HMAC (Hash-Based Message Authentication Code)

Quick Navigation:
- HMAC Definition
- HMAC Explained Easy
- HMAC Origin
- HMAC Etymology
- HMAC Usage Trends
- HMAC Usage
- HMAC Examples in Context
- HMAC FAQ
- HMAC Related Words
HMAC Definition
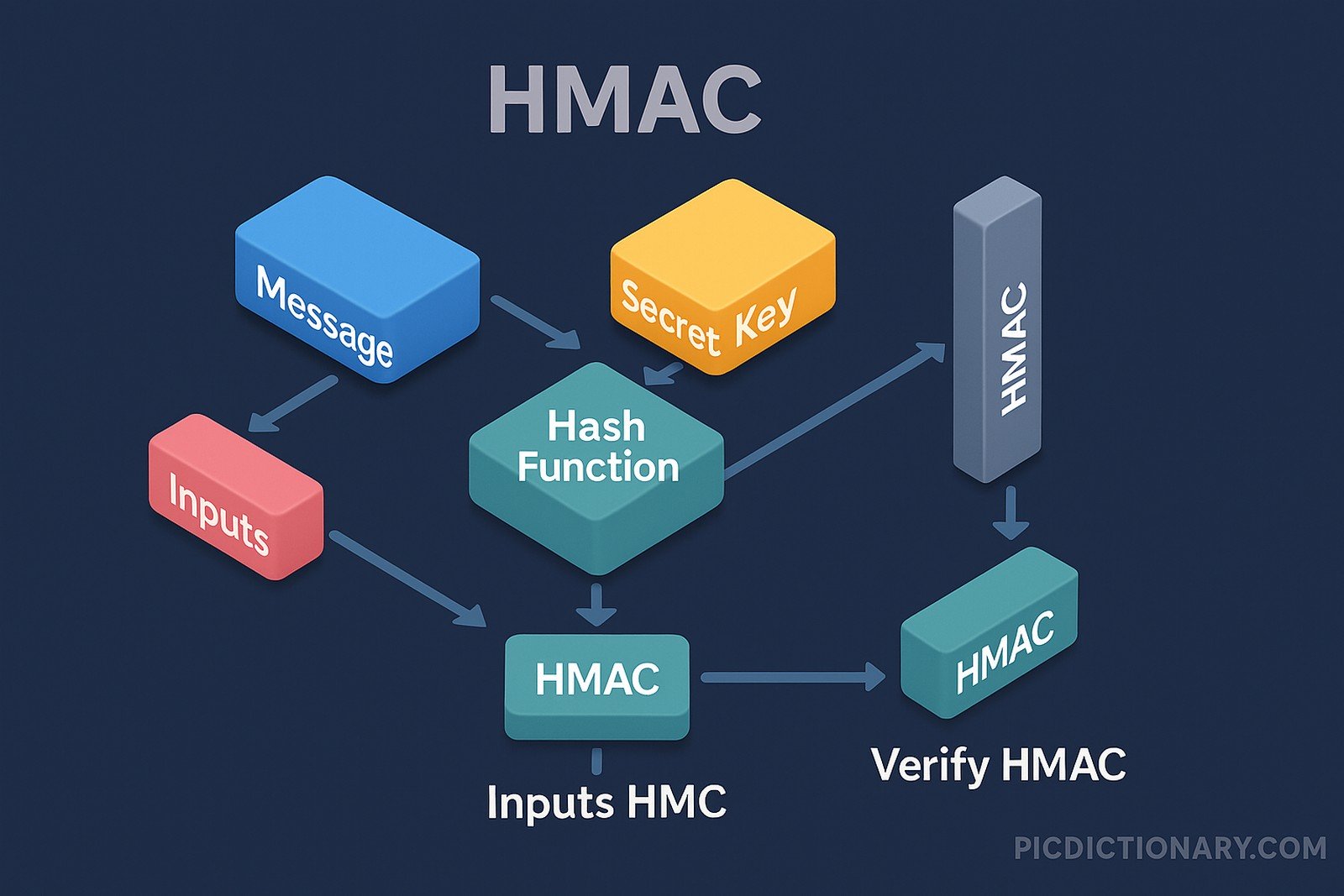
HMAC, or Hash-Based Message Authentication Code, is a specific construction for creating a message authentication code (MAC) involving a cryptographic hash function and a secret cryptographic key. It provides both data integrity and authenticity by allowing the receiver to verify that the message was not altered in transit and originated from the expected sender. HMAC is widely used in secure protocols, including SSL/TLS, IPsec, and HTTPS. It leverages underlying hash functions like SHA-256 or SHA-512.
HMAC Explained Easy
Think of HMAC like a secret handshake between two friends. If you receive a message with the handshake, you know it’s really from your friend and not changed. It uses secret keys and a special formula so no one else can guess the handshake or fake a message.
HMAC Origin
HMAC was introduced by Mihir Bellare, Ran Canetti, and Hugo Krawczyk in 1996. It was standardized in RFC 2104 by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) to provide a method for message authentication that is both secure and simple to implement using hash functions.
HMAC Etymology
The name "HMAC" is formed from the combination of "hash-based," "message," and "authentication code," highlighting its functional components in verifying message integrity.
HMAC Usage Trends
HMAC’s usage has grown extensively alongside the development of web security and API authentication. It has become a key component in cloud-based services, financial transactions, and secure communications protocols. Its continued adoption reflects trust in cryptographic strength and efficiency, even with evolving security challenges.
HMAC Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Cryptography
- Cybersecurity
- Data Integrity
- Authentication Protocols - Typical Collocations:
- "HMAC signature"
- "HMAC key generation"
- "secure API with HMAC"
- "HMAC verification process"
HMAC Examples in Context
- Cloud services use HMAC to sign API requests, ensuring only authorized users access data.
- Financial applications rely on HMAC to confirm that transaction data has not been tampered with.
- HMAC helps secure communication channels in VPNs by authenticating packets.
HMAC FAQ
- What is HMAC?
HMAC is a cryptographic technique combining hash functions and a secret key to ensure data authenticity and integrity. - How does HMAC work?
HMAC applies a hash function to the message combined with a secret key in a specific pattern, generating a unique code that validates the message. - Where is HMAC used?
HMAC is used in secure web communications, API request authentication, digital signatures, and data integrity checks. - Can HMAC be broken?
HMAC is considered very secure when used with strong keys and reliable hash functions like SHA-256 or SHA-512. - What algorithms are used with HMAC?
Common hash algorithms include SHA-1, SHA-256, SHA-512, and sometimes MD5 (though MD5 is outdated and discouraged). - Is HMAC the same as digital signatures?
Not exactly. While both authenticate data, digital signatures use asymmetric cryptography, while HMAC uses symmetric keys. - Can I use HMAC for password storage?
No, HMAC is not recommended for password storage. Use key derivation functions like bcrypt or PBKDF2 instead. - Does HMAC ensure confidentiality?
No, HMAC ensures data integrity and authenticity, but not confidentiality. - Is HMAC resistant to replay attacks?
HMAC alone isn’t; systems need additional protections like timestamps or nonces to prevent replay attacks. - Is HMAC fast to compute?
Yes, HMAC is computationally efficient, making it suitable for high-throughput systems.
HMAC Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Cryptographic Hashes
- Data Security
- Network Protocols
- Authentication Methods
Did you know?
Amazon Web Services (AWS) uses HMAC for authenticating API requests in its Signature Version 4 process. Every request is signed with HMAC using a secret access key, ensuring that each API call is verified for authenticity and integrity.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment