SATA (Serial ATA)

Quick Navigation:
- SATA (Serial ATA) Definition
- SATA (Serial ATA) Explained Easy
- SATA (Serial ATA) Origin
- SATA (Serial ATA) Etymology
- SATA (Serial ATA) Usage Trends
- SATA (Serial ATA) Usage
- SATA (Serial ATA) Examples in Context
- SATA (Serial ATA) FAQ
- SATA (Serial ATA) Related Words
SATA (Serial ATA) Definition
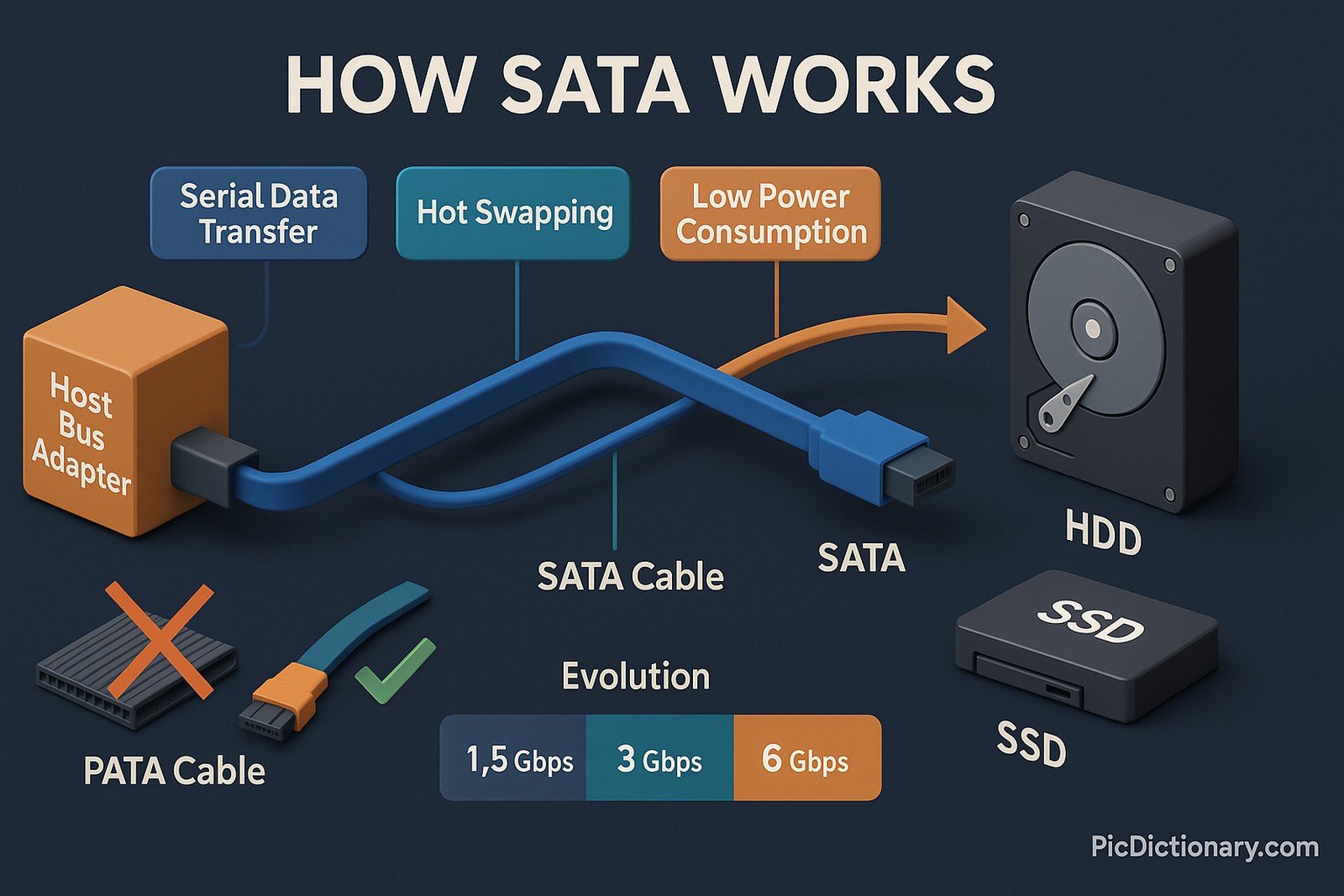
SATA (Serial ATA) is a computer bus interface used to connect host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), and optical drives. It was introduced to replace the older PATA (Parallel ATA) standard, offering faster data transfer rates, thinner cables, and more efficient power consumption. SATA supports hot-swapping, meaning devices can be connected or disconnected without shutting down the computer. Over time, SATA has evolved through multiple revisions, improving speed, reliability, and compatibility across various devices and systems.
SATA (Serial ATA) Explained Easy
Think of SATA as a highway that helps your computer and storage drives talk to each other very quickly. Instead of using an old, slow, and bulky road (like PATA), SATA gives them a fast, smooth, and efficient highway so they can share files, pictures, and programs easily. It even allows you to connect new drives without turning the computer off — like adding more cars to the highway without stopping traffic!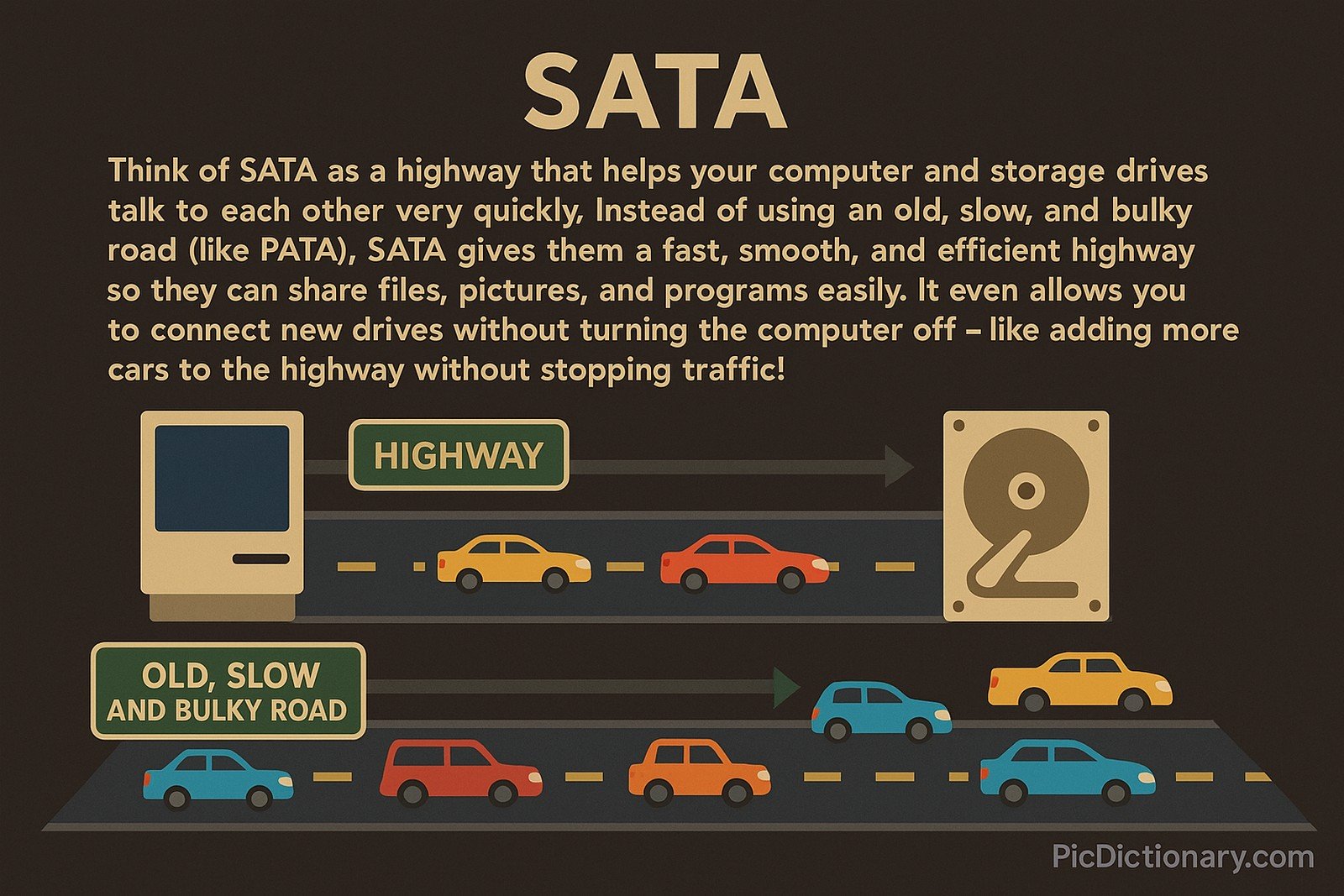
SATA (Serial ATA) Origin
SATA was first introduced in 2000 by the Serial ATA Working Group, a consortium formed by major technology companies like Intel, Dell, and Maxtor. It was developed to overcome the limitations of the aging PATA interface, aiming for faster speeds, improved design, and broader support for growing storage needs.
SATA (Serial ATA) Etymology
The name SATA comes from combining the terms "serial" and "ATA" (Advanced Technology Attachment), reflecting its data transfer method and its evolution from the ATA standard.
SATA (Serial ATA) Usage Trends
Since its introduction, SATA has become the dominant interface for consumer storage devices. With rapid adoption across personal computers, laptops, and servers, SATA replaced PATA in most systems by the mid-2000s. Although newer interfaces like NVMe and PCIe are now gaining popularity, SATA remains widely used for cost-effective and large-capacity storage solutions.
SATA (Serial ATA) Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Storage Interface
- Data Transfer
- Computer Hardware - Typical Collocations:
- "SATA cable"
- "SATA port"
- "SATA hard drive"
- "SATA data transfer speed"
SATA (Serial ATA) Examples in Context
- Many desktop computers still come with multiple SATA ports for connecting hard drives and SSDs.
- External storage devices often use SATA inside to interface with their drive hardware.
- SATA connectors are commonly found on the motherboard alongside power connectors.
SATA (Serial ATA) FAQ
- What is SATA (Serial ATA)?
SATA is a computer interface used to connect storage devices like hard drives and SSDs to the motherboard. - How is SATA different from PATA?
SATA uses serial communication for faster speeds and has thinner, more flexible cables compared to the wider PATA cables. - Can I connect an SSD using SATA?
Yes, most SSDs are designed to connect via SATA ports. - What speeds can SATA achieve?
Depending on the version, SATA speeds range from 1.5 Gbps to 6 Gbps. - Is SATA still used today?
Yes, especially in desktops and large storage arrays, though faster technologies are also emerging. - Can I hot-swap drives with SATA?
Yes, SATA supports hot-swapping, allowing devices to be connected or removed while the system is running. - Does SATA support optical drives?
Yes, SATA is commonly used to connect optical drives like DVD and Blu-ray players to computers. - What's the difference between SATA I, II, and III?
They represent different generations, with SATA I offering 1.5 Gbps, SATA II 3 Gbps, and SATA III 6 Gbps speeds. - Are SATA cables universal?
Most SATA cables are interchangeable, but always ensure they meet the specification for your device. - What replaced SATA?
Technologies like NVMe and PCIe are gradually replacing SATA for faster storage solutions.
SATA (Serial ATA) Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Computer Hardware
- Data Storage
- Data Transfer
- Computer Interfaces
Did you know?
In 2004, the first consumer motherboards featuring native SATA support became available, marking the end of bulky parallel cables and transforming how computers looked inside — much neater and better ventilated.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment