Deep Packet Inspection (DPI)
Quick Navigation:
- Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) Definition
- Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) Explained Easy
- Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) Origin
- Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) Etymology
- Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) Usage Trends
- Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) Usage
- Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) Examples in Context
- Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) FAQ
- Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) Related Words
Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) Definition
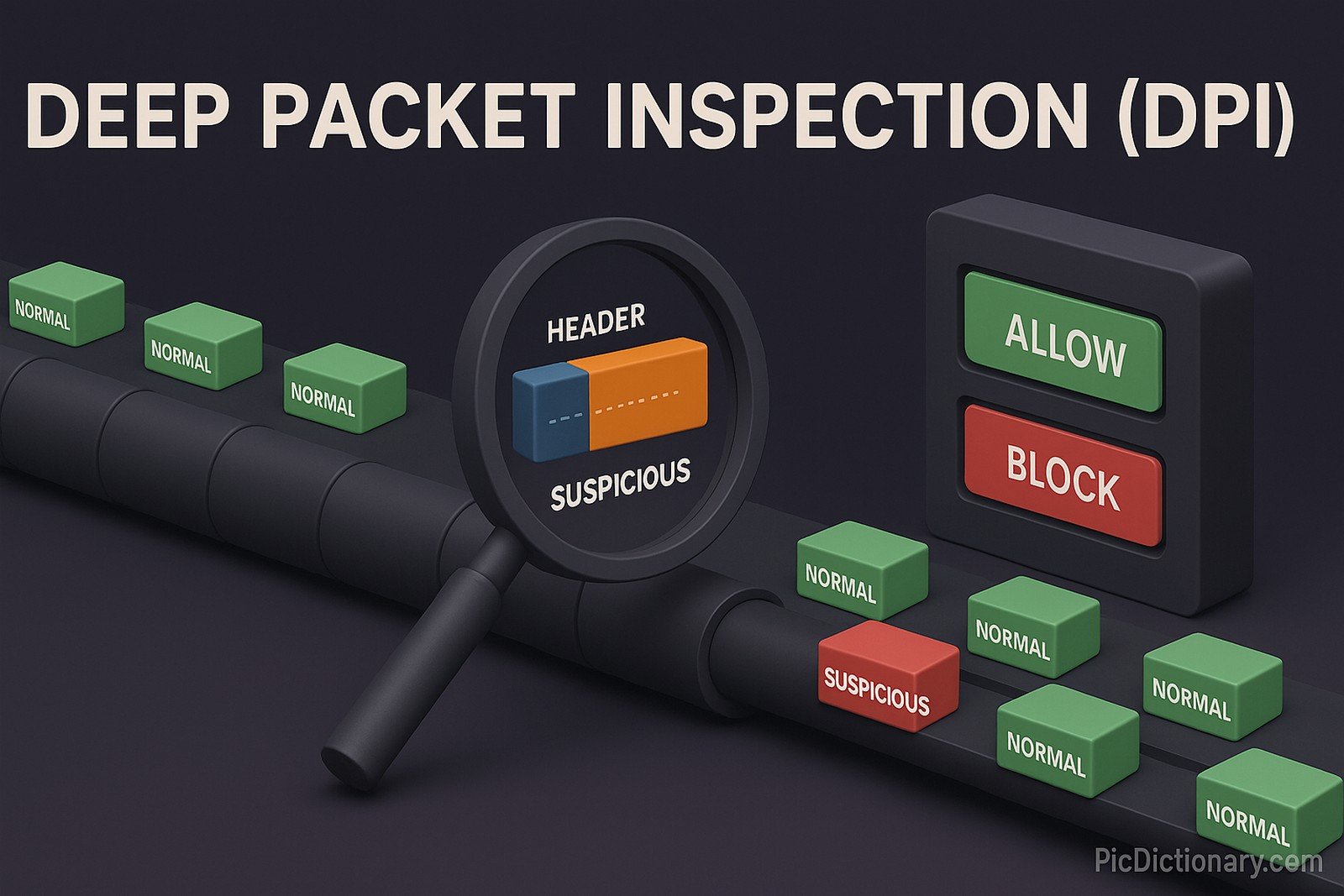
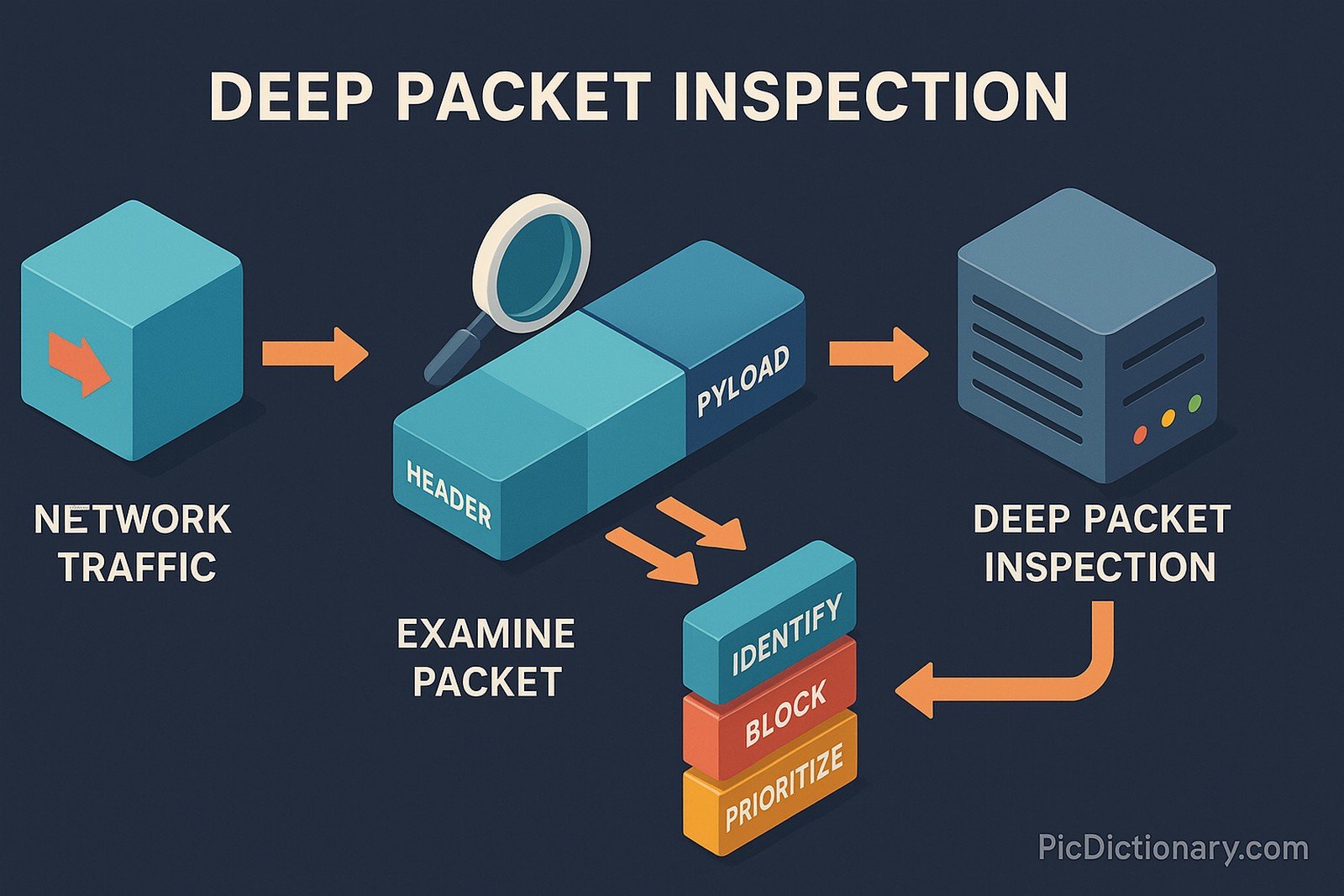
Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) is a form of computer network filtering and analysis that examines the full content of data packets transmitted across a network. Unlike standard filtering, which only looks at packet headers, DPI inspects both the header and the data payload. It is used to identify, block, or prioritize specific types of traffic, enabling advanced network management, security monitoring, intrusion detection, and enforcement of usage policies. DPI is employed by internet service providers (ISPs), enterprises, and governments to detect malicious activity, manage bandwidth, and ensure compliance with regulations.
Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) Explained Easy
Imagine sending a letter through the mail. Most postal workers only look at the envelope (the address), but DPI is like opening the envelope and reading the entire letter to check if it follows rules. In the same way, DPI looks inside the data being sent on the internet to see if it’s safe, allowed, or needs special handling.
Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) Origin
The concept of DPI emerged in the early 2000s alongside increasing internet usage and cyber threats. Initially used for network troubleshooting and simple traffic analysis, it evolved into a powerful tool for security, regulatory enforcement, and commercial applications as networks became more complex and threats more sophisticated.
Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) Etymology
The term “deep packet inspection” is derived from the combination of "deep" meaning thorough or extensive, and "inspection" referring to the act of examining something closely. "Packet" refers to the basic unit of data transmitted over a network.
Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) Usage Trends
DPI has seen significant growth in deployment due to rising cybersecurity challenges and the need for bandwidth management. Telecom companies, governments, and enterprises use it for content filtering, network optimization, and regulatory compliance. Recently, DPI technology has also been integrated with artificial intelligence to improve accuracy in threat detection and encrypted traffic analysis.
Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Network Security
- Cybersecurity
- Traffic Management - Typical Collocations:
- "DPI engine"
- "deep packet inspection firewall"
- "real-time DPI analysis"
- "DPI-based traffic shaping"
Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) Examples in Context
- An ISP uses DPI to block illegal content and ensure lawful use of the internet.
- Enterprises rely on DPI to prevent sensitive data leaks by scanning outbound traffic.
- Governments deploy DPI to monitor and regulate internet usage for national security.
Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) FAQ
- What is deep packet inspection?
DPI is a technology used to examine the entire content of data packets on a network for security and management purposes. - How is DPI different from standard packet filtering?
Standard filtering only looks at packet headers; DPI inspects both headers and payloads for deeper analysis. - Who uses deep packet inspection?
ISPs, enterprises, and government agencies use DPI for network security, bandwidth control, and compliance monitoring. - Is DPI legal?
DPI is legal in most countries but subject to privacy and data protection regulations. - Does DPI slow down internet connections?
When implemented efficiently, DPI has minimal impact, but complex filtering on high volumes of data can cause delays. - Can DPI detect encrypted traffic?
DPI can identify encrypted traffic but cannot inspect the encrypted content unless paired with decryption technologies. - What are the risks of using DPI?
Potential risks include privacy concerns, misuse for censorship, and the possibility of over-inspection leading to false positives. - Is DPI used in mobile networks?
Yes, mobile carriers use DPI to manage bandwidth and detect harmful traffic. - Can DPI block specific applications?
Yes, DPI can block or throttle applications like peer-to-peer sharing or streaming services. - How does DPI help in cybersecurity?
DPI identifies malicious payloads, detects intrusions, and enforces security policies in real-time.
Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Network Security
- Intrusion Detection Systems
- Bandwidth Management
Did you know?
In 2010, Canada’s ISPs faced public backlash for using DPI to throttle peer-to-peer traffic. The controversy sparked national debates about net neutrality, transparency in traffic management, and the ethical use of deep packet inspection technology.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment