DNS (Domain Name System)

Quick Navigation:
- DNS Definition
- DNS Explained Easy
- DNS Origin
- DNS Etymology
- DNS Usage Trends
- DNS Usage
- DNS Examples in Context
- DNS FAQ
- DNS Related Words
DNS Definition
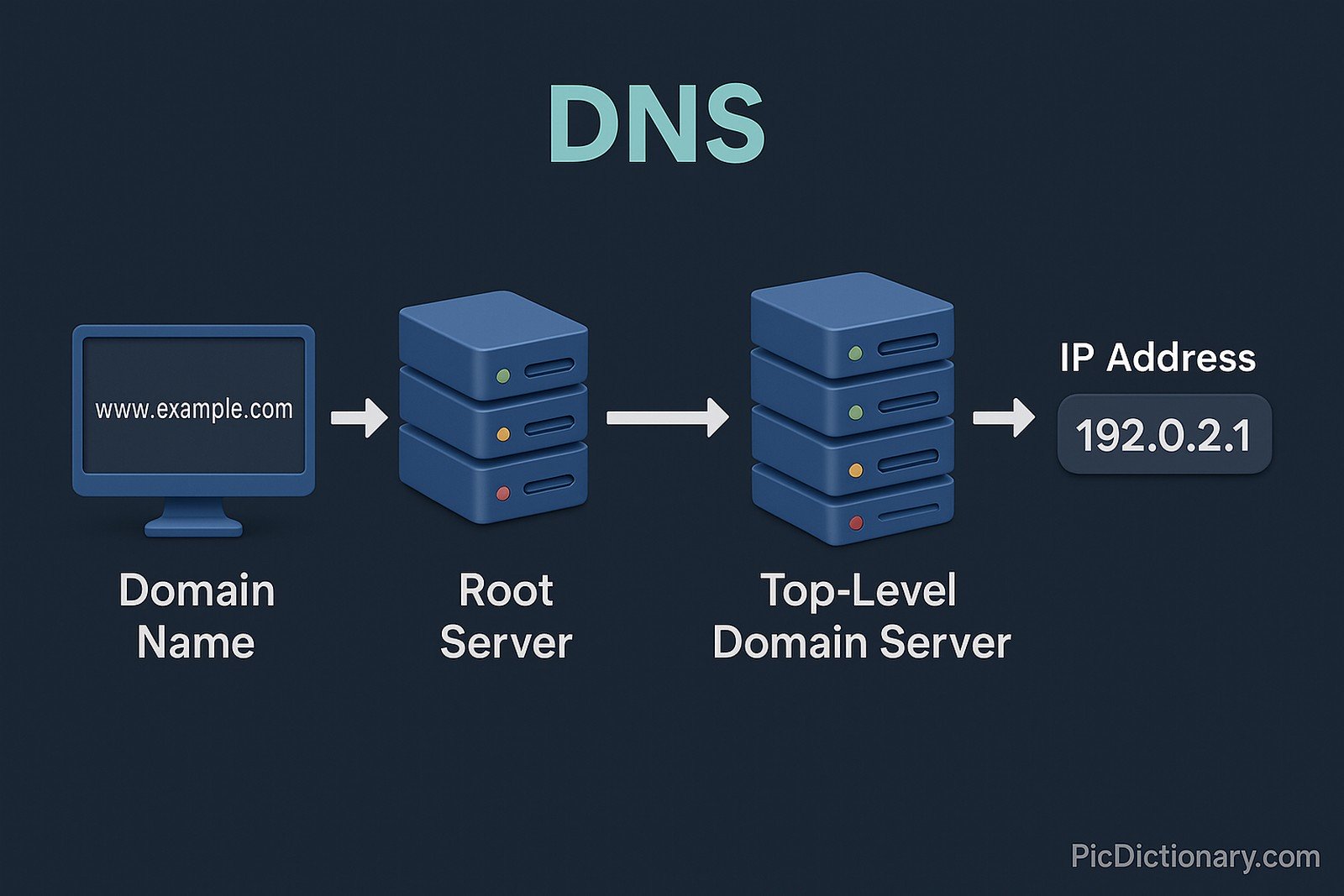
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical and decentralized naming system used to resolve human-friendly domain names, such as www.example.com, into machine-readable IP addresses like 192.0.2.1. It acts like the internet’s phonebook. DNS servers handle requests, starting from root servers to top-level domain servers and then to authoritative servers, finally returning the corresponding IP address. DNS operates using UDP and TCP protocols over port 53, ensuring that when users enter a website name, they are seamlessly directed to the correct web server.
DNS Explained Easy
Imagine typing your friend’s name into a phone to find their number. DNS works the same way for the internet — when you type a website name, DNS finds the right address and tells your computer where to go.
DNS Origin
DNS was introduced in 1983 by Paul Mockapetris to replace the cumbersome hosts.txt file that initially mapped hostnames to IP addresses. The system was designed to scale alongside the rapid growth of the internet and distributed networking.
DNS Etymology
The term DNS comes from “domain,” referring to names grouped under a namespace, and “system,” indicating its structured and hierarchical design for resolving queries.
DNS Usage Trends
With the explosion of internet services, DNS has become a critical backbone of the web. It’s used not only for website access but also in email delivery and cloud services. Over time, DNS security enhancements like DNSSEC have gained popularity, protecting users from spoofing attacks. Public DNS resolvers like Google DNS and Cloudflare DNS have also made DNS services faster and more reliable for everyday users.
DNS Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Networking
- Internet Protocols
- Web Infrastructure - Typical Collocations:
- "DNS resolution"
- "DNS server"
- "DNS query"
- "DNS propagation"
- "DNS lookup"
- "recursive DNS resolver"
DNS Examples in Context
- A user typing www.google.com in a browser gets directed to Google's IP via DNS resolution.
- DNS servers are used by email systems to find the mail servers of the recipient's domain.
- When a website changes hosting, DNS propagation ensures new IP addresses are spread across global servers.
DNS FAQ
- What is DNS?
DNS translates domain names into IP addresses, making internet browsing user-friendly. - Why is DNS important?
Without DNS, users would need to remember numerical IP addresses to access websites. - What are DNS servers?
They are systems that store and resolve domain names into IP addresses. - How long does DNS propagation take?
Typically between 24 to 72 hours globally. - What is DNS caching?
A temporary storage that keeps DNS query results to speed up future requests. - What happens if DNS fails?
Users cannot access websites using domain names. - What is DNS spoofing?
A cyberattack where incorrect DNS responses are provided to mislead users. - What’s the difference between recursive and authoritative DNS servers?
Recursive servers handle the entire DNS query process; authoritative servers hold specific DNS records. - Can DNS queries be encrypted?
Yes, technologies like DNS-over-HTTPS (DoH) and DNS-over-TLS (DoT) encrypt DNS queries. - How can I flush DNS cache?
On Windows, use the command "ipconfig /flushdns"; on macOS, "sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder."
DNS Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Networking
- Internet Infrastructure
- Cybersecurity
Did you know?
The first DNS root servers were deployed in 1984 and continue to be critical components of the global internet infrastructure, handling billions of DNS queries every day.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment