Restore Automation

Quick Navigation:
- Restore Automation Definition
- Restore Automation Explained Easy
- Restore Automation Origin
- Restore Automation Etymology
- Restore Automation Usage Trends
- Restore Automation Usage
- Restore Automation Examples in Context
- Restore Automation FAQ
- Restore Automation Related Words
Restore Automation Definition
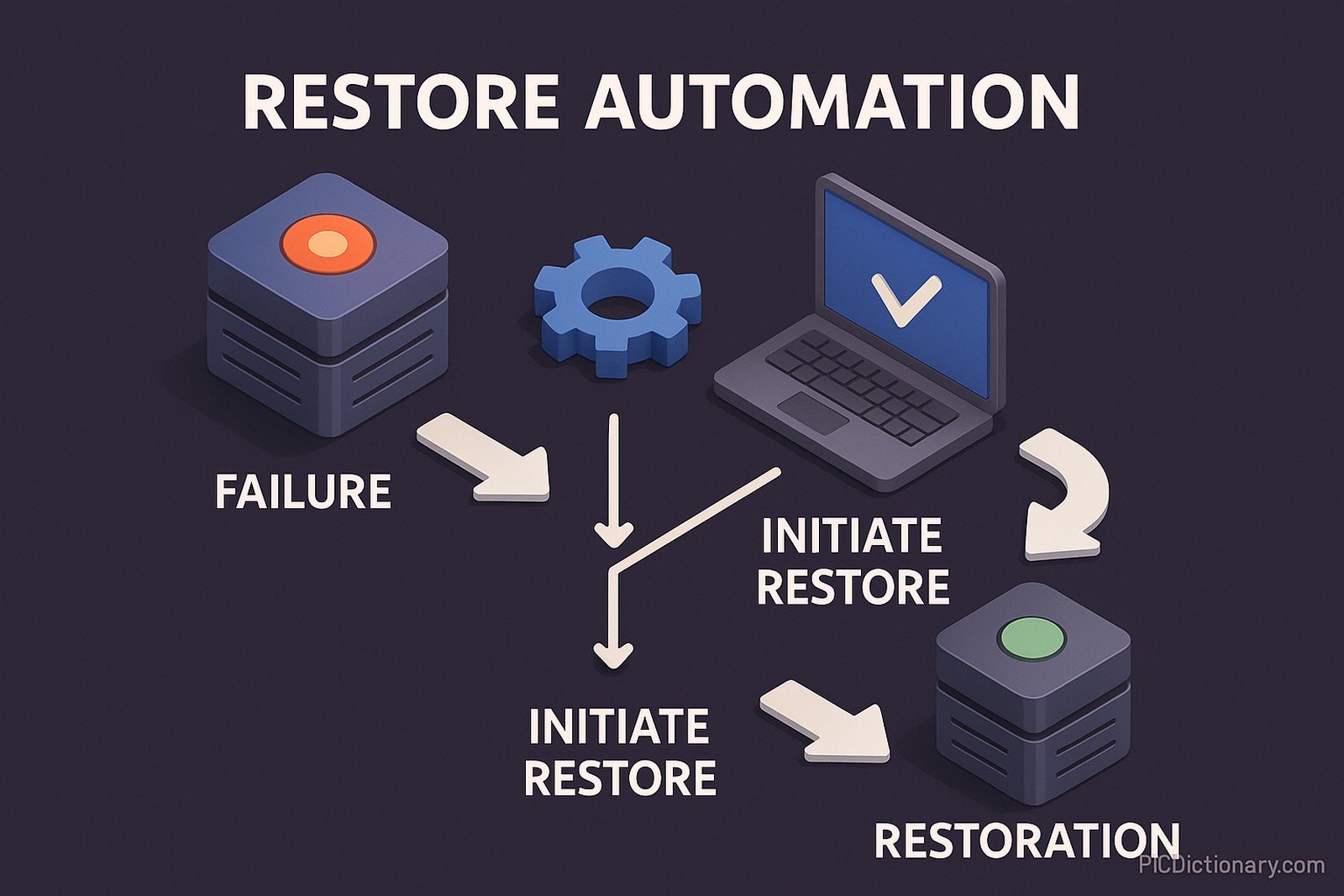
Restore automation refers to the process of automating the restoration of systems, files, applications, or infrastructure after a failure, data corruption, or disaster. It ensures minimal downtime by using scripts, policies, and tools to quickly and efficiently restore data and services to their last known good state. Restore automation is widely used in cloud computing, disaster recovery, and system administration, helping organizations maintain business continuity with minimal manual intervention.
Restore Automation Explained Easy
Imagine you have a toy castle that keeps getting knocked over. Instead of rebuilding it from scratch every time, you have a magical button that instantly puts all the pieces back together just the way they were before. Restore automation is like that button but for computers—it brings back lost files and fixes broken systems without needing to do everything manually.
Restore Automation Origin
The concept of restore automation emerged as computing environments grew more complex. Early backup and recovery methods were manual, requiring extensive human effort. With the rise of cloud computing and virtualization in the 2000s, automated recovery solutions became essential to ensure quick restoration of critical systems.
Restore Automation Etymology
The term “restore” comes from the Latin word restaurare, meaning "to rebuild or repair," while “automation” is derived from the Greek automatos, meaning "acting of itself." Together, they define a process that restores data or systems automatically.
Restore Automation Usage Trends
Restore automation has become increasingly important with the rise of cloud computing, cybersecurity threats, and large-scale enterprise systems. Organizations rely on automated restore solutions for disaster recovery, ransomware mitigation, and data integrity assurance. The shift to hybrid and multi-cloud infrastructures has further accelerated the adoption of automated restore strategies.
Restore Automation Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Disaster Recovery
- Backup and Restore
- Cloud Computing
- System Administration - Typical Collocations:
- "automated restore process"
- "restore automation tools"
- "disaster recovery automation"
- "automated data restoration"
Restore Automation Examples in Context
- A cloud service provider uses restore automation to recover customer data after a hardware failure.
- A company experiencing a ransomware attack quickly restores encrypted files using an automated recovery system.
- IT administrators set up automated backup policies to restore lost configurations with minimal downtime.
Restore Automation FAQ
- What is restore automation?
Restore automation is the process of automatically restoring data, applications, or systems after failure, corruption, or disaster. - How does restore automation work?
It uses scripts, scheduled backups, and intelligent recovery systems to detect failures and restore data with minimal manual effort. - Why is restore automation important?
It minimizes downtime, reduces human error, and ensures business continuity in the event of data loss or cyberattacks. - What industries benefit from restore automation?
IT services, cloud computing, healthcare, finance, and any industry requiring secure data recovery solutions. - How does restore automation help in cybersecurity?
It allows organizations to quickly recover from ransomware attacks and malicious data alterations. - What are common restore automation tools?
Solutions like Veeam, Acronis, AWS Backup, and Microsoft Azure Site Recovery. - Can restore automation be used for databases?
Yes, many database management systems offer automated restore options for quick recovery. - Does restore automation require human intervention?
While mostly automated, some cases require validation or manual approval before initiating recovery. - Is restore automation expensive?
Costs vary depending on the system, but automated solutions save money by reducing downtime and labor costs. - Can small businesses use restore automation?
Yes, even small businesses can implement basic automated restore solutions for critical data protection.
Restore Automation Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Data Recovery
- Disaster Recovery
- Cloud Infrastructure
- IT Automation
Did you know?
One of the first large-scale uses of restore automation was in NASA’s space missions, where automated backup and recovery systems ensured that mission-critical data could be restored instantly in case of failures. Today, similar technologies are used in banking, healthcare, and even gaming industries to maintain seamless digital operations.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment