NTFS (New Technology File System)
 (Representational Image | Source: Dall-E)
(Representational Image | Source: Dall-E)
Quick Navigation:
- NTFS Definition
- NTFS Explained Easy
- NTFS Origin
- NTFS Etymology
- NTFS Usage Trends
- NTFS Usage
- NTFS Examples in Context
- NTFS FAQ
- NTFS Related Words
NTFS Definition
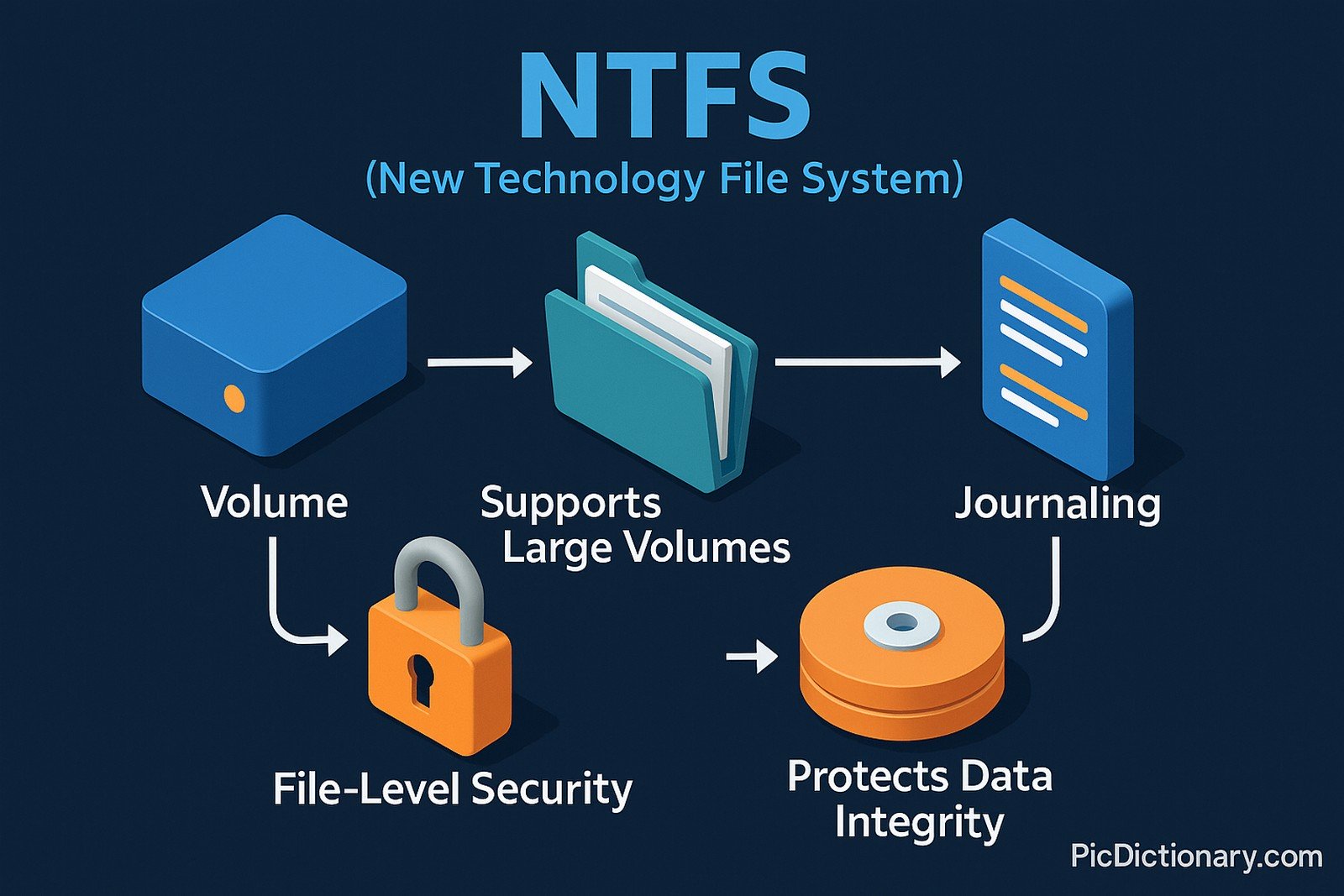
NTFS (New Technology File System) is a proprietary file system developed by Microsoft for its Windows operating systems. It supports large volumes, long file names, and advanced data structures for performance, reliability, and disk space utilization. NTFS includes features like file-level security, compression, encryption, and disk quotas. It also supports journaling to protect data integrity in case of unexpected shutdowns or power failures, making it a robust solution for both personal and enterprise.
NTFS Explained Easy
Think of NTFS like a super-organized library. In this library, every book (file) has a special place, and you can quickly find it. The library keeps a list of where each book is, keeps them safe from damage, and can even lock certain books so only some people can read them. NTFS does this for your computer's files—keeping everything in order, safe, and secure.
NTFS Origin
NTFS was introduced by Microsoft in 1993 with the release of Windows NT 3.1. It was created to overcome the limitations of its predecessor, the FAT (File Allocation Table) file system, and to meet the demands of more sophisticated computing environments.
NTFS Etymology
The name NTFS is derived from Microsoft’s NT (New Technology) project and "File System" referring to the method of storing and organizing files on disk drives.
NTFS Usage Trends
Since its inception, NTFS has become the standard file system for all modern Windows operating systems. It is widely used in business and enterprise environments due to its stability and advanced security features. NTFS is also employed in external storage devices and servers, though other file systems may be used for cross-platform compatibility.
NTFS Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- File Systems
- Windows OS
- Data Storage
- Disk Management - Typical Collocations:
- "NTFS file system"
- "format drive in NTFS"
- "NTFS permissions"
- "convert FAT32 to NTFS"
NTFS Examples in Context
- When setting up a new hard drive on Windows, users are often prompted to format it using NTFS.
- NTFS permissions are used in corporate environments to restrict access to confidential documents.
- External hard drives formatted in NTFS can store files larger than 4GB, unlike FAT32.
NTFS FAQ
- What does NTFS stand for?
It stands for New Technology File System. - Why was NTFS introduced?
It was introduced to address the limitations of older file systems like FAT and to offer more advanced features. - Can NTFS drives be read on macOS or Linux?
macOS can read NTFS but cannot write without additional software. Linux can both read and write with the help of drivers. - What are the advantages of NTFS?
NTFS provides better security, supports large files, disk quotas, and file compression. - Can I convert FAT32 to NTFS without losing data?
Yes, Windows provides a command-line tool to convert FAT32 to NTFS without data loss. - Does NTFS support file encryption?
Yes, NTFS includes the Encrypting File System (EFS) for file-level encryption. - Is NTFS suitable for USB drives?
It can be used, but FAT32 or exFAT are more commonly used for cross-platform compatibility. - What is journaling in NTFS?
Journaling keeps track of changes, protecting data integrity in case of sudden shutdowns. - What file size can NTFS handle?
NTFS can handle files up to 16 exabytes in theory, but practical limits are much smaller. - Does NTFS have limitations?
Yes, it’s primarily supported on Windows; compatibility issues may arise on other systems.
NTFS Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- File Systems
- Windows OS
- Data Management
- Storage Technology
Did you know?
NTFS supports something called "hard links" and "symbolic links," which allow a file to appear in multiple folders without taking up extra space. This advanced feature helps developers and power users manage complex file structures efficiently.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment