Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA)

Quick Navigation:
- Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) Definition
- Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) Explained Easy
- Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) Origin
- Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) Etymology
- Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) Usage Trends
- Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) Usage
- Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) Examples in Context
- Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) FAQ
- Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) Related Words
Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) Definition
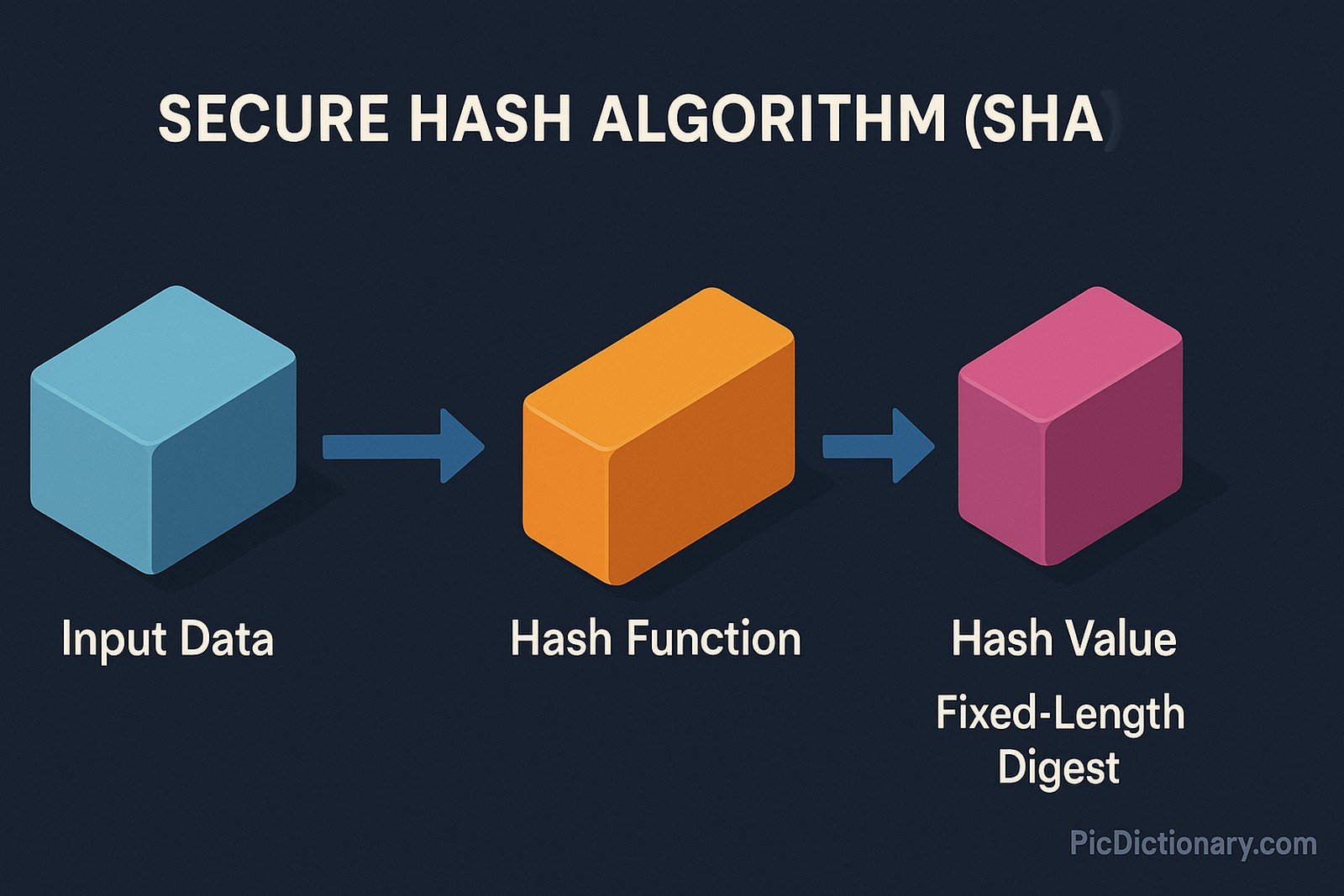
Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) refers to a family of cryptographic hash functions designed to provide data integrity and security. It processes input data into a fixed-length hash value or digest, ensuring that any change in the input results in a different hash. SHA algorithms, including SHA-1, SHA-2, and SHA-3, are widely used in digital signatures, SSL certificates, and blockchain technologies, making data verification secure and reliable.
Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) Explained Easy
Imagine you have a secret recipe, and you write a unique short code on the top to make sure no one changes it. If someone tries to change even one ingredient, the short code changes completely. Secure Hash Algorithm works like that secret code for digital data, making sure nothing has been altered.
Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) Origin
The Secure Hash Algorithm was first developed by the United States' National Security Agency (NSA) and published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 1993. Over time, new versions like SHA-2 and SHA-3 were introduced to address vulnerabilities and improve security standards.
Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) Etymology
The term "hash" relates to the process of transforming input data into a fixed-size value that represents the original input in a scrambled but predictable format.
Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) Usage Trends
SHA algorithms have seen widespread use in cybersecurity, from password storage and data integrity checks to cryptocurrency and digital signatures. The rise of digital transactions and decentralized finance has pushed SHA-256 and SHA-3 into the spotlight, maintaining their relevance in modern cryptographic applications.
Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Cryptography
- Cybersecurity
- Blockchain
- Data Integrity - Typical Collocations:
- "SHA-256 hash function"
- "secure hash verification"
- "SHA algorithm standard"
- "data hashing with SHA"
Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) Examples in Context
- Websites use SHA algorithms to secure connections through SSL certificates.
- Blockchain transactions rely on SHA-256 to create secure and immutable blocks.
- Passwords are stored as SHA hashes to prevent direct access to user credentials.
Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) FAQ
- What is Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA)?
SHA is a family of cryptographic hash functions that convert data into a secure, fixed-length digest. - How does SHA protect data integrity?
By generating a unique hash for each piece of data, any tampering results in a different hash, signaling unauthorized changes. - What are the common SHA versions?
The most used versions are SHA-1, SHA-2 (including SHA-256 and SHA-512), and SHA-3. - Why was SHA-1 replaced?
SHA-1 was found to be vulnerable to collision attacks, leading to the adoption of SHA-2 and SHA-3. - Where is SHA used in daily life?
SHA is used in SSL certificates, secure online transactions, and storing passwords. - Is SHA used in blockchain?
Yes, SHA-256 is the core hashing function in Bitcoin and other blockchain systems. - Can SHA hashes be reversed?
No, SHA hashes are one-way functions, meaning you cannot retrieve the original data from the hash. - How long is an SHA-256 hash?
An SHA-256 hash is 256 bits long, represented as a 64-character hexadecimal string. - What happens if two pieces of data generate the same hash?
That’s called a collision, and modern SHA versions are designed to make collisions extremely unlikely. - Is SHA still secure?
SHA-2 and SHA-3 are currently considered secure and widely trusted in cryptographic applications.
Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Cryptography
- Digital Security
- Blockchain Technology
- Data Verification
Did you know?
SHA-256 is so critical to blockchain that without it, Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies would not be able to ensure secure, immutable transactions. This mathematical function has become a backbone of decentralized finance.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment