Quality of Service (QoS)
Quick Navigation:
- Quality of Service (QoS) Definition
- Quality of Service (QoS) Explained Easy
- Quality of Service (QoS) Origin
- Quality of Service (QoS) Etymology
- Quality of Service (QoS) Usage Trends
- Quality of Service (QoS) Usage
- Quality of Service (QoS) Examples in Context
- Quality of Service (QoS) FAQ
- Quality of Service (QoS) Related Words
Quality of Service (QoS) Definition
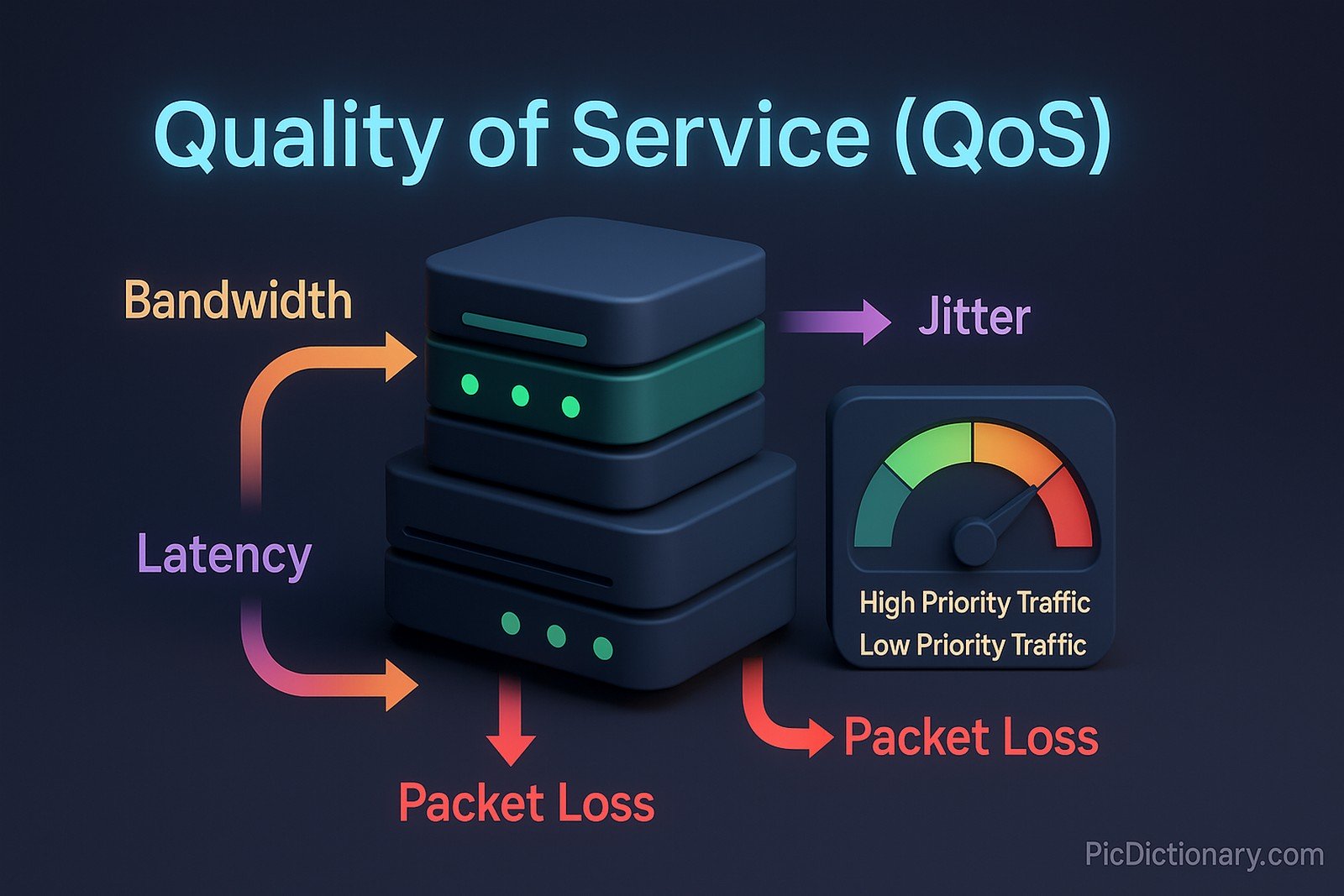
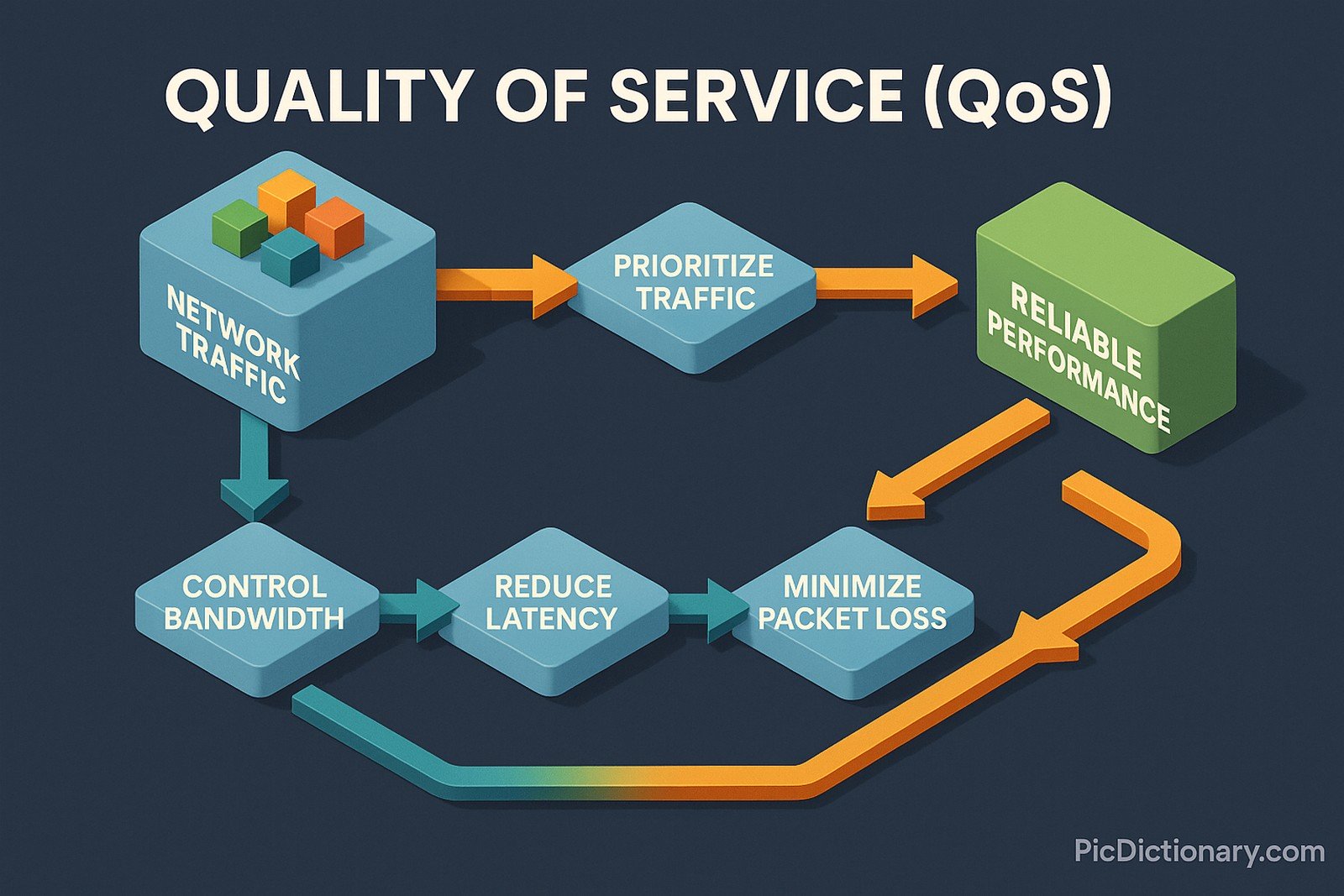
Quality of Service (QoS) refers to the ability of a network to manage traffic by prioritizing specific types of data, ensuring reliable and predictable performance for critical applications. This is achieved by controlling bandwidth, reducing latency, minimizing packet loss, and avoiding network congestion. QoS is particularly important for real-time services like VoIP, video conferencing, and streaming, where interruptions or delays can degrade user experience.
Quality of Service (QoS) Explained Easy
Imagine you have a toy store with many customers. Some customers are in a hurry, and others are not. You decide to serve the ones in a hurry first to keep them happy. In a network, QoS does the same—it makes sure important data gets through first, so calls or videos don’t freeze or stop.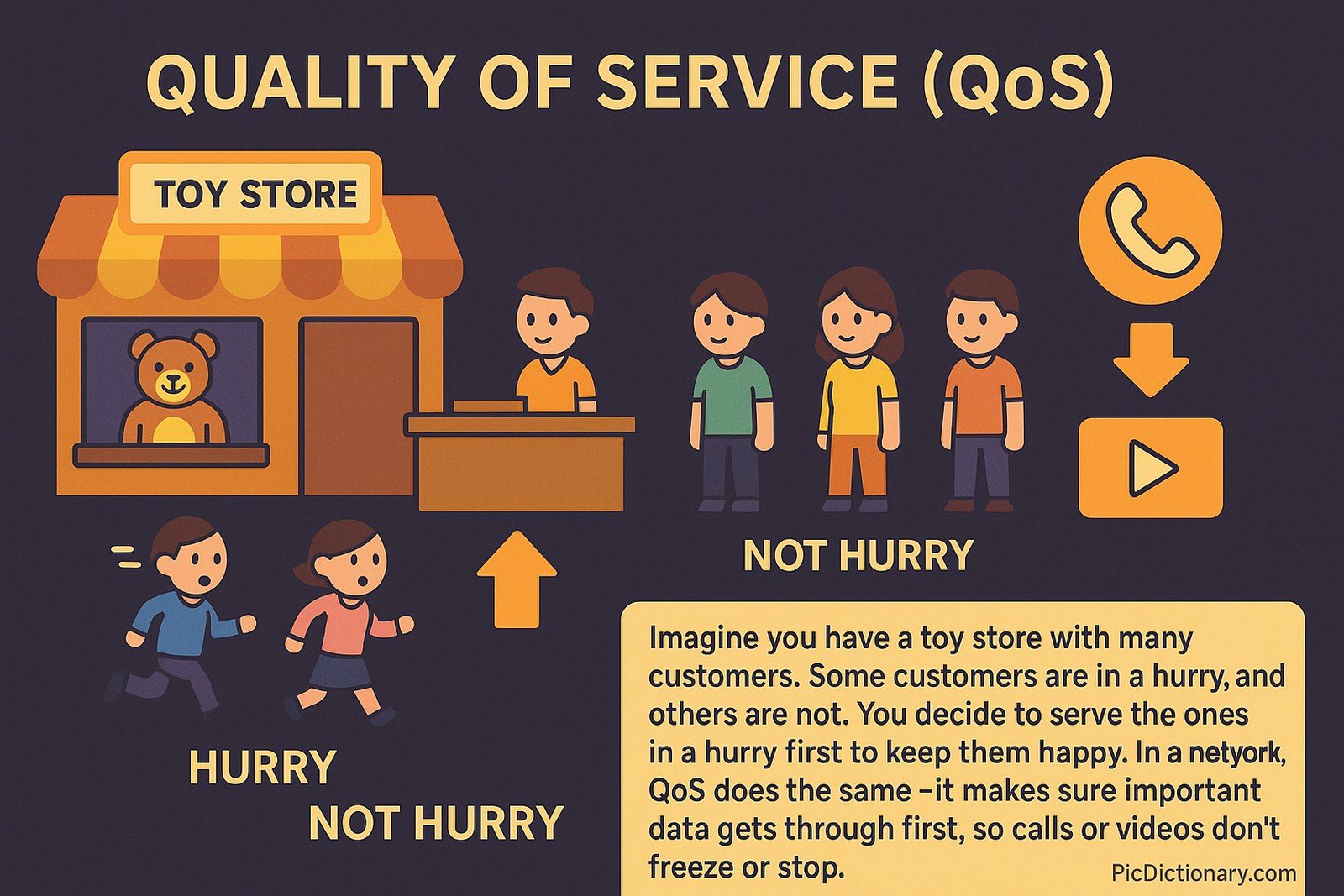
Quality of Service (QoS) Origin
The concept of QoS emerged in the 1980s alongside the growth of digital networks and the increasing demand for consistent, uninterrupted communication. Early research focused on providing predictable service in packet-switched networks, which laid the foundation for today’s sophisticated QoS protocols and frameworks.
Quality of Service (QoS) Etymology
The term "quality of service" was coined to describe the measurable and controllable features of network performance that impact user satisfaction.
Quality of Service (QoS) Usage Trends
Over the years, the adoption of cloud services, online gaming, remote work, and real-time communication has driven the widespread deployment of QoS in both enterprise and consumer-grade networks. Service providers increasingly rely on QoS to ensure customer satisfaction and competitive advantage, particularly with the rise of 5G networks and IoT ecosystems.
Quality of Service (QoS) Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Network Management
- Traffic Control
- Performance Optimization - Typical Collocations:
- "QoS settings"
- "high QoS performance"
- "QoS policy"
- "network QoS configuration"
Quality of Service (QoS) Examples in Context
- Video conferencing platforms use QoS to prioritize video and audio packets over background data.
- Internet service providers apply QoS policies to ensure streaming services run smoothly even during peak hours.
- Large enterprises implement QoS to guarantee mission-critical applications are not slowed by less important traffic.
Quality of Service (QoS) FAQ
- What is Quality of Service (QoS)?
It is a network feature that prioritizes certain types of data traffic to ensure smooth and reliable performance. - Why is QoS important?
It prevents congestion and ensures that critical applications like voice and video function without interruptions. - How does QoS work?
It manages bandwidth, prioritizes traffic, and controls data flow using techniques like traffic shaping and queuing. - Is QoS only for businesses?
No, home routers also use QoS settings to manage streaming, gaming, and other data-heavy activities. - Does QoS improve internet speed?
Not directly, but it ensures the most important traffic gets through without delays or loss. - Where is QoS most commonly used?
In VoIP, video conferencing, streaming services, and gaming networks. - What challenges are associated with QoS?
Complex configuration and potential trade-offs between different types of data traffic. - Can QoS be configured on home networks?
Yes, many modern routers come with QoS settings for better control over home network traffic. - Does QoS apply to wireless networks?
Yes, wireless networks also implement QoS to maintain performance standards. - Will QoS be important in the future?
Absolutely, with 5G, IoT, and remote work on the rise, QoS will remain critical.
Quality of Service (QoS) Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Network Performance
- Traffic Management
- Connectivity
- Telecommunications
Did you know?
In 1994, the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) formally began working on integrated services and differentiated services models, which eventually shaped the foundation for QoS in modern IP networks.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment