Virtualized I/O

Quick Navigation:
- Virtualized I/O Definition
- Virtualized I/O Explained Easy
- Virtualized I/O Origin
- Virtualized I/O Etymology
- Virtualized I/O Usage Trends
- Virtualized I/O Usage
- Virtualized I/O Examples in Context
- Virtualized I/O FAQ
- Virtualized I/O Related Words
Virtualized I/O Definition
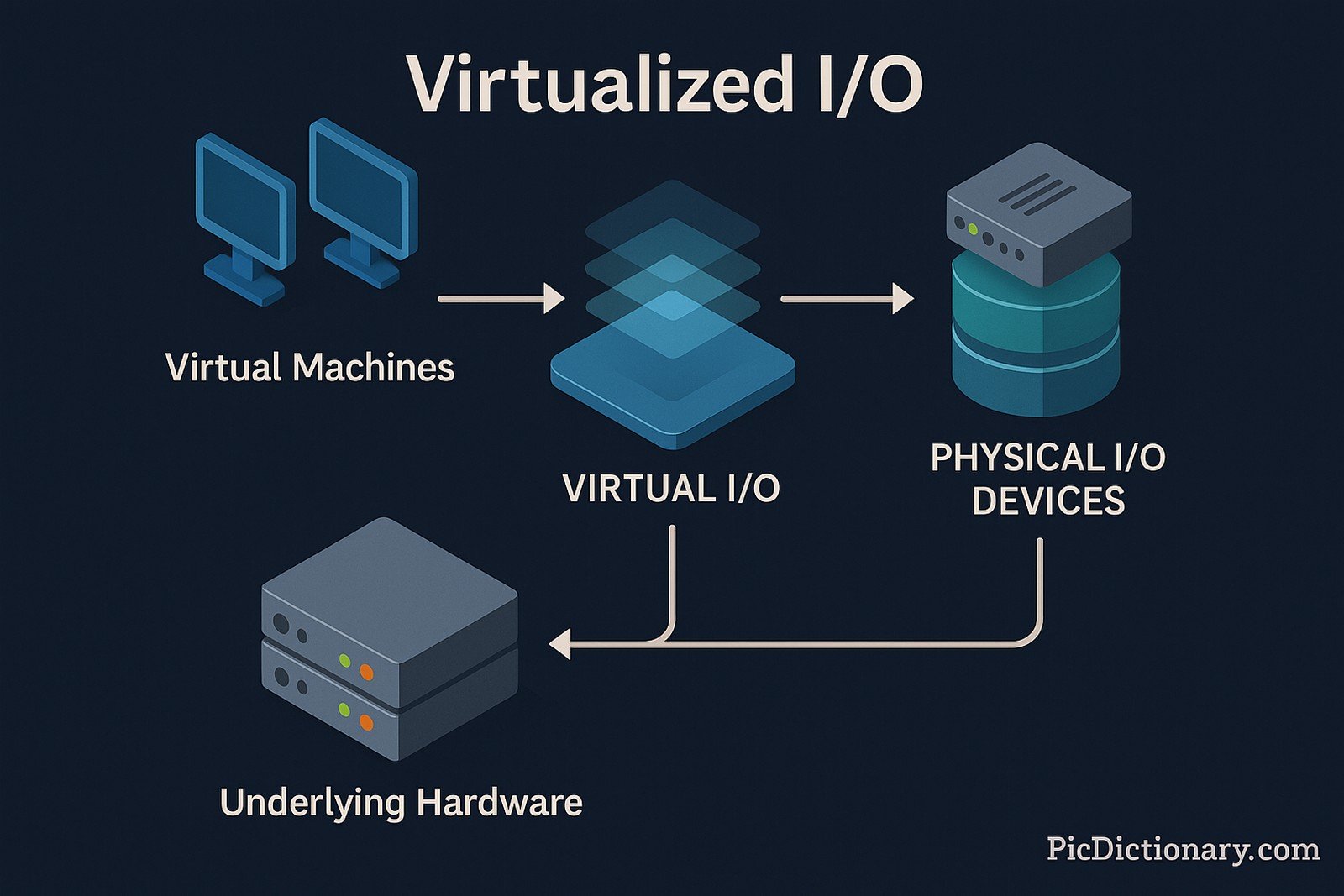
Virtualized I/O (Input/Output) is a technology that abstracts physical input and output operations from the underlying hardware, enabling multiple virtual machines (VMs) to share and manage I/O resources efficiently. By leveraging techniques such as Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) and software-defined networking (SDN), Virtualized I/O improves resource allocation, reduces hardware dependencies, and enhances overall system performance in cloud computing and virtualized environments.
Virtualized I/O Explained Easy
Imagine you have a single printer at home, but multiple people in your family need to use it. Instead of plugging and unplugging cables, you connect it to a network, allowing everyone to print from their own devices. Virtualized I/O works similarly—it lets different virtual machines share the same hardware resources, like network cards and storage, without needing separate physical connections for each one.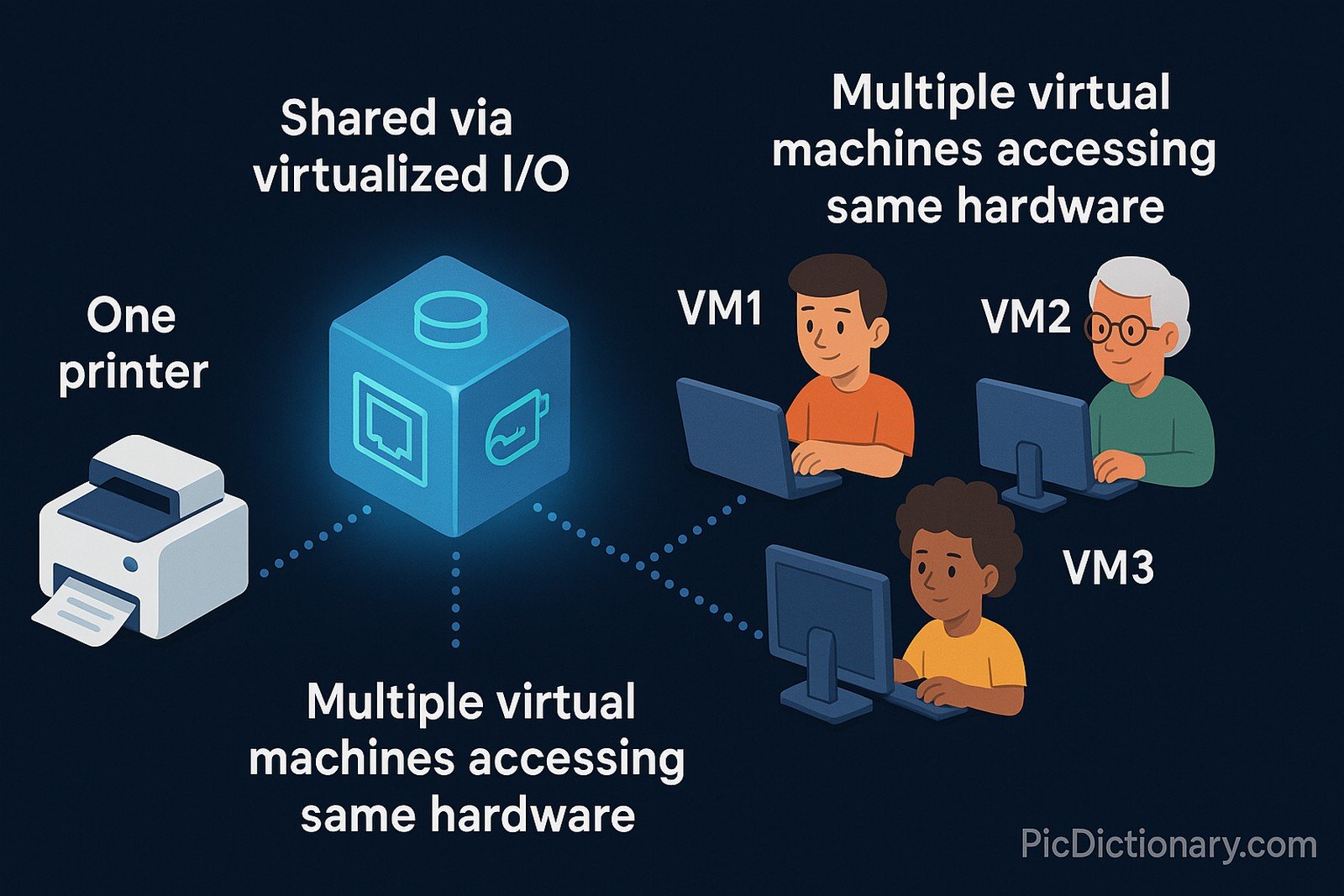
Virtualized I/O Origin
The concept of Virtualized I/O emerged as data centers transitioned from traditional physical servers to virtualized infrastructures. With the rise of cloud computing, companies needed a way to efficiently share hardware resources between multiple virtual machines, leading to the development of software-driven I/O management techniques.
Virtualized I/O Etymology
The term "virtualized" comes from "virtualization," meaning the creation of virtual (rather than physical) versions of computing resources. "I/O" stands for Input/Output, referring to the data transfer processes between computer systems and external devices.
Virtualized I/O Usage Trends
Virtualized I/O has gained widespread adoption with the growth of cloud computing, high-performance data centers, and network function virtualization (NFV). Organizations increasingly use Virtualized I/O to optimize workloads, reduce latency in high-demand applications, and improve scalability. Emerging trends include the use of AI-driven optimization and software-defined storage solutions for managing virtualized I/O more effectively.
Virtualized I/O Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Cloud Computing
- Virtualization
- Data Center Infrastructure - Typical Collocations:
- "Virtualized I/O performance"
- "I/O virtualization in cloud computing"
- "Virtualized network interfaces"
- "SR-IOV for virtualized environments"
Virtualized I/O Examples in Context
- Cloud providers use Virtualized I/O to enable seamless data transfer between virtual machines without physical constraints.
- High-performance computing environments rely on Virtualized I/O to optimize network traffic and storage access.
- Virtualized I/O allows enterprises to reduce costs by consolidating multiple workloads onto fewer physical devices.
Virtualized I/O FAQ
- What is Virtualized I/O?
Virtualized I/O is a technology that allows multiple virtual machines to share and manage input/output resources without requiring direct physical hardware connections. - How does Virtualized I/O improve performance?
It reduces hardware bottlenecks by enabling efficient resource allocation, minimizing latency, and optimizing data flow in virtualized environments. - What is SR-IOV in Virtualized I/O?
Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) is a PCIe feature that allows a physical network device to present multiple virtual instances, enhancing I/O performance in virtualized systems. - Is Virtualized I/O only used in cloud computing?
No, it's also used in enterprise data centers, high-performance computing (HPC), and software-defined networking (SDN) environments. - How does Virtualized I/O benefit cloud providers?
It enables efficient scaling, improves network flexibility, and reduces hardware dependency, making cloud services more cost-effective. - What are some common Virtualized I/O technologies?
Technologies include SR-IOV, virtual network interfaces, software-defined storage, and NVMe over Fabrics (NVMe-oF). - Can Virtualized I/O help with security?
Yes, it can enhance security by isolating workloads and controlling data flow between virtual machines. - What challenges come with Virtualized I/O?
Challenges include increased complexity, potential I/O contention, and the need for specialized hardware support. - Is Virtualized I/O relevant for AI workloads?
Absolutely. Virtualized I/O helps manage high-speed data transfer between AI models and storage, reducing latency in deep learning applications. - What’s the future of Virtualized I/O?
The future includes AI-driven optimizations, hardware acceleration, and deeper integration with software-defined data centers.
Virtualized I/O Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Cloud Infrastructure
- Virtualization Technologies
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
Did you know?
Virtualized I/O plays a critical role in modern cloud gaming services. By enabling ultra-low-latency data transfer between game servers and users, technologies like NVIDIA’s virtualized GPUs and high-speed NVMe storage ensure smooth gaming experiences without requiring powerful hardware on the user's side.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment