Paravirtualization
Quick Navigation:
- Paravirtualization Definition
- Paravirtualization Explained Easy
- Paravirtualization Origin
- Paravirtualization Etymology
- Paravirtualization Usage Trends
- Paravirtualization Usage
- Paravirtualization Examples in Context
- Paravirtualization FAQ
- Paravirtualization Related Words
Paravirtualization Definition
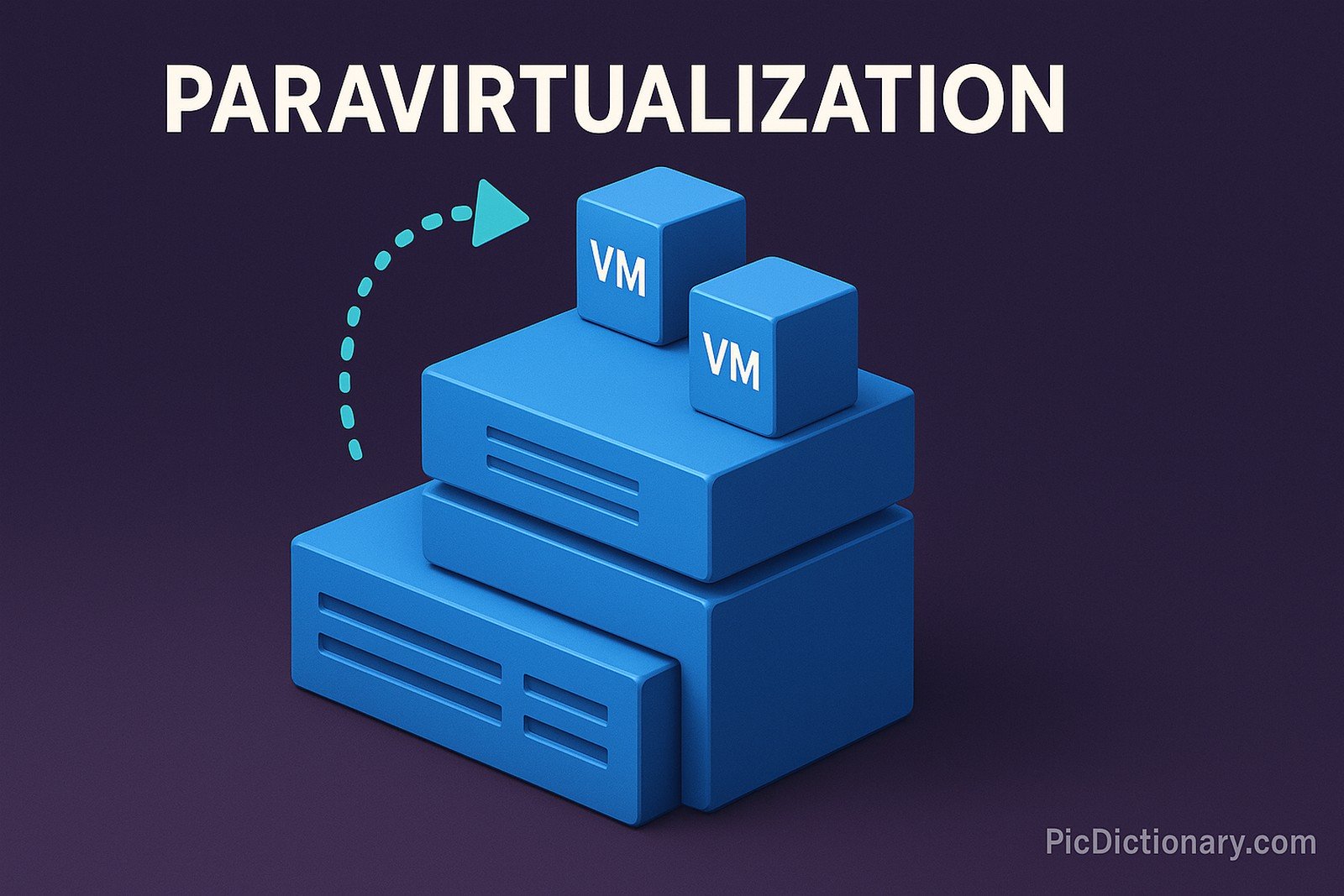
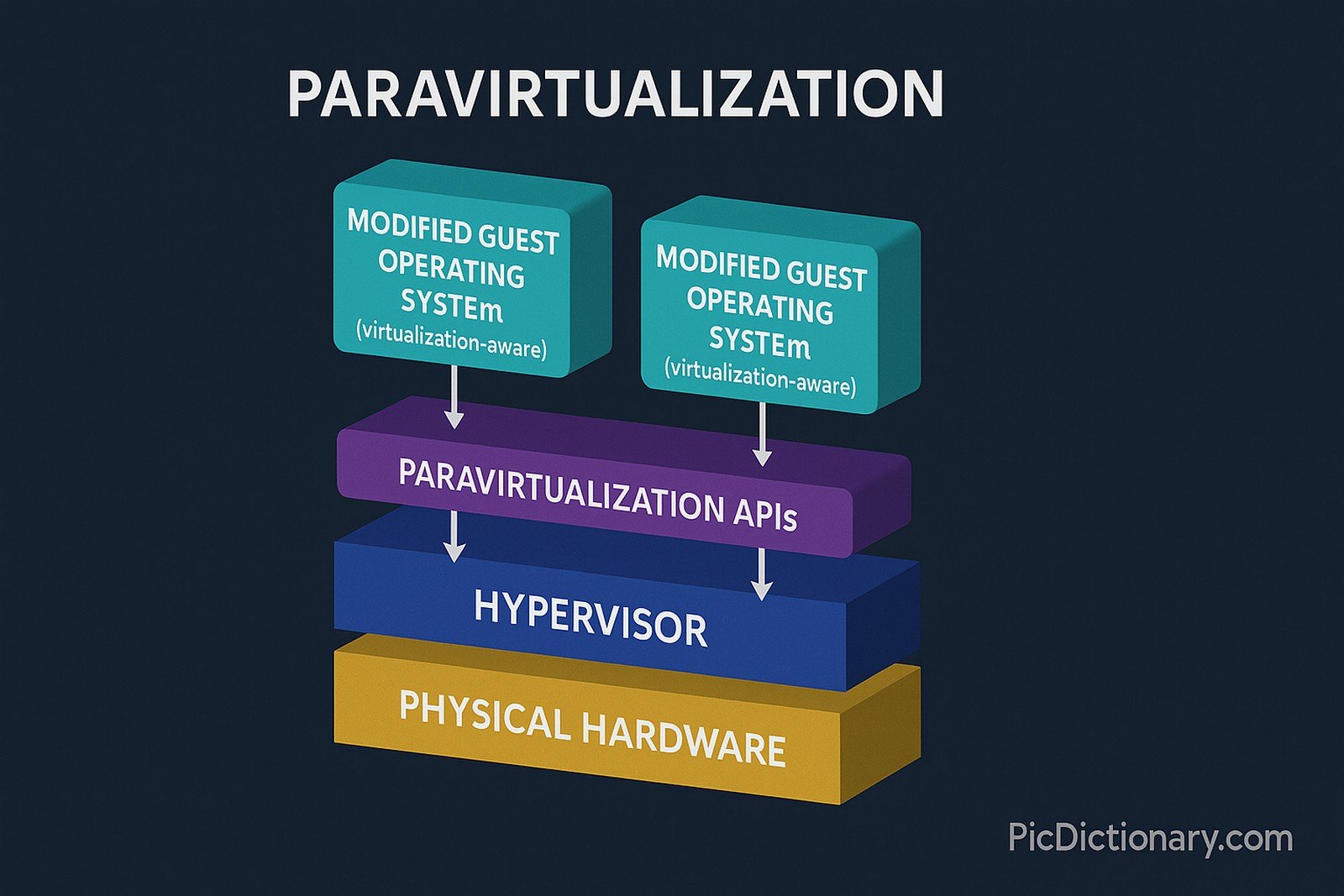
Paravirtualization is a virtualization technique that enhances performance by modifying the guest operating system to interact more efficiently with the hypervisor. Unlike full virtualization, where the hypervisor emulates hardware, paravirtualization enables the guest OS to communicate directly with the hypervisor using special APIs. This reduces overhead, improving efficiency and speed, making it ideal for cloud computing and enterprise-level virtualization solutions.
Paravirtualization Explained Easy
Imagine you're learning to drive a car, but instead of using a steering wheel and pedals, you control it by giving instructions to a friend who drives for you. This is like full virtualization. Now, imagine that you are the one driving the car directly, with some guidance from a smart assistant. This is how paravirtualization works—it allows software to interact with the computer more efficiently, avoiding unnecessary middle steps.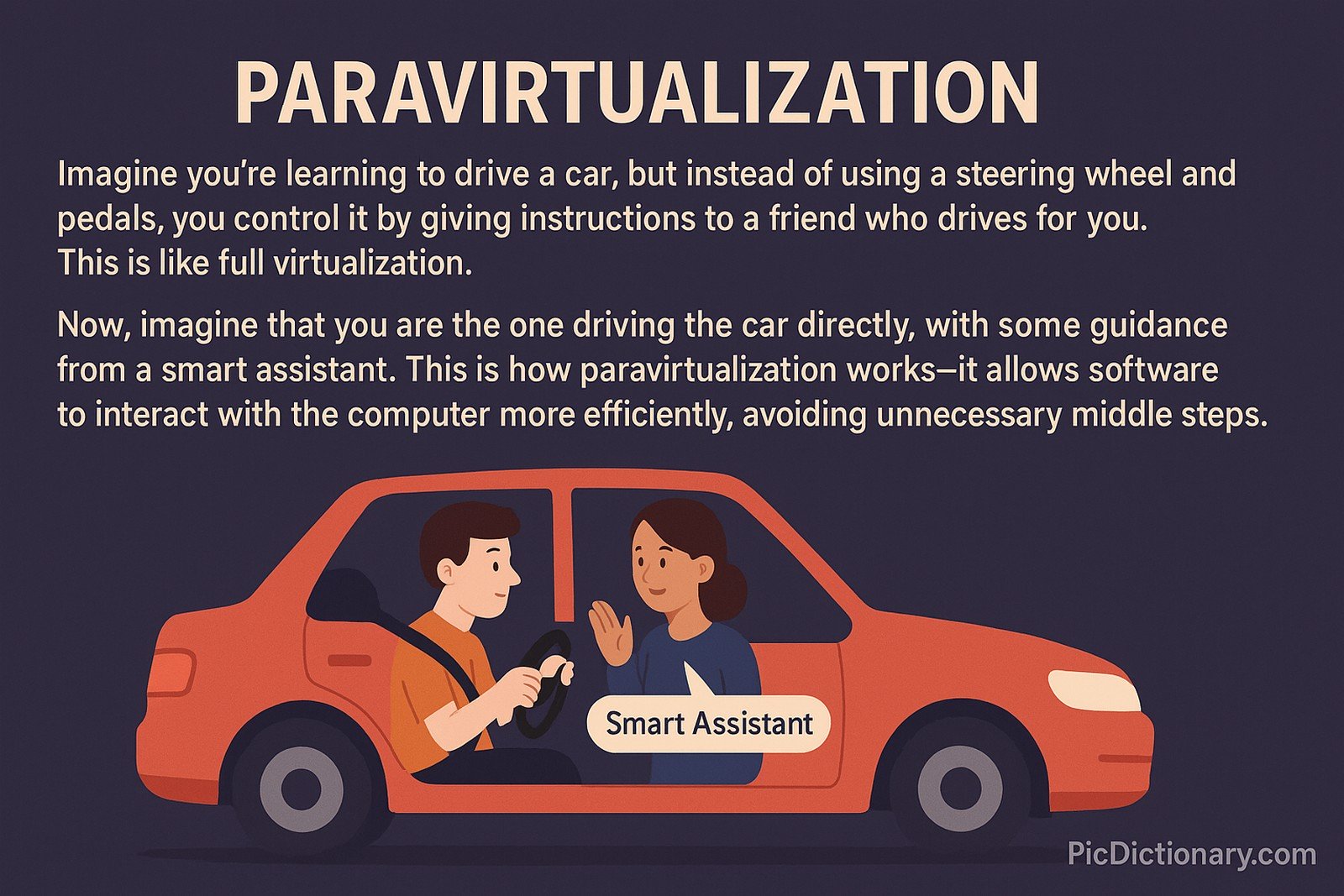
Paravirtualization Origin
Paravirtualization was first introduced as part of the Xen hypervisor project in the early 2000s. It gained traction as an alternative to traditional virtualization methods that relied on complete hardware emulation. With increasing demand for efficient virtualization in data centers and cloud computing, paravirtualization became a preferred approach due to its lower performance overhead.
Paravirtualization Etymology
The term “paravirtualization” combines “para-,” meaning “beside” or “alongside,” with “virtualization.” This reflects the way the guest OS cooperates more closely with the hypervisor rather than being fully abstracted from the hardware.
Paravirtualization Usage Trends
Paravirtualization has been widely adopted in cloud computing environments, particularly in infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) platforms. Technologies such as Xen, VMware ESXi, and KVM support paravirtualization to optimize performance. Over the years, as hardware-assisted virtualization has advanced, paravirtualization has evolved, focusing on hybrid approaches that blend efficiency with compatibility.
Paravirtualization Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Virtualization
- Cloud Computing
- Hypervisors - Typical Collocations:
- "paravirtualized guest OS"
- "paravirtualization drivers"
- "paravirtualization in cloud infrastructure"
- "hypervisor with paravirtualization support"
Paravirtualization Examples in Context
- Many cloud providers use paravirtualization to improve the performance of virtual machines without relying solely on hardware virtualization.
- A paravirtualized guest OS running on Xen can achieve near-native performance due to its optimized interactions with the hypervisor.
- Companies deploying VMware vSphere often enable paravirtualization for disk and network drivers to improve I/O efficiency.
Paravirtualization FAQ
- What is paravirtualization?
Paravirtualization is a virtualization technique that allows a guest operating system to communicate directly with the hypervisor for better performance. - How does paravirtualization differ from full virtualization?
Unlike full virtualization, which emulates hardware, paravirtualization requires modifications to the guest OS to improve efficiency. - What are the advantages of paravirtualization?
Paravirtualization reduces virtualization overhead, improves performance, and enhances resource utilization in cloud environments. - Does paravirtualization require special drivers?
Yes, paravirtualization typically requires specialized drivers or kernel modifications to enable communication between the guest OS and hypervisor. - Which hypervisors support paravirtualization?
Xen, KVM, and VMware ESXi support paravirtualization, often through optimized drivers and APIs. - Is paravirtualization still widely used?
Yes, but it is often combined with hardware-assisted virtualization to balance compatibility and performance.
Paravirtualization Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Virtualization
- Cloud Infrastructure
- Hypervisors
Did you know?
The Xen hypervisor, one of the first platforms to introduce paravirtualization, was originally developed at the University of Cambridge and later became a key component of cloud services used by Amazon Web Services (AWS).
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment