Virtual Private Network (VPN)

Quick Navigation:
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) Definition
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) Explained Easy
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) Origin
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) Etymology
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) Usage Trends
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) Usage
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) Examples in Context
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) FAQ
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) Related Words
Virtual Private Network (VPN) Definition
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a secure technology that creates an encrypted connection over the internet between your device and a remote server. This connection masks your IP address, making your online actions virtually untraceable, and protects your data from hackers and surveillance. VPNs use tunneling protocols such as OpenVPN, IPSec, and WireGuard to ensure that data is securely transmitted, even on unsecured networks. They are commonly used in corporate environments to grant employees secure access to private company resources and by individuals for privacy, security, and access to geo-restricted content.
Virtual Private Network (VPN) Explained Easy
Imagine sending a secret message to a friend through a tunnel that nobody can see inside. A VPN is like that tunnel on the internet. It keeps your online activities hidden and safe from strangers. So when you watch videos or play games online, a VPN makes sure nobody is spying on you or stealing your personal information.
Virtual Private Network (VPN) Origin
The concept of VPNs began in the mid-1990s when Microsoft created the Peer-to-Peer Tunneling Protocol (PPTP). This was aimed at providing employees with a secure way to access corporate networks remotely. Over the years, VPN technology has evolved with stronger encryption and advanced protocols, becoming a staple in both enterprise security and personal privacy.
Virtual Private Network (VPN) Etymology
The term “virtual” signifies something that exists digitally rather than physically, and “private network” refers to a closed, secure communication channel.
Virtual Private Network (VPN) Usage Trends
VPN usage has grown exponentially with rising concerns over data privacy and cyber threats. Particularly after high-profile data breaches and revelations about government surveillance, more individuals and organizations adopted VPNs. The pandemic further boosted VPN usage, as remote work became the norm and companies needed to secure remote connections for their employees.
Virtual Private Network (VPN) Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Network Security
- Cybersecurity
- Privacy Protection - Typical Collocations:
- "VPN connection"
- "encrypted VPN tunnel"
- "VPN server"
- "secure VPN access"
Virtual Private Network (VPN) Examples in Context
- A company employee connects to the corporate network from home using a VPN to access confidential documents.
- Travelers use a VPN to access websites from their home country that might be blocked in the country they are visiting.
- Gamers use VPNs to bypass geo-restrictions and reduce lag by connecting to faster servers.
Virtual Private Network (VPN) FAQ
- What is a VPN?
A VPN is a secure network connection that protects your data and privacy online. - How does a VPN protect me?
It encrypts your internet traffic and hides your IP address, making it hard for others to track you. - Is using a VPN legal?
In most countries, yes, but using it for illegal activities is still prohibited. - Does a VPN slow down internet speed?
It can slightly reduce speed, but premium VPNs minimize this impact. - Can I use a VPN on mobile devices?
Yes, most VPN services offer apps for smartphones and tablets. - Do VPNs keep logs of user activity?
Some do, but many premium VPNs have a strict no-logs policy. - Can a VPN bypass streaming restrictions?
Yes, VPNs can help you access geo-restricted content. - Is a free VPN safe to use?
Free VPNs often lack strong security and may sell your data; premium services are recommended. - How do I choose a good VPN?
Look for strong encryption, no-logs policy, fast servers, and good reviews. - Does a VPN protect me from viruses?
No, VPNs protect privacy and data but do not replace antivirus protection.
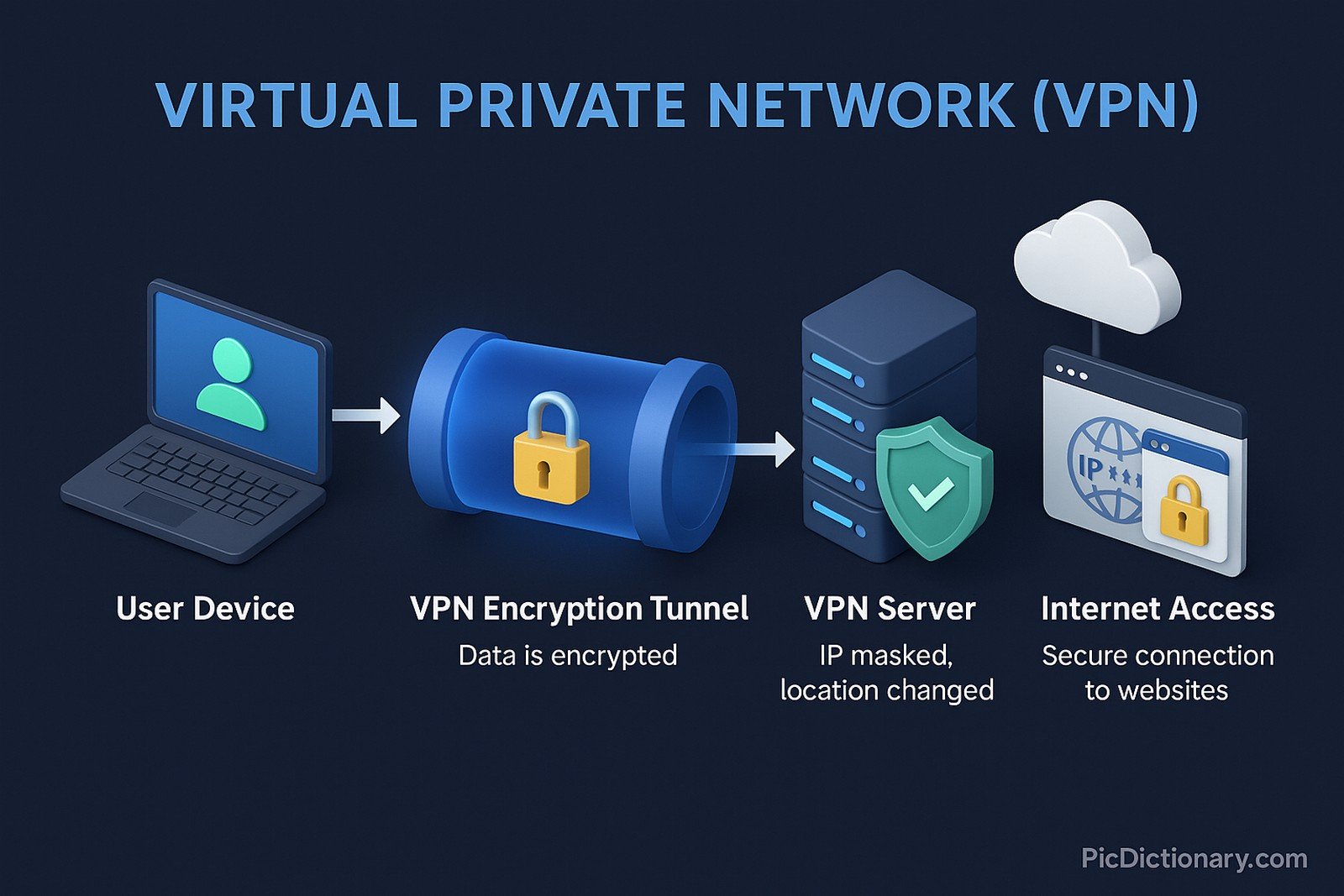
Virtual Private Network (VPN) Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Network Security
- Data Encryption
- Privacy Tools
Did you know?
In 2017, the Chinese government banned VPN services that were not government-approved. Despite this, millions of users continued using VPNs to access the open internet, showcasing how essential VPNs have become for digital freedom.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment