High-Level Formatting

(Representational Image | Source: Dall-E)
Quick Navigation:
- High-Level Formatting Definition
- High-Level Formatting Explained Easy
- High-Level Formatting Origin
- High-Level Formatting Etymology
- High-Level Formatting Usage Trends
- High-Level Formatting Usage
- High-Level Formatting Examples in Context
- High-Level Formatting FAQ
- High-Level Formatting Related Words
High-Level Formatting Definition
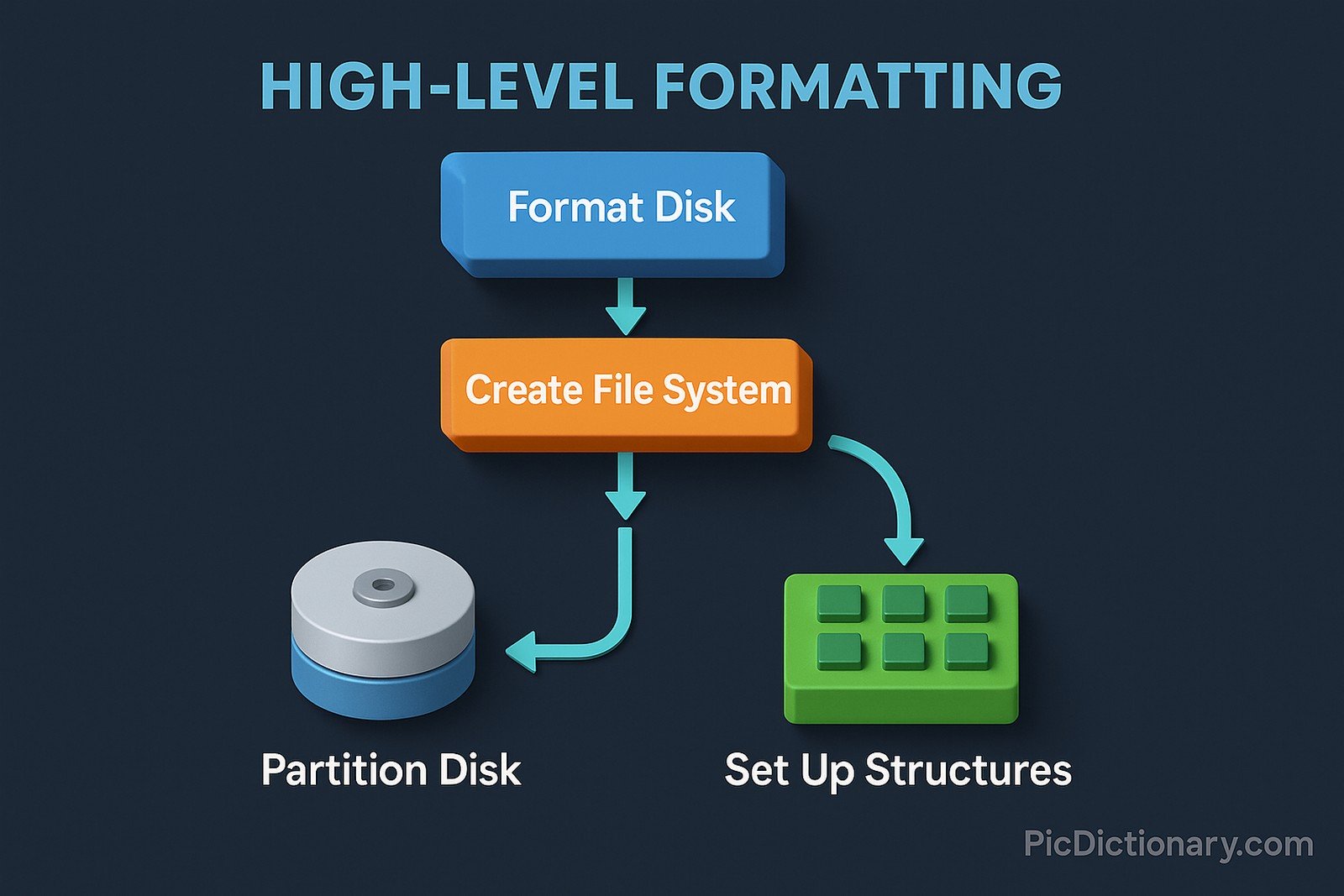
High-level formatting is a process that prepares a storage device, such as a hard drive or a USB flash drive, for use by creating a file system. This process organizes the disk into partitions and sets up structures like the master file table (MFT) or file allocation table (FAT), allowing an operating system to read and write data efficiently. Unlike low-level formatting, which sets the physical structure of a disk, high-level formatting deals with logical data structures. It is commonly performed when installing an operating system or reinitializing a storage device.
High-Level Formatting Explained Easy
Imagine you have a brand-new notebook, and you divide its pages into sections with labels so you can easily find what you need later. High-level formatting does something similar to a storage device, setting up an organized way for your computer to store and find files. It makes sure everything has a place, just like labeling sections in your notebook.
High-Level Formatting Origin
The concept of formatting storage devices dates back to the early days of computing when magnetic disks were first used. High-level formatting became widely adopted as operating systems like MS-DOS and Windows introduced file systems such as FAT and NTFS. Over time, advanced file systems like ext4 (Linux) and APFS (Mac) have improved efficiency and security.
High-Level Formatting Etymology
The term “high-level formatting” derives from the idea of working at a logical level, organizing the data structure rather than dealing with the physical disk surface, which is handled in low-level formatting.
High-Level Formatting Usage Trends
High-level formatting is an essential process in computing, especially in the following areas:
- Operating System Installation: Preparing a disk for OS installation.
- Data Wiping: Removing old data while keeping the disk functional.
- Drive Reinitialization: Converting between different file systems, such as NTFS to FAT32 or ext4 to Btrfs.
- Cloud and Virtual Storage: Formatting virtual drives for cloud and container-based environments.
High-Level Formatting Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Disk Management
- File Systems
- Storage Devices - Typical Collocations:
- "Format a hard drive"
- "NTFS high-level formatting"
- "Reformatting a USB drive"
- "Disk partitioning and high-level formatting"
High-Level Formatting Examples in Context
- "Before installing Linux, you need to perform a high-level formatting of the drive to use the ext4 file system."
- "When repurposing an old laptop, high-level formatting ensures a clean slate for a fresh OS installation."
- "Flash drives often require high-level formatting when switching between Windows and Mac systems."
High-Level Formatting FAQ
- What is high-level formatting?
High-level formatting is the process of setting up a file system on a storage device, allowing an operating system to read and write data. - How is high-level formatting different from low-level formatting?
Low-level formatting defines the physical structure of a disk, while high-level formatting organizes logical data structures like file systems. - Does high-level formatting erase all data?
Yes, but it does not remove data at a physical level. Specialized recovery tools may still retrieve formatted data. - What file systems are created by high-level formatting?
Common file systems include NTFS (Windows), ext4 (Linux), HFS+ (Mac), and FAT32 (universal). - When should I perform a high-level format?
You should perform high-level formatting when installing an OS, reinitializing a drive, or switching between file systems. - Can high-level formatting fix a corrupted drive?
In some cases, it can repair logical errors, but physical damage requires hardware solutions. - How long does high-level formatting take?
It depends on the disk size and speed. A quick format takes seconds, while a full format may take hours. - Does high-level formatting affect SSDs differently than HDDs?
Yes, frequent formatting can wear out SSDs faster due to write cycles, but modern SSDs manage this well. - Can I undo a high-level format?
Data recovery tools may restore lost files if no new data has been written over them. - Is high-level formatting necessary for new drives?
Yes, most new drives need high-level formatting before use to create a compatible file system.
High-Level Formatting Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Disk Management
- Data Recovery
- Computer Storage
Did you know?
In the early days of computing, formatting a hard drive was a time-consuming and manual process requiring user input for sector allocation. Today, modern operating systems automate high-level formatting, making disk setup almost instantaneous.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment