Multi-Master Replication
 (Representational Image | Source: Dall-E)
(Representational Image | Source: Dall-E)
Quick Navigation:
- Multi-Master Replication Definition
- Multi-Master Replication Explained Easy
- Multi-Master Replication Origin
- Multi-Master Replication Etymology
- Multi-Master Replication Usage Trends
- Multi-Master Replication Usage
- Multi-Master Replication Examples in Context
- Multi-Master Replication FAQ
- Multi-Master Replication Related Words
Multi-Master Replication Definition
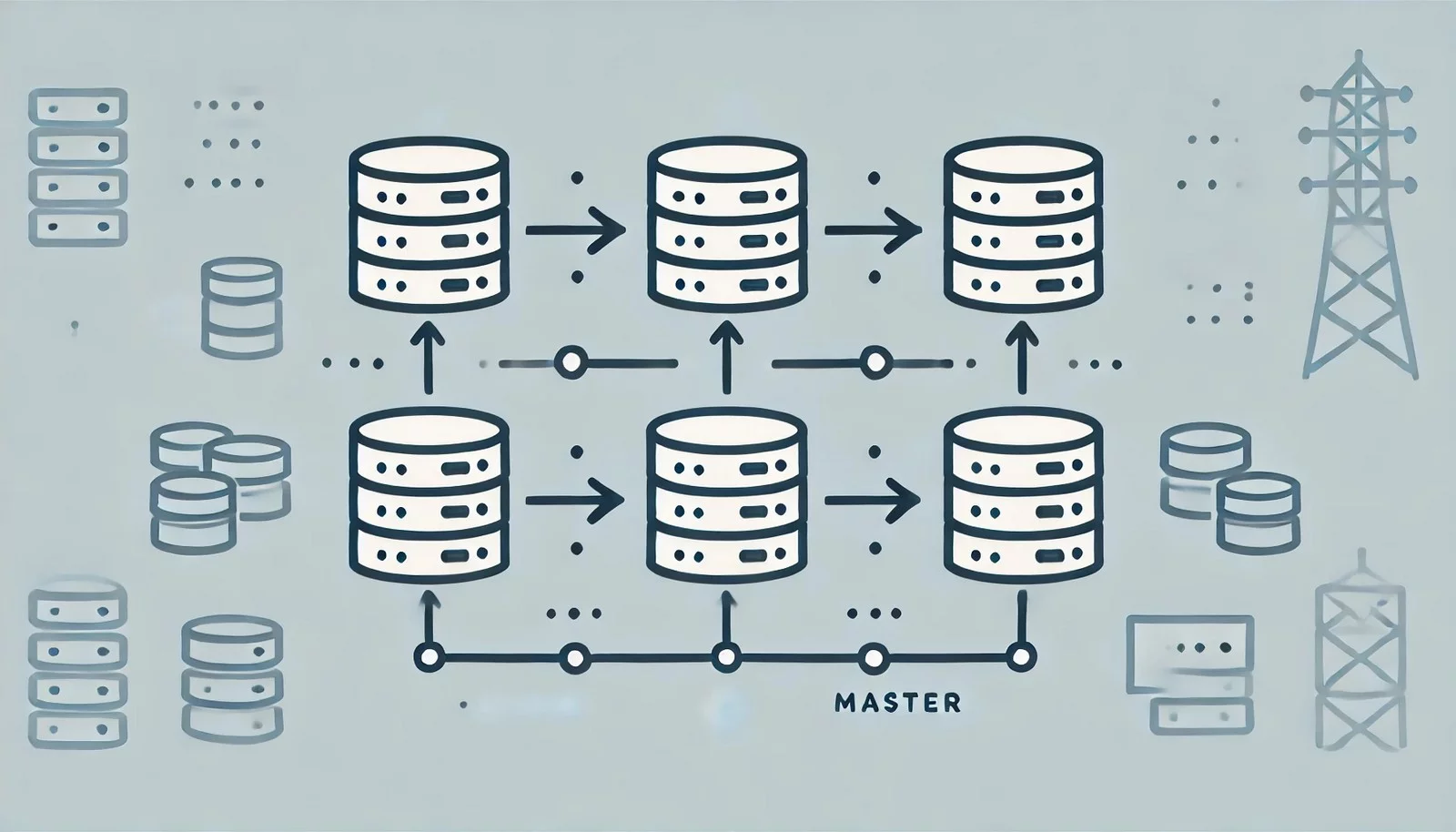
Multi-Master Replication is a database replication method where multiple database servers (masters) are capable of receiving and processing write operations simultaneously. Changes made on any master are synchronized across all other masters, ensuring consistency.
This approach is often used in distributed database systems to enhance availability, fault tolerance, and load balancing. It is widely implemented in systems like MySQL Group Replication, PostgreSQL BDR, and Microsoft SQL Server Peer-to-Peer Replication.
Multi-Master Replication Explained Easy
Imagine you have a notebook, and your friend has an identical one. Every time you write something, it magically appears in your friend’s notebook too, and when your friend writes something, it appears in yours. Multi-Master Replication works just like that in databases—multiple computers (masters) can make updates, and they all stay synchronized.
Multi-Master Replication Origin
The concept of Multi-Master Replication emerged with the need for scalable, high-availability databases. It was first explored in distributed computing research in the 1980s and gained prominence with enterprise database solutions in the late 1990s and early 2000s.
Multi-Master Replication Etymology
The term “Multi-Master Replication” is derived from the words "multi" (many), "master" (a database that can perform writes), and "replication" (copying data across systems).
Multi-Master Replication Usage Trends
Multi-Master Replication has gained popularity due to the increasing demand for high-availability systems and real-time data synchronization across multiple locations. It is heavily utilized in e-commerce platforms, banking applications, content delivery networks, and globally distributed databases.
Multi-Master Replication Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Distributed Databases
- High-Availability Systems
- Data Synchronization - Typical Collocations:
- "Multi-Master Replication setup"
- "Distributed database synchronization"
- "Multi-master database conflicts"
- "Conflict resolution in Multi-Master Replication"
Multi-Master Replication Examples in Context
- A multinational e-commerce platform uses Multi-Master Replication to ensure customer orders are updated instantly, regardless of the user's geographic location.
- A banking system synchronizes transaction data across multiple data centers in real time, preventing discrepancies in account balances.
- A cloud-based document collaboration tool ensures that edits made on one server are instantly reflected on others, maintaining a consistent version of the document.
Multi-Master Replication FAQ
- What is Multi-Master Replication?
Multi-Master Replication is a database replication model where multiple database servers can handle write operations and synchronize changes with each other. - How is Multi-Master Replication different from Master-Slave Replication?
In Master-Slave Replication, only one master handles writes, while slaves replicate data from it. Multi-Master allows multiple nodes to process writes simultaneously. - What are the benefits of Multi-Master Replication?
It provides high availability, better load balancing, and reduced downtime in case of server failures. - What challenges does Multi-Master Replication face?
Challenges include conflict resolution, increased network overhead, and maintaining data consistency across all nodes. - Which databases support Multi-Master Replication?
Databases such as MySQL Group Replication, PostgreSQL BDR, Microsoft SQL Server Peer-to-Peer Replication, and MongoDB support this replication model. - How is data consistency maintained in Multi-Master Replication?
Various techniques like conflict detection, timestamp-based ordering, and quorum-based decision-making ensure data consistency.
Multi-Master Replication Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Database Replication
- Distributed Systems
- High Availability
Did you know?
One of the first large-scale implementations of Multi-Master Replication was in financial trading systems, where real-time data consistency was crucial for high-frequency transactions. Today, even social media platforms use it to ensure that user posts and interactions remain synchronized across multiple data centers worldwide.
Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.
I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.















Comments (0)
Comments powered by CComment