Type-1 Hypervisor
Quick Navigation:
- Type-1 Hypervisor Definition
- Type-1 Hypervisor Explained Easy
- Type-1 Hypervisor Origin
- Type-1 Hypervisor Etymology
- Type-1 Hypervisor Usage Trends
- Type-1 Hypervisor Usage
- Type-1 Hypervisor Examples in Context
- Type-1 Hypervisor FAQ
- Type-1 Hypervisor Related Words
Type-1 Hypervisor Definition
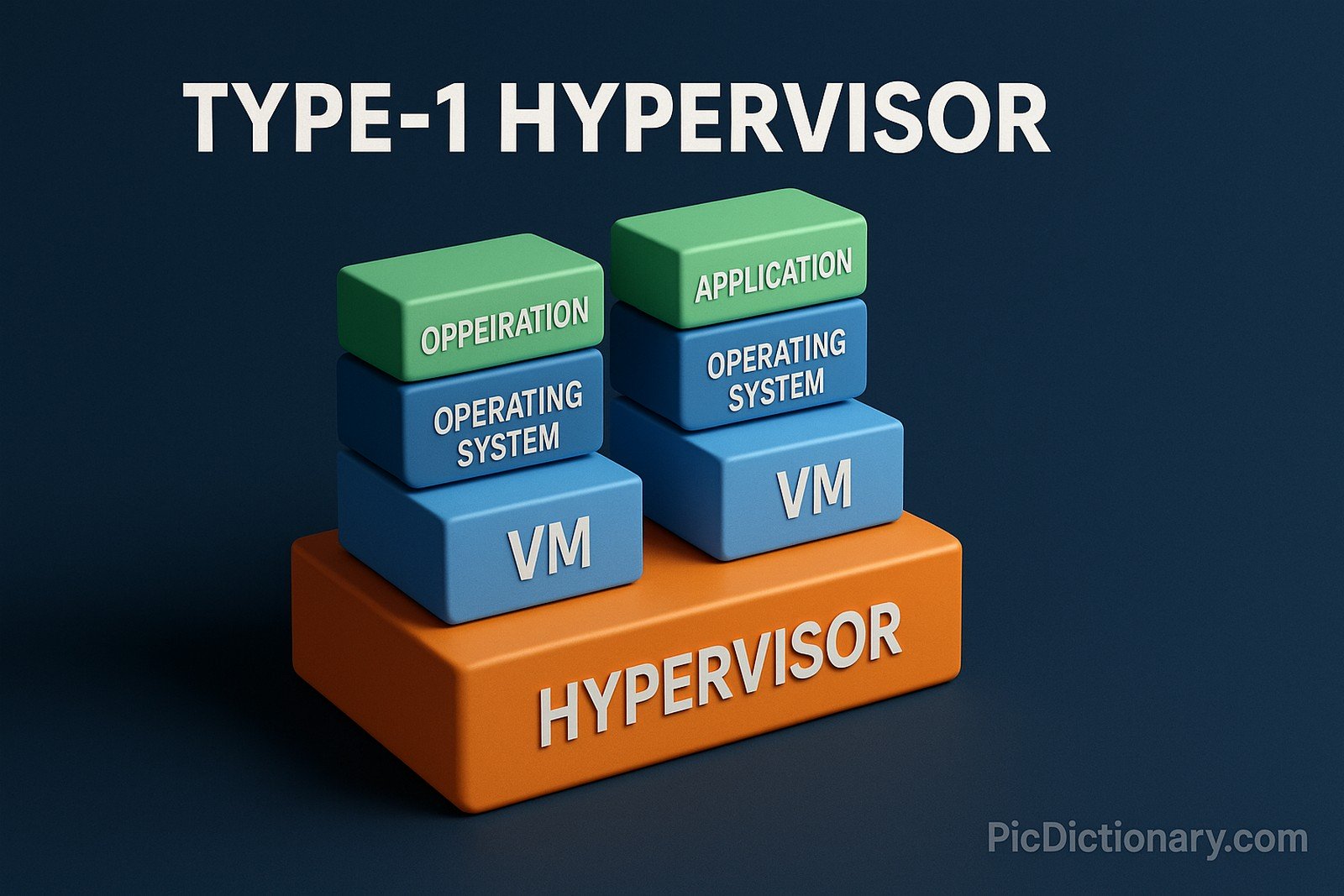
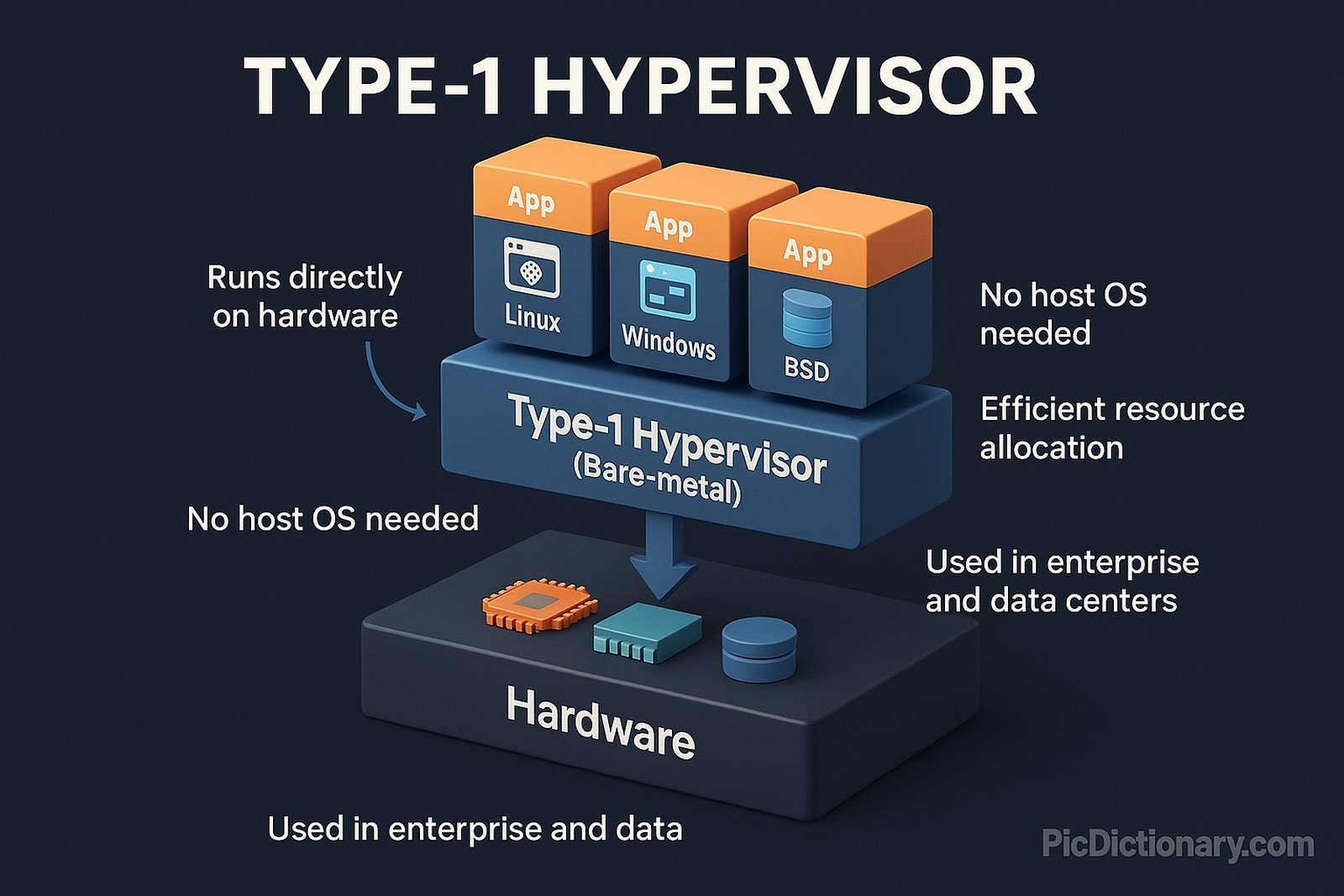
A Type-1 Hypervisor, also known as a bare-metal hypervisor, is virtualization software that runs directly on hardware, managing multiple virtual machines efficiently. Examples include VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, and Xen.
Type-1 Hypervisor Explained Easy
Think of a powerful computer divided into smaller ones, each running its own OS. A Type-1 Hypervisor manages this division directly on the hardware, making it fast and efficient.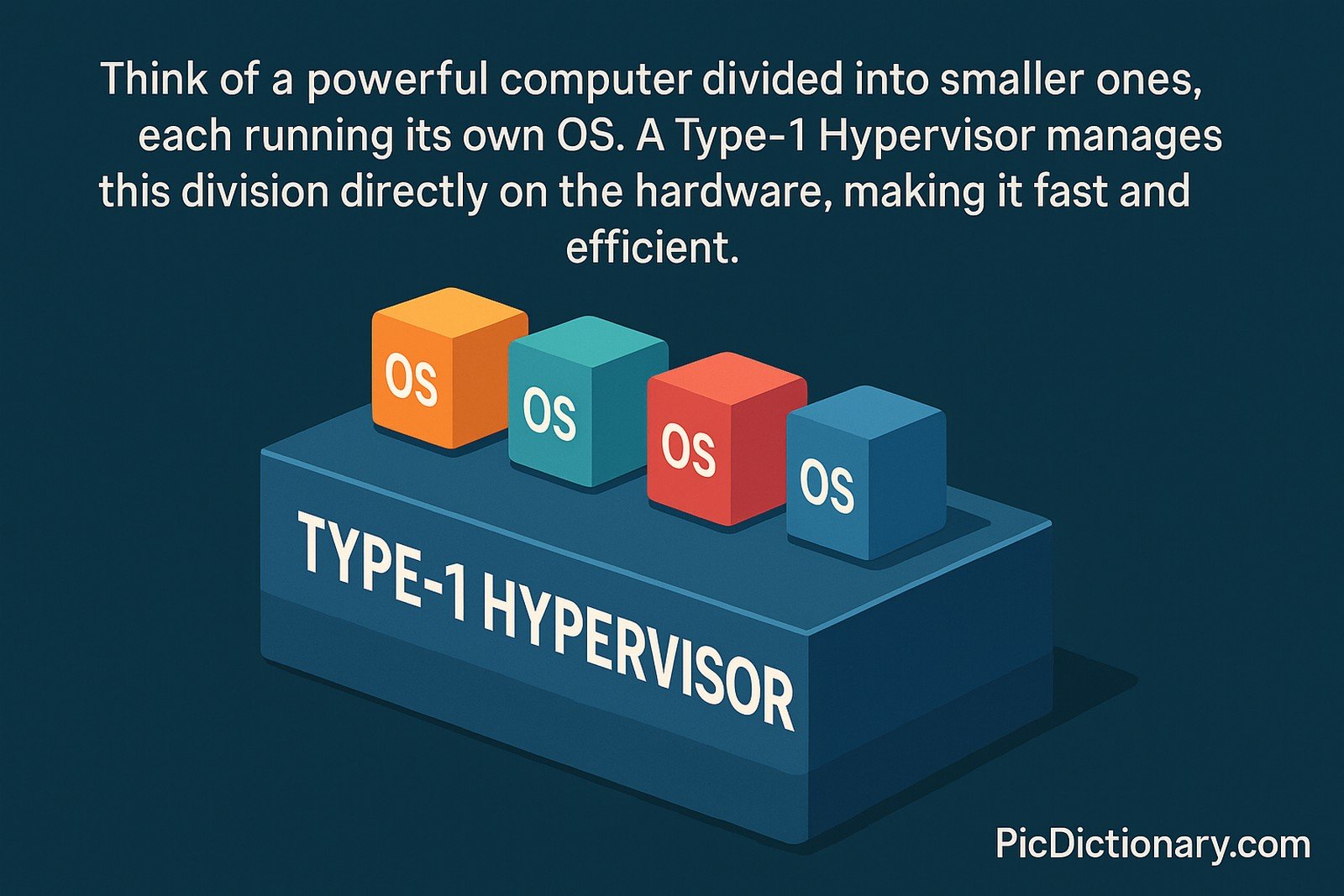
Type-1 Hypervisor Origin
The concept began in the 1960s with IBM’s virtual machine technology, later evolving into today’s cloud-based hypervisors.
Type-1 Hypervisor Etymology
The word "hypervisor" comes from "supervisor," indicating its role in managing virtual machines directly on hardware.
Type-1 Hypervisor Usage Trends
With cloud computing and enterprise IT growth, Type-1 Hypervisors have become essential for virtualization, edge computing, and data centers.
Type-1 Hypervisor Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Virtualization
- Cloud Computing
- Data Center Management - Typical Collocations:
- "Type-1 hypervisor architecture"
- "bare-metal virtualization"
- "enterprise hypervisor solution"
- "hardware-based hypervisor security"
Type-1 Hypervisor Examples in Context
- Cloud providers like AWS and Azure use Type-1 Hypervisors to run virtual servers.
- Enterprises deploy Type-1 Hypervisors to optimize resources in data centers.
- Financial institutions use Type-1 Hypervisors for secure, high-availability applications.
Type-1 Hypervisor FAQ
- What is a Type-1 Hypervisor?
It’s a hypervisor that runs directly on hardware to manage virtual machines. - How does it differ from a Type-2 Hypervisor?
Type-1 Hypervisors operate on hardware, whereas Type-2 Hypervisors run on an OS. - Examples of Type-1 Hypervisors?
VMware ESXi, Hyper-V, and Xen. - Why are they preferred for enterprises?
They provide better performance, security, and resource efficiency. - Can they be used on personal computers?
They are mainly designed for server environments. - Are Type-1 Hypervisors secure?
Yes, due to their isolated architecture. - Do they support different OSes?
Yes, they can run multiple operating systems on one machine. - Industries using them?
Cloud, finance, healthcare, and government sectors. - Performance benefits?
They reduce overhead and enhance resource efficiency. - Are there free versions?
Some, like Xen, are open-source, while others require licenses.
Type-1 Hypervisor Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Virtualization
- Cloud Infrastructure
- IT Security
Did you know?
IBM’s CP-40, the first Type-1 Hypervisor, paved the way for modern cloud computing.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment