ARP (Address Resolution Protocol)

Quick Navigation:
- ARP Definition
- ARP Explained Easy
- ARP Origin
- ARP Etymology
- ARP Usage Trends
- ARP Usage
- ARP Examples in Context
- ARP FAQ
- ARP Related Words
ARP Definition
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a communication protocol used for discovering the link-layer address (such as MAC address) associated with a given network-layer address (such as an IP address) in a local area network. ARP allows devices on the same network segment to find each other’s hardware addresses, facilitating communication. It plays a critical role in the TCP/IP stack, ensuring that IP addresses are mapped to the correct physical hardware devices.
ARP Explained Easy
Imagine you want to send a letter to a friend, but you only know their name and not their house number. You ask around, and someone tells you their house number. Now you can deliver your letter! ARP does the same in computer networks — it finds the right hardware address to send information to when only the IP address is known.
ARP Origin
ARP was first defined in 1982 in RFC 826 by David C. Plummer. It became an integral part of network communication standards, especially in IPv4-based networking systems.
ARP Etymology
The term combines the idea of "address resolution" — converting one type of address into another — with "protocol," which is a defined set of communication rules.
ARP Usage Trends
ARP has been widely used since the inception of IPv4 networks and remains essential in local area network communications. However, with the rise of IPv6, Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) has started to replace ARP. In modern secure networks, ARP spoofing threats have led to the development of protective measures like Dynamic ARP Inspection.
ARP Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Networking
- TCP/IP
- Data Link Layer - Typical Collocations:
- "ARP table"
- "ARP cache"
- "send ARP request"
- "receive ARP reply"
- "ARP spoofing protection"
ARP Examples in Context
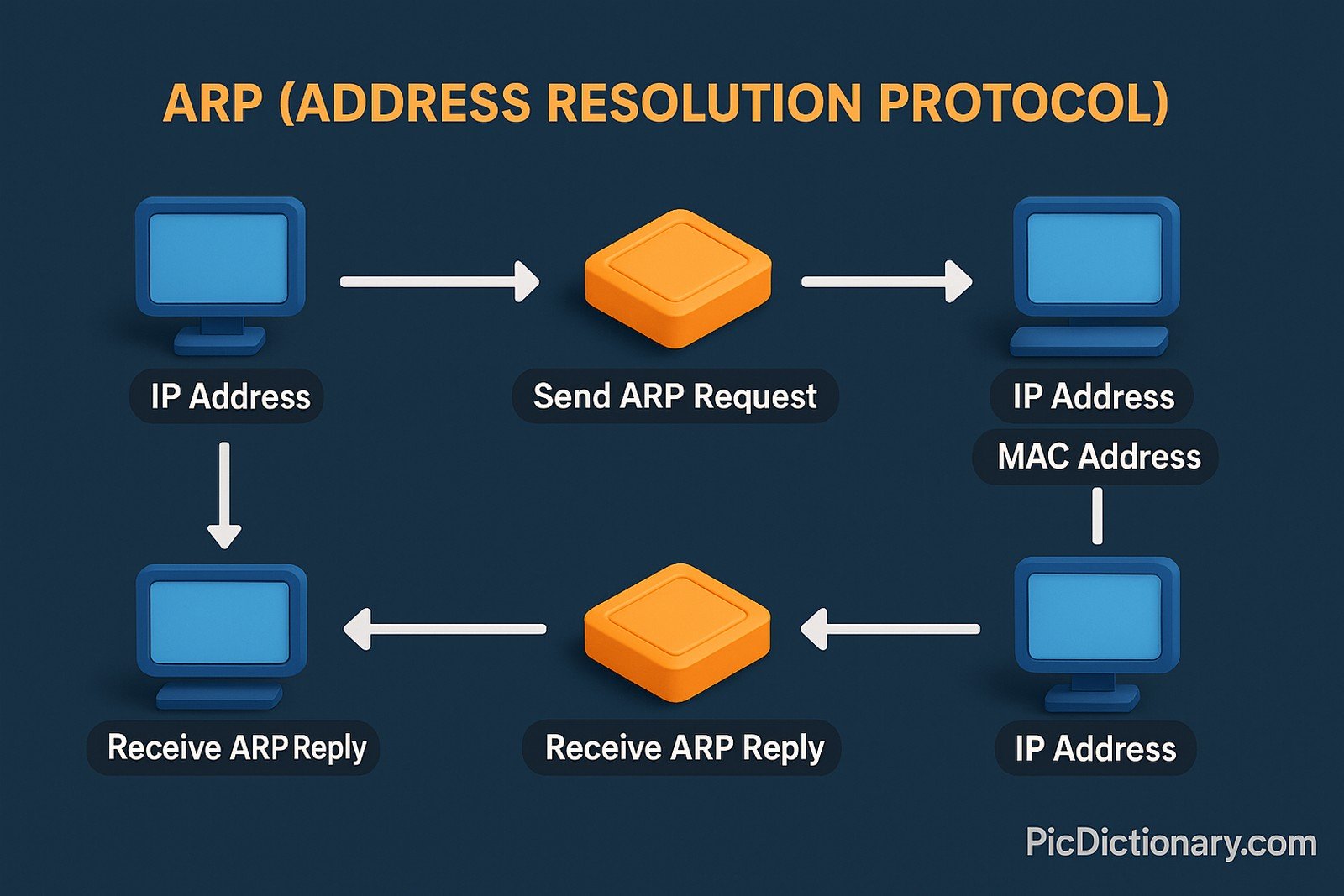
- A computer broadcasts an ARP request asking, “Who has IP 192.168.1.1?” and receives an ARP reply with the corresponding MAC address.
- Network administrators often check the ARP table to troubleshoot connectivity issues.
- Security systems monitor ARP traffic to detect and prevent ARP spoofing attacks.
ARP FAQ
- What is ARP?
ARP is a protocol used to map IP addresses to physical hardware addresses (MAC) in a local network. - How does ARP work?
It sends out a broadcast message asking who owns a specific IP address, and the device with that IP responds with its MAC address. - Why is ARP important?
Without ARP, devices in a local network wouldn’t know where to send packets. - Can ARP be used in IPv6?
No, IPv6 uses Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) instead. - What is an ARP table?
An ARP table is a cache that stores mappings of IP addresses to MAC addresses. - What is ARP spoofing?
It’s a type of attack where a malicious actor sends fake ARP messages to redirect traffic. - Can ARP be manually configured?
Yes, static ARP entries can be configured for security or stability reasons. - How often is ARP used?
ARP requests happen every time a device needs to find another device's MAC address and doesn’t already know it. - Does ARP work across networks?
No, ARP is limited to local network segments. - Is ARP still relevant today?
Yes, ARP is essential in IPv4 networking but gradually being replaced by NDP in IPv6.
ARP Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Networking
- TCP/IP Stack
- Cybersecurity
Did you know?
Hackers use ARP spoofing techniques to intercept traffic between devices, making it one of the most common vulnerabilities in local networks. Many enterprise-level routers now include ARP inspection features to prevent these attacks.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment