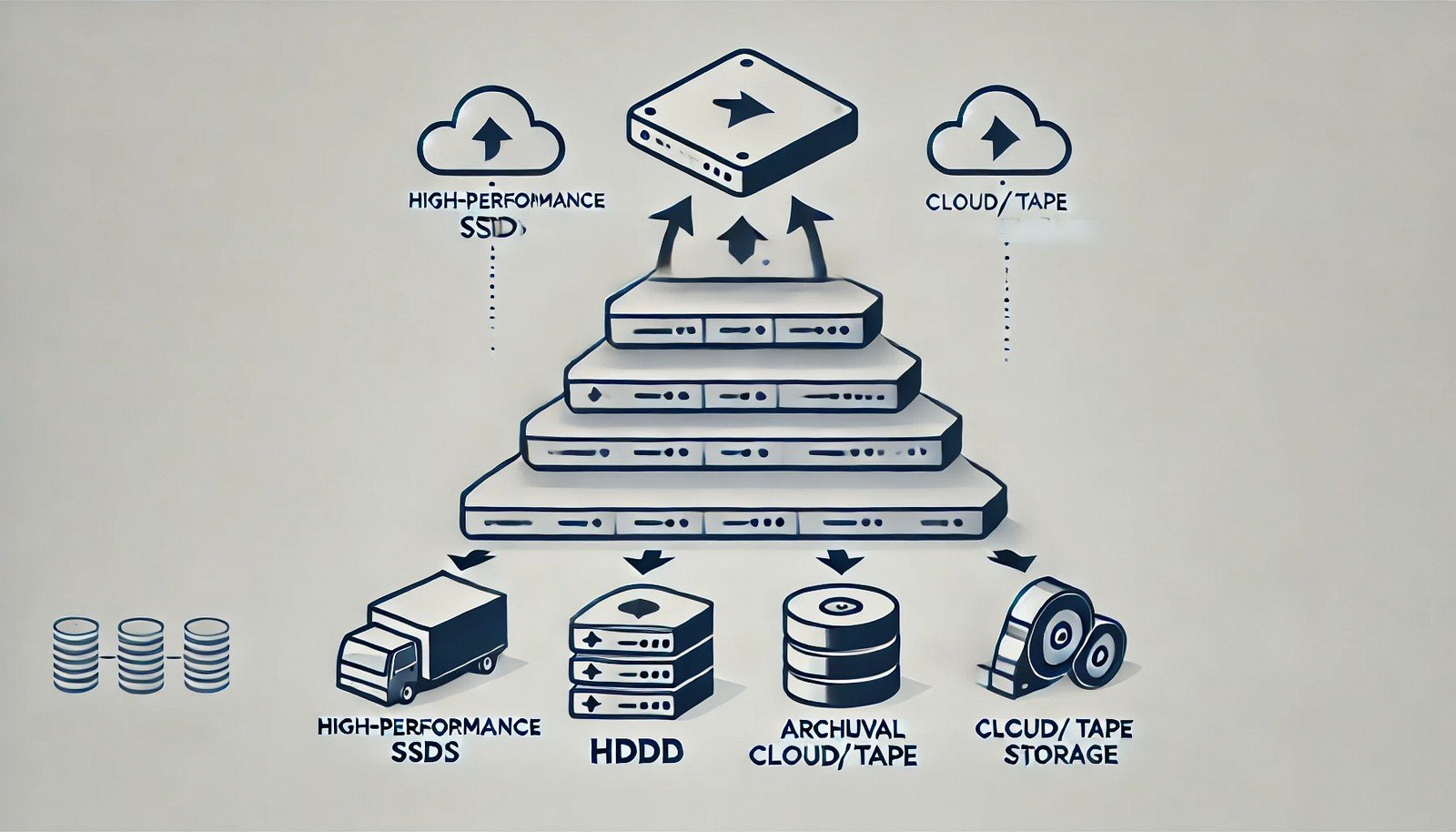
Storage tiers refer to a hierarchical storage architecture that classifies and organizes data based on factors such as access speed, cost, and frequency of use. Typically, storage tiers range from high-performance solid-state drives (SSDs) for frequently accessed data to slower, more cost-effective storage like hard disk drives (HDDs) or cloud archival storage for infrequently accessed data. This approach helps optimize costs and performance by automatically moving data between different tiers based on pre-set policies or machine learning algorithms.
Storage Tiers Explained Easy
Imagine you have a toy box. You put your favorite toys on the top shelf where you can grab them quickly, while the ones you play with less often go in a lower drawer. Very old toys might go into a storage box in the attic. Storage tiers work the same way for computers: important and frequently used files are stored in fast storage, while less-used files are moved to cheaper, slower storage.
Storage Tiers Origin
The concept of tiered storage emerged in enterprise computing during the late 20th century as businesses sought ways to balance performance and cost. Early implementations involved manual data migration between storage media, but modern advancements now allow automated tiering using artificial intelligence and machine learning.
Storage Tiers Etymology
The term "storage tiers" originates from the word "tier," meaning a level or layer in a hierarchical structure. In computing, it signifies different levels of data storage based on performance and cost.
Storage Tiers Usage Trends
With the explosion of big data and cloud computing, storage tiering has become an essential practice. Businesses increasingly leverage multi-tiered storage architectures to optimize costs while ensuring critical data remains accessible. Cloud providers like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure offer tiered storage solutions that dynamically move data based on usage patterns.
Storage Tiers Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Data Storage
- Cloud Computing
- Enterprise IT - Typical Collocations:
- "multi-tier storage"
- "hot, warm, and cold storage"
- "storage tiering strategies"
- "automated data tiering"
Storage Tiers Examples in Context
- A financial institution keeps real-time transaction data in high-speed SSD storage, while old transaction logs move to lower-cost archival storage.
- A cloud-based streaming service stores frequently watched movies on fast-access servers, while rarely accessed films are kept in long-term storage.
- A corporate IT department uses tiered storage to manage employee files, keeping frequently edited documents on fast local storage and archiving old files in cloud cold storage.
Storage Tiers FAQ
- What is storage tiering?
Storage tiering is the process of categorizing and managing data storage based on performance, access frequency, and cost considerations. - How does automated storage tiering work?
Automated storage tiering uses software or machine learning to move data between storage tiers based on predefined rules or real-time usage analysis. - What are the typical storage tiers?
Common storage tiers include high-speed SSDs for frequently accessed data, HDDs for moderately accessed data, and cloud or tape storage for archival purposes. - Why is storage tiering important?
It helps optimize performance and reduce costs by storing data in the most appropriate type of storage medium based on its usage frequency. - Can cloud storage be tiered?
Yes, cloud providers offer tiered storage plans, such as AWS S3’s Standard, Infrequent Access, and Glacier tiers. - What is the difference between hot, warm, and cold storage?
Hot storage: Fast and frequently accessed data.
Warm storage: Moderately accessed data with balanced cost and speed.
Cold storage: Rarely accessed data stored at the lowest cost. - Does storage tiering affect data retrieval speed?
Yes, data stored in lower-cost, cold tiers may have longer retrieval times compared to high-performance storage tiers. - How do businesses implement storage tiers?
Businesses use hybrid storage solutions with automated tiering systems to manage data placement efficiently. - Is storage tiering useful for personal use?
Yes, users can organize personal data by keeping frequently used files on fast SSDs and backing up older files on external HDDs or cloud storage. - What industries benefit most from storage tiering?
Industries handling large datasets, such as healthcare, finance, media, and cloud services, benefit significantly from tiered storage strategies.
Storage Tiers Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Data Management
- Cloud Storage
- Enterprise IT Infrastructure
Did you know?
The concept of storage tiering isn’t limited to digital storage. Libraries have used a similar method for centuries—keeping frequently borrowed books in easy-to-access locations while moving older or less popular books to archives or off-site storage.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment