Dynamic Kernel Modules
Quick Navigation:
- Dynamic Kernel Modules Definition
- Dynamic Kernel Modules Explained Easy
- Dynamic Kernel Modules Origin
- Dynamic Kernel Modules Etymology
- Dynamic Kernel Modules Usage Trends
- Dynamic Kernel Modules Usage
- Dynamic Kernel Modules Examples in Context
- Dynamic Kernel Modules FAQ
- Dynamic Kernel Modules Related Words
Dynamic Kernel Modules Definition
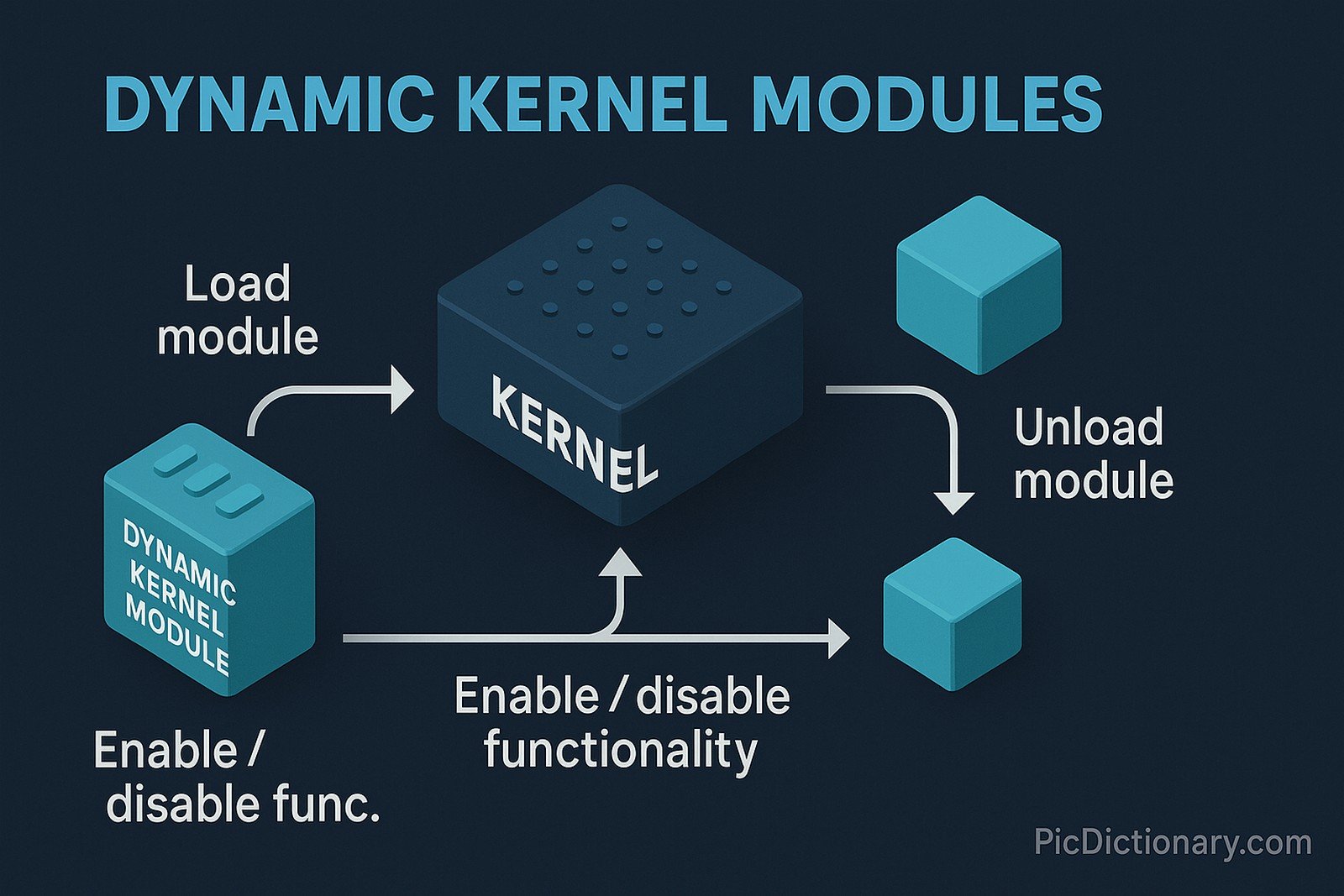
Dynamic Kernel Modules (DKMs) are software components that can be loaded and unloaded into the operating system kernel at runtime. Unlike static kernel components, DKMs provide flexibility by enabling or disabling specific functionalities without requiring a system reboot. They are crucial in modern operating systems for tasks such as device driver management, security enhancements, and system optimizations. DKMs interact with the kernel through predefined APIs, ensuring stability while allowing seamless integration of new hardware or software features.
Dynamic Kernel Modules Explained Easy
Imagine your computer is like a giant Lego set. Normally, once you build it, you can’t change things without breaking everything apart. But with Dynamic Kernel Modules, it's like having Lego pieces you can swap in and out anytime without taking the whole structure apart. This helps your computer add new abilities, like using a new printer or making it more secure, without restarting.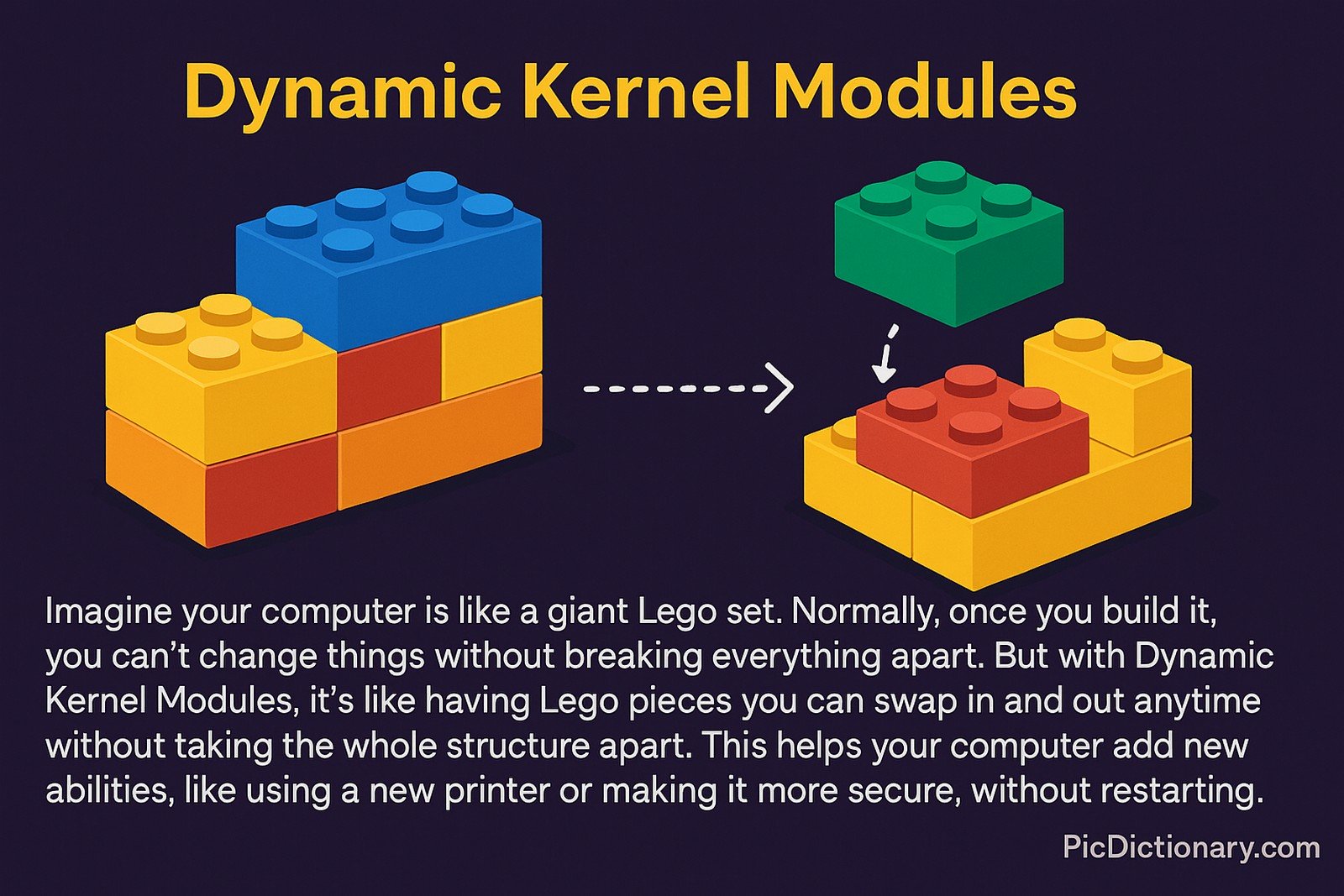
Dynamic Kernel Modules Origin
The concept of dynamic kernel modules emerged as a solution to the limitations of monolithic kernel designs. Early operating systems required complete recompilation for any kernel modification. With the rise of modular kernel architectures in the 1990s, particularly in Linux and BSD systems, DKMs became a practical approach for updating system functionality dynamically.
Dynamic Kernel Modules Etymology
The term "dynamic kernel module" comes from:
- Dynamic – referring to its ability to be loaded and unloaded at runtime
- Kernel – the core part of an operating system
- Module – an independent piece of software that can be integrated with a system
Dynamic Kernel Modules Usage Trends
DKMs have gained prominence with the increasing need for real-time system updates and security patches. They are widely used in Linux-based operating systems, allowing developers to update drivers or security modules without downtime. Cloud computing and virtualization technologies also leverage DKMs for resource management and performance optimization.
Dynamic Kernel Modules Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Operating Systems
- Kernel Development
- Device Drivers - Typical Collocations:
- "loadable kernel module"
- "Dynamically linked kernel module"
- "Kernel module management"
- "Unload kernel module safely"
Dynamic Kernel Modules Examples in Context
- A graphics card manufacturer releases a new driver as a dynamic kernel module, allowing users to install it without rebooting their system.
- A security firm patches a vulnerability by deploying an updated kernel module dynamically across cloud servers.
- Linux users enable experimental filesystem support by loading a specific kernel module without modifying the entire OS.
Dynamic Kernel Modules FAQ
- What are Dynamic Kernel Modules?
Dynamic Kernel Modules are software components that can be loaded or removed from an operating system kernel at runtime, without rebooting. - Why are DKMs important?
They allow systems to update functionality, add support for new hardware, and apply security patches without requiring a full system restart. - Which operating systems support DKMs?
Linux, BSD, and certain Unix-based systems widely support dynamic kernel modules. Windows has a similar concept with dynamically loadable drivers. - How do DKMs differ from static kernel modules?
Static modules are built into the kernel and require recompilation for modifications, whereas DKMs can be added or removed dynamically. - Can DKMs impact system stability?
Yes, improperly designed DKMs can cause system crashes or security vulnerabilities. Therefore, they are carefully developed and tested. - How do you load a DKM in Linux?
You can use themodprobeorinsmodcommand to load a module andrmmodto unload it. - Are DKMs only used for device drivers?
No, while commonly used for drivers, DKMs are also employed for security updates, performance monitoring, and network enhancements. - Do DKMs require kernel source code?
Not necessarily. Precompiled modules can be used if they are built for a compatible kernel version. - How does the Linux kernel manage DKMs?
Linux provides tools likelsmod(to list modules) anddmesg(to check kernel logs) for module management. - Can DKMs be used in real-time systems?
Yes, they are essential in real-time and embedded systems where uptime is critical.
Dynamic Kernel Modules Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Operating Systems
- Linux Kernel Development
- Loadable Modules
Did you know?
The Linux kernel contains thousands of dynamic kernel modules, and even basic functionalities like USB device detection rely on them. Some Linux distributions, such as Ubuntu and Fedora, allow automatic DKM updates through package management systems, ensuring security patches are applied seamlessly.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment