Advanced Persistent Threat (APT)

Quick Navigation:
- Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Definition
- Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Explained Easy
- Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Origin
- Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Etymology
- Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Usage Trends
- Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Usage
- Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Examples in Context
- Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) FAQ
- Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Related Words
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Definition
An Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) is a sophisticated, continuous cyberattack in which an intruder gains unauthorized access to a network and remains undetected for an extended period. The goal is often to steal data rather than cause damage. APTs are typically orchestrated by well-funded, highly skilled attackers, including nation-states or organized criminal groups. They leverage multiple attack vectors, including social engineering, zero-day exploits, and custom malware.
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Explained Easy
Imagine someone sneaks into a library, hides in a secret room, and keeps coming out quietly to take books without anyone noticing. They keep doing this for a long time, learning how to avoid the librarian. In computers, an APT is like that sneaky intruder, but instead of books, they steal data while avoiding detection.
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Origin
The term Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) originated in the mid-2000s when security experts needed a term to describe state-sponsored, continuous hacking campaigns targeting critical infrastructure and sensitive data. The term became widely known after several high-profile cyber-espionage cases.
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Etymology
The term "advanced" refers to the use of sophisticated methods and tools. "Persistent" indicates that attackers maintain long-term access. "Threat" highlights the constant danger posed to security.
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Usage Trends
Over the past decade, awareness and occurrences of APTs have surged due to high-profile incidents like the Stuxnet worm and Operation Aurora. As cybersecurity technologies advance, so do APT techniques, leading to a constant cat-and-mouse dynamic between attackers and defenders. Industries such as defense, finance, healthcare, and technology are the most common targets.
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Cybersecurity
- Network Security
- Threat Intelligence - Typical Collocations:
- "APT attack"
- "APT group"
- "nation-state APT"
- "APT malware campaign"
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Examples in Context
- The APT group targeted the energy sector, gaining long-term access to sensitive industrial control systems.
- An APT attack on a financial institution resulted in the theft of millions of customer records.
- Cybersecurity experts continuously monitor APT activities to protect national security assets.
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) FAQ
- What is an Advanced Persistent Threat (APT)?
An APT is a long-term, sophisticated cyberattack where intruders maintain stealthy access to steal data. - How do attackers carry out APT attacks?
They use phishing, zero-day exploits, malware, and social engineering to infiltrate and stay hidden in networks. - Who are the usual perpetrators of APT attacks?
APTs are generally carried out by nation-states, cybercriminal groups, or highly skilled hackers. - How can organizations detect an APT?
Detection involves monitoring for unusual network behavior, endpoint activity, and using advanced threat intelligence tools. - What are common targets of APTs?
Government agencies, critical infrastructure, financial institutions, and major corporations. - Are APT attacks preventable?
While prevention is difficult, good cybersecurity hygiene and layered defenses help reduce risk. - What is an example of a known APT attack?
Operation Aurora and the Stuxnet worm are well-known examples of sophisticated APT campaigns. - How long can APTs remain undetected?
Some APTs stay undetected for months or even years, continuously adapting to evade discovery. - What damage can APTs cause?
They can result in data theft, financial loss, reputational damage, and national security threats. - How do defenders combat APTs?
Through constant monitoring, threat intelligence, incident response, and security awareness training.
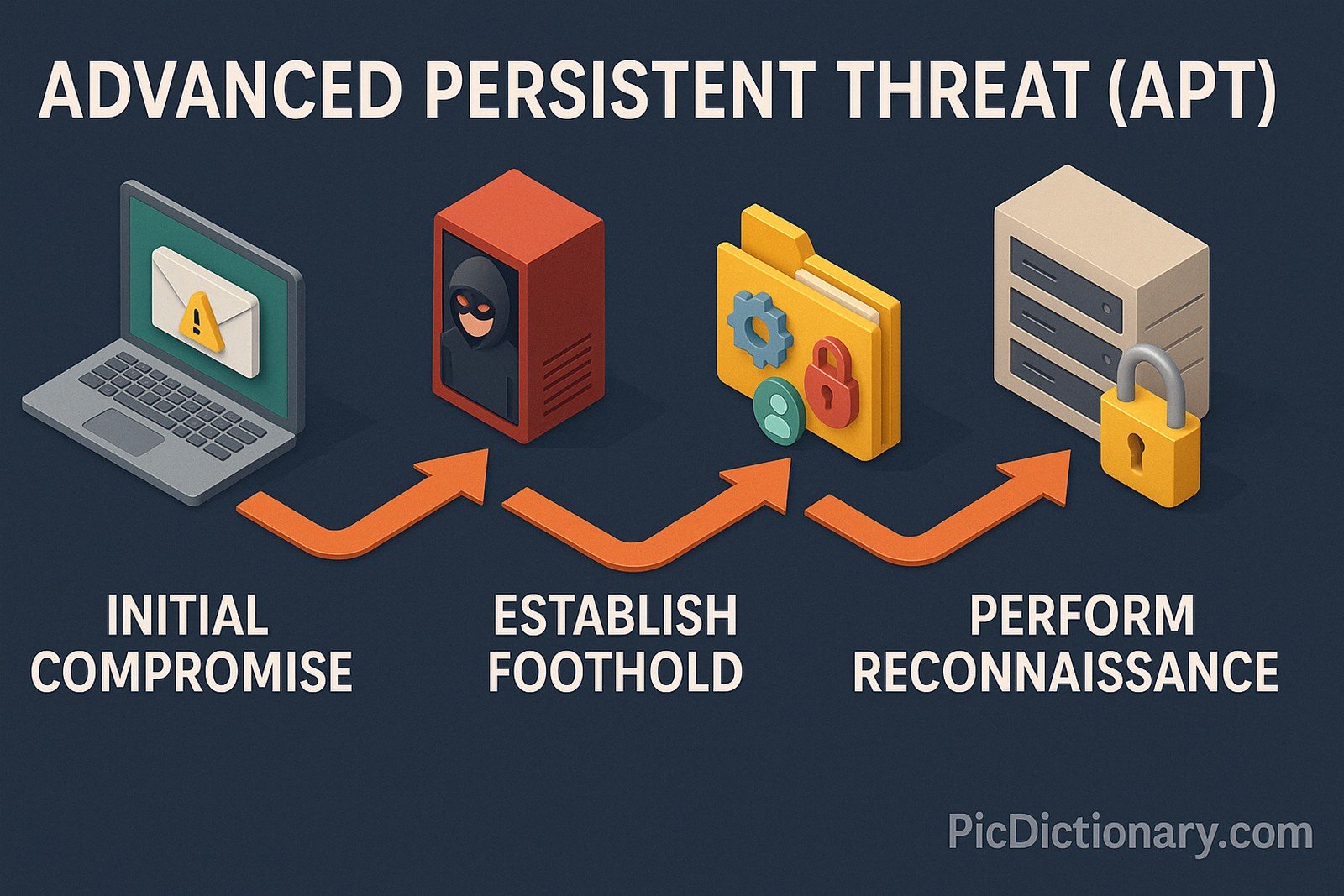
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Cybersecurity
- Malware
- Cyber-espionage
- Threat Detection
Did you know?
In 2010, the Stuxnet worm—widely believed to be an APT developed by nation-states—was used to sabotage Iran’s nuclear facilities. It marked one of the first known instances of cyber warfare, demonstrating the power and complexity of advanced persistent threats.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment