Meltdown Vulnerability

Quick Navigation:
- Meltdown Vulnerability Definition
- Meltdown Vulnerability Explained Easy
- Meltdown Vulnerability Origin
- Meltdown Vulnerability Etymology
- Meltdown Vulnerability Usage Trends
- Meltdown Vulnerability Usage
- Meltdown Vulnerability Examples in Context
- Meltdown Vulnerability FAQ
- Meltdown Vulnerability Related Words
Meltdown Vulnerability Definition
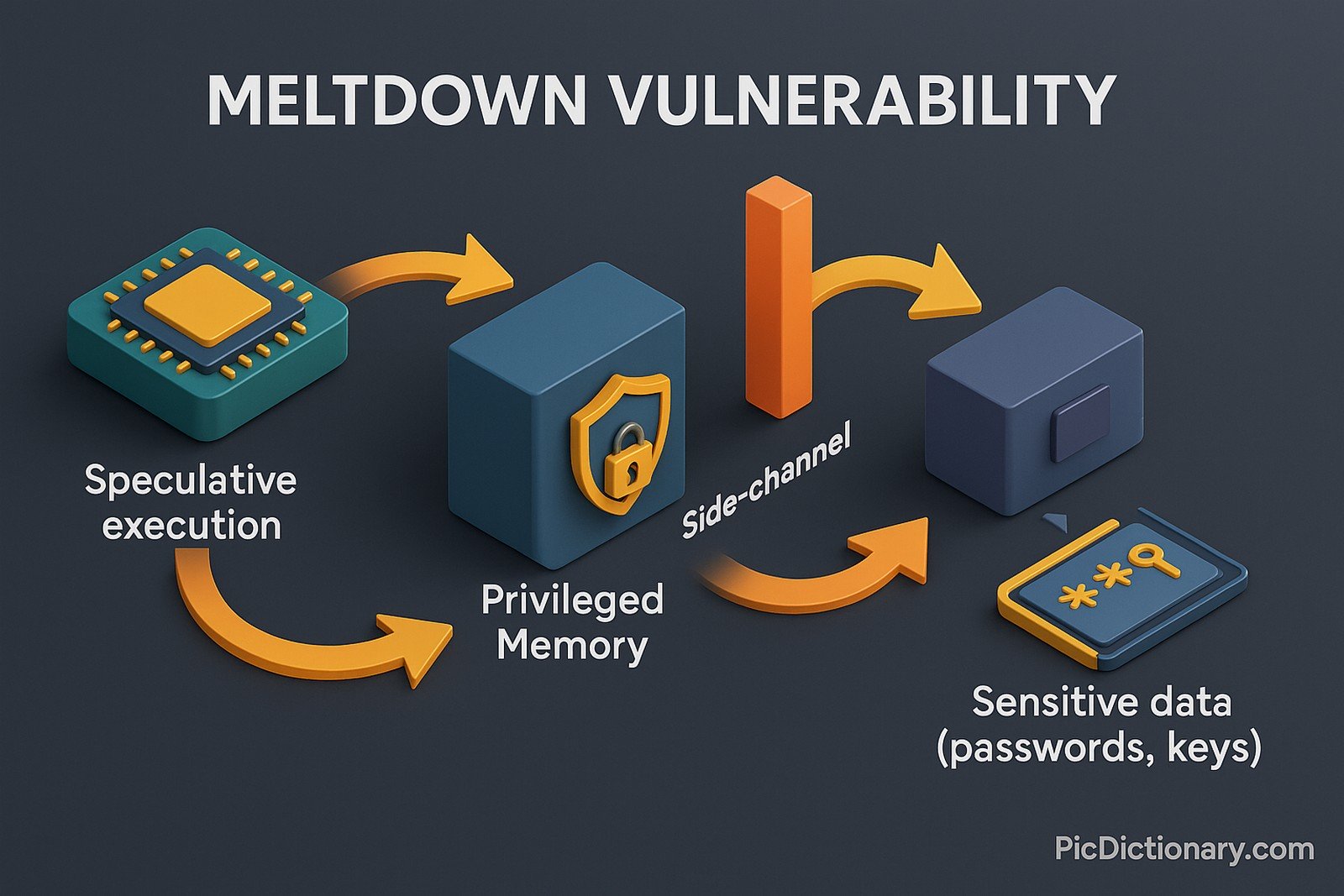
Meltdown is a security vulnerability affecting modern microprocessors, allowing unauthorized access to protected memory areas. It exploits speculative execution, a performance optimization technique, to bypass security boundaries and read sensitive data from privileged memory. This vulnerability primarily impacts Intel CPUs and, to a lesser extent, ARM-based processors. It poses a significant risk, as attackers can potentially extract passwords, encryption keys, and other confidential data directly from memory.
Meltdown Vulnerability Explained Easy
Imagine your computer is like a big library where some books are locked away because they contain secret information. Meltdown is like a trick that lets someone read those locked books, even though they’re supposed to be off-limits. This means someone could see important stuff, like passwords, that they shouldn’t be able to access.
Meltdown Vulnerability Origin
Meltdown was discovered in 2017 by security researchers from Google’s Project Zero, Cyberus Technology, and academic institutions. The vulnerability was publicly disclosed in January 2018 alongside another major flaw called Spectre. These vulnerabilities shook the tech industry, as they revealed fundamental security flaws in modern processor architectures.
Meltdown Vulnerability Etymology
The name "Meltdown" was chosen because the vulnerability "melts" security boundaries normally enforced by the hardware, allowing access to restricted data.
Meltdown Vulnerability Usage Trends
Since its disclosure, Meltdown has had a lasting impact on cybersecurity. Hardware and software vendors rushed to release patches, but mitigating the issue often came with performance penalties. Over time, researchers developed more efficient workarounds, but Meltdown highlighted the importance of hardware-level security in computing. Its discovery led to widespread security audits and redesigns in processor architectures to prevent similar vulnerabilities.
Meltdown Vulnerability Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Cybersecurity
- Processor Security
- Speculative Execution - Typical Collocations:
- "Meltdown vulnerability exploit"
- "Mitigating Meltdown attacks"
- "Meltdown security patches"
- "Processor vulnerability in Meltdown"
Meltdown Vulnerability Examples in Context
- Security researchers demonstrated how Meltdown could extract sensitive information, such as passwords, from a computer’s memory.
- Operating system vendors like Microsoft, Apple, and Linux maintainers released emergency patches to mitigate the effects of Meltdown.
- Cloud computing providers had to reconfigure their infrastructure to prevent Meltdown-based attacks between virtual machines.
Meltdown Vulnerability FAQ
- What is the Meltdown vulnerability?
Meltdown is a security flaw in modern processors that allows unauthorized access to protected memory. - How does Meltdown work?
It exploits speculative execution to read privileged memory that should be inaccessible. - Which processors are affected by Meltdown?
Mainly Intel processors, but some ARM processors are also vulnerable. - How serious is Meltdown?
It’s a critical vulnerability, as attackers can extract sensitive data, including passwords and encryption keys. - How was Meltdown discovered?
It was found by security researchers from Google’s Project Zero and other organizations in 2017. - Can Meltdown be fixed?
Yes, through operating system patches, firmware updates, and architectural changes in new processors. - Does fixing Meltdown slow down computers?
Yes, some patches reduce performance, particularly in data-heavy workloads. - Is Meltdown still a threat today?
While patches mitigate it, older unpatched systems remain vulnerable. - Does Meltdown affect all operating systems?
Yes, all major OS vendors had to release security updates to address it. - What is the difference between Meltdown and Spectre?
Meltdown allows access to privileged memory, while Spectre tricks programs into leaking sensitive data across applications.
Meltdown Vulnerability Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Cybersecurity
- Processor Security
- Hardware Vulnerabilities
Did you know?
Shortly after Meltdown’s disclosure, cloud service providers like Amazon, Google, and Microsoft had to implement emergency security updates to prevent attackers from exploiting the vulnerability in shared computing environments. Some of these mitigations caused temporary slowdowns for cloud users.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment