AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)

(Representational Image | Source: Dall-E)
Quick Navigation:
- AES Definition
- AES Explained Easy
- AES Origin
- AES Etymology
- AES Usage Trends
- AES Usage
- AES Examples in Context
- AES FAQ
- AES Related Words
AES Definition
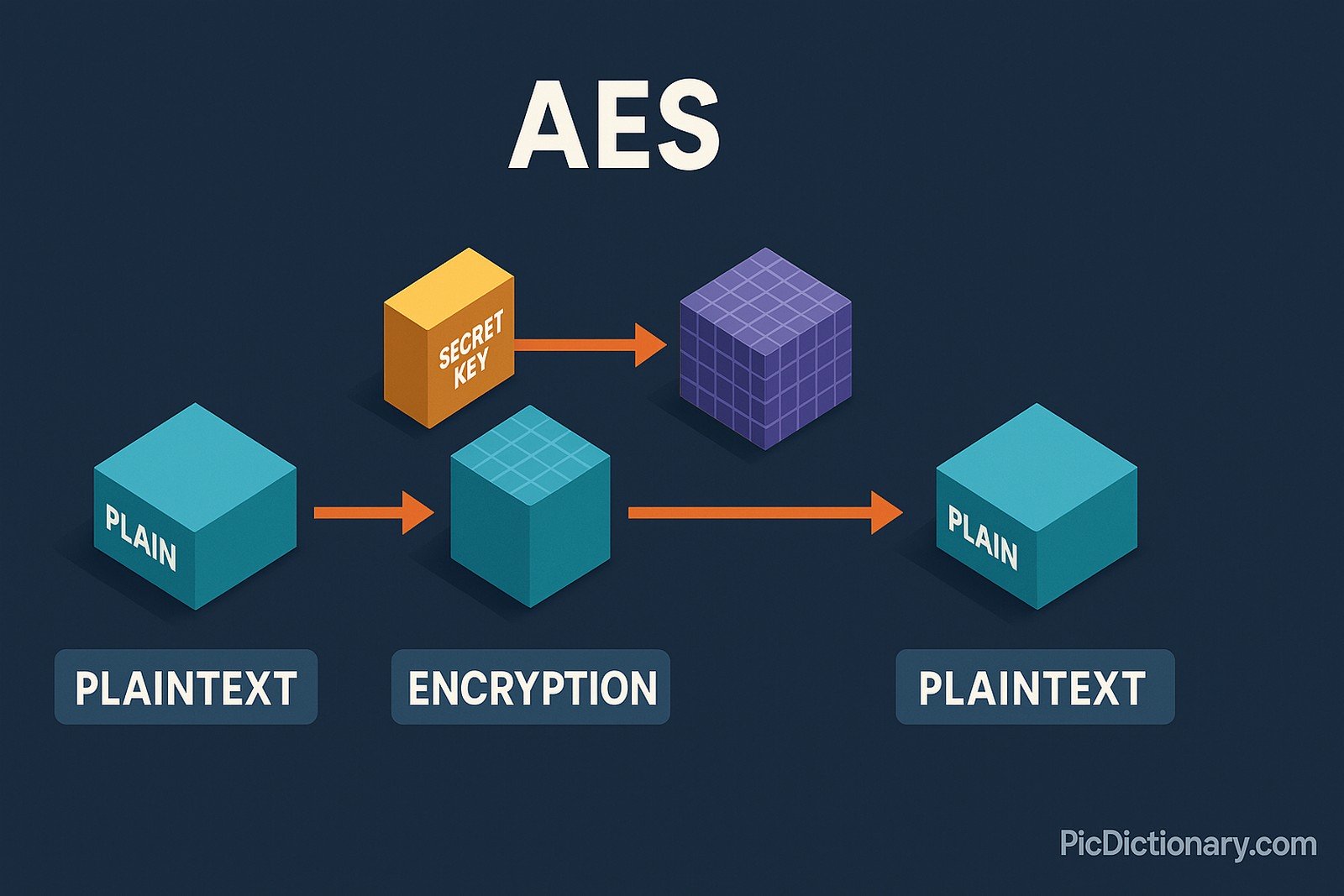
AES is a symmetric encryption algorithm that secures data by converting it into unreadable ciphertext and then back into readable plaintext with the same secret key. Established by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2001, it uses block ciphers with key sizes of 128, 192, or 256 bits. It is widely regarded for its speed, security, and efficiency and is used globally in applications like online banking, file encryption, and secure communications.
AES Explained Easy
Imagine you have a secret box that only opens with a special key. If you put a message inside and lock the box, nobody can read it unless they have that key. AES works just like that box for digital information—it scrambles your message and only someone with the key can make sense of it.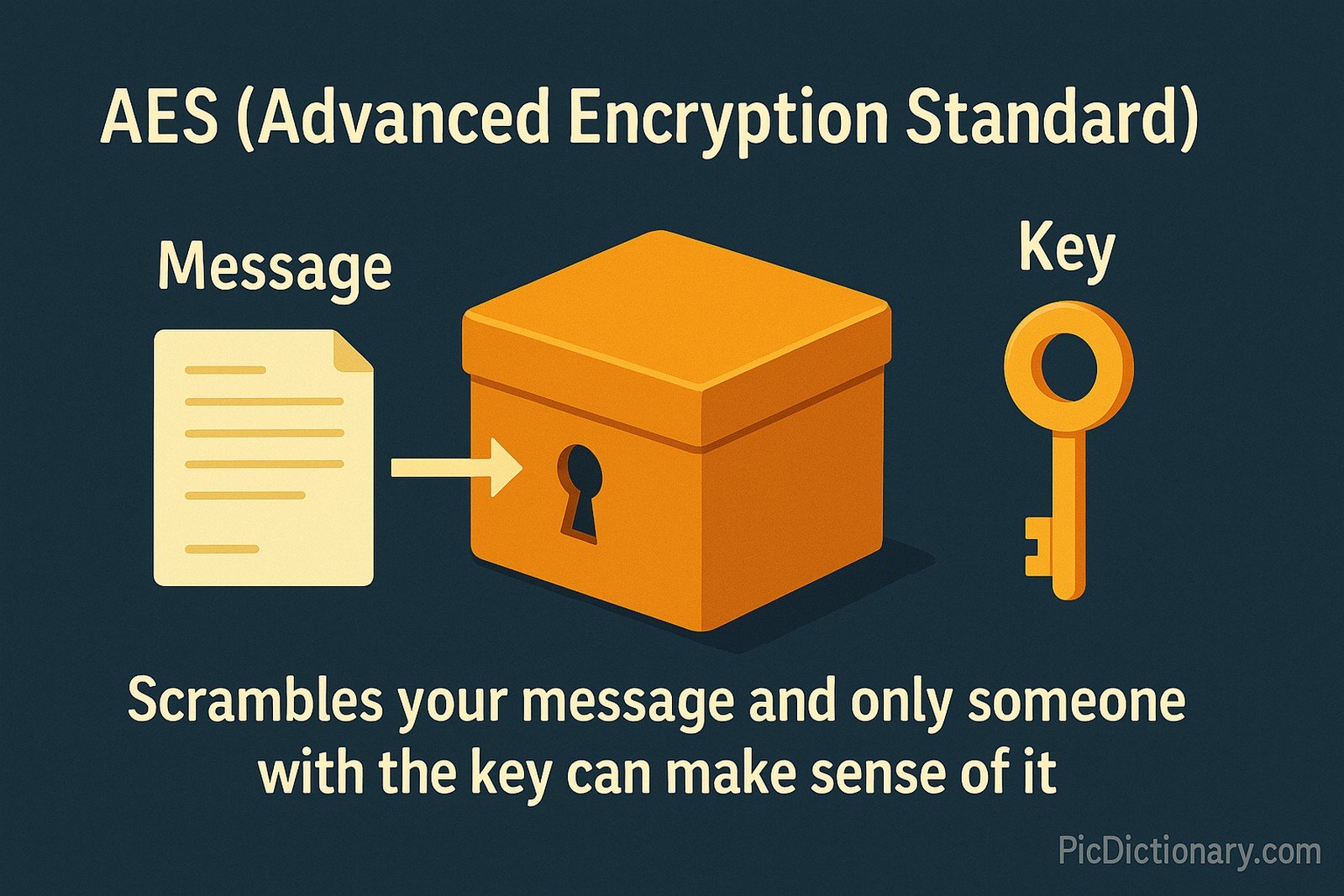
AES Origin
AES was developed as a successor to the Data Encryption Standard (DES), which became vulnerable over time. After a global competition, the Rijndael algorithm, created by Belgian cryptographers Vincent Rijmen and Joan Daemen, was selected by NIST in 2001 to become AES.
AES Etymology
The name AES reflects its purpose as an internationally recognized encryption standard established for advanced security needs.
AES Usage Trends
AES has become the gold standard for encryption in both personal and enterprise applications. With the rise of cybersecurity threats, its usage has extended from secure websites and online transactions to cloud storage and mobile communications. Regulatory standards worldwide also require AES-based encryption for data protection.
AES Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Cryptography
- Information Security
- Data Encryption - Typical Collocations:
- "AES encryption standard"
- "AES 256-bit security"
- "encrypting files with AES"
- "AES-based protection protocol"
AES Examples in Context
- Online banking platforms use AES to secure transaction data.
- Cloud storage services encrypt users’ files using AES for confidentiality.
- Wi-Fi routers often rely on AES encryption for secure wireless communication.
AES FAQ
- What is AES?
AES is a symmetric encryption algorithm that uses the same key for both encrypting and decrypting data. - Why was AES developed?
It was developed to replace DES, which became insecure due to advances in computing power. - Who created AES?
The Rijndael algorithm by Vincent Rijmen and Joan Daemen was selected as AES by NIST. - How secure is AES?
AES with 256-bit keys is considered virtually unbreakable with current technology. - Where is AES used?
It is used in banking, secure communications, encrypted storage, and internet security protocols. - What makes AES better than DES?
AES supports longer key lengths and uses more robust mathematical structures, making it far more secure. - Can AES be used for file encryption?
Yes, many file encryption tools and programs rely on AES to protect data. - Is AES suitable for mobile devices?
Absolutely, AES is efficient and light enough for use in smartphones and other mobile devices. - What is the difference between AES-128 and AES-256?
The numbers refer to key lengths; AES-256 provides stronger security due to a larger key size. - Is AES approved by governments?
Yes, AES is approved and recommended for use by the U.S. government and many international organizations.
AES Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Cryptography
- Cybersecurity
- Data Protection
Did you know?
AES is so trusted that it's used to secure classified government documents up to the top-secret level, demonstrating its high level of trust and reliability.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment