High-Bandwidth Memory (HBM)
Quick Navigation:
- High-Bandwidth Memory Definition
- High-Bandwidth Memory Explained Easy
- High-Bandwidth Memory Origin
- High-Bandwidth Memory Etymology
- High-Bandwidth Memory Usage Trends
- High-Bandwidth Memory Usage
- High-Bandwidth Memory Examples in Context
- High-Bandwidth Memory FAQ
- High-Bandwidth Memory Related Words
High-Bandwidth Memory Definition
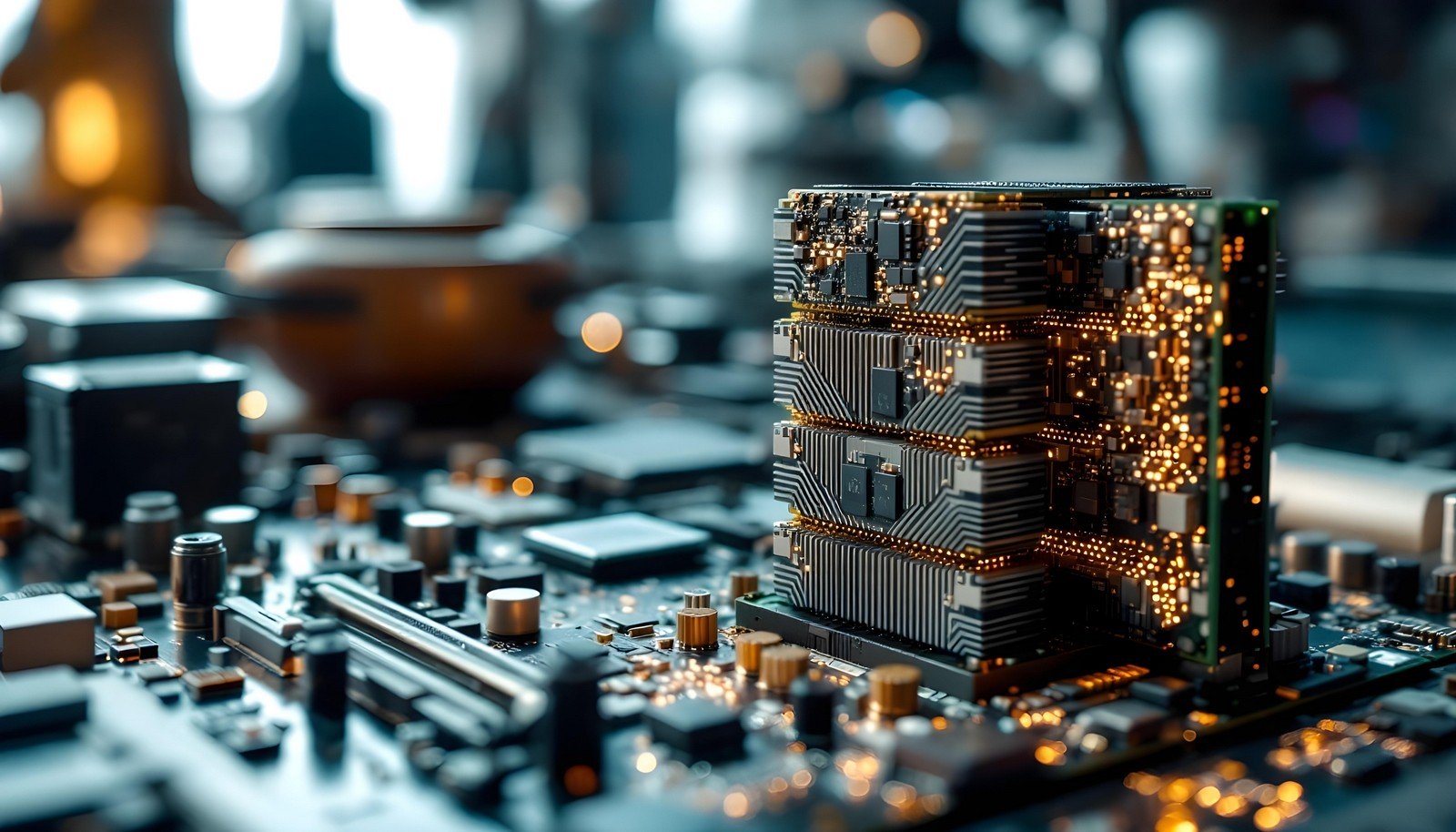
High-Bandwidth Memory (HBM) is a high-speed memory technology designed for data-intensive applications. Unlike traditional memory, HBM uses a 3D stacking structure where memory chips are vertically layered and connected with through-silicon vias (TSVs). This architecture enables extremely high data transfer rates while reducing power consumption and latency, making it ideal for GPUs, AI accelerators, and high-performance computing (HPC) systems.
High-Bandwidth Memory Explained Easy
Imagine stacking books on top of each other and connecting them with a straw for fast communication. This is how HBM works—memory chips stacked and linked to talk super quickly, making computers much faster for big tasks like gaming or predicting the weather.
High-Bandwidth Memory Origin
HBM was developed as a joint effort by JEDEC, AMD, and Hynix in the early 2010s to overcome the limitations of traditional memory technologies. It was first introduced in AMD's Fiji GPUs in 2015.
High-Bandwidth Memory Etymology
The term "high-bandwidth" refers to its capability to transfer a vast amount of data in a short time.
High-Bandwidth Memory Usage Trends
HBM adoption has grown in recent years due to its application in AI, machine learning, and data analytics. Tech giants integrate it into GPUs, AI processors, and gaming consoles for enhanced performance and energy efficiency.
High-Bandwidth Memory Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Memory Architecture
- High-Performance Computing
- 3D Memory Stacking - Typical Collocations:
- "HBM technology"
- "high-bandwidth memory interface"
- "HBM-powered GPU"
- "energy-efficient memory"
High-Bandwidth Memory Examples in Context
- HBM is used in AI systems to process massive datasets faster than conventional memory.
- Gaming consoles with HBM technology deliver smoother graphics.
- Supercomputers employ HBM for rapid simulations in fields like climate modeling.
High-Bandwidth Memory FAQ
- What is High-Bandwidth Memory?
It’s a memory technology designed for high-speed data transfer and low power consumption. - How does HBM differ from traditional memory?
HBM stacks memory vertically for faster communication, unlike traditional flat chips. - What are the main uses of HBM?
It's used in AI, gaming, and HPC systems for high-speed processing. - What are TSVs in HBM?
Through-silicon vias are tiny holes connecting stacked memory layers for fast communication. - Why is HBM energy efficient?
Its compact 3D design reduces energy loss compared to traditional memory. - Can HBM be used in laptops?
It's typically used in high-performance systems, not standard laptops. - Who invented HBM?
JEDEC, AMD, and Hynix collaborated to develop HBM. - What’s the future of HBM?
HBM continues to evolve with higher bandwidths and wider adoption in AI and HPC. - How does HBM benefit AI?
Its high speed enables faster processing of AI tasks like image recognition. - What’s the difference between HBM and DDR memory?
HBM is stacked vertically for speed, while DDR memory is planar and slower.
High-Bandwidth Memory Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Memory Technology
- Artificial Intelligence
- Graphics Processing
Did you know?
HBM’s 3D stacking design allows it to achieve speeds up to 1 TB/s, enabling groundbreaking advancements in AI and rendering massive datasets quickly.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment