SAN (Storage Area Network)
 (Representational Image | Source: Dall-E)
(Representational Image | Source: Dall-E)
Quick Navigation:
- SAN Definition
- SAN Explained Easy
- SAN Origin
- SAN Etymology
- SAN Usage Trends
- SAN Usage
- SAN Examples in Context
- SAN FAQ
- SAN Related Words
SAN Definition
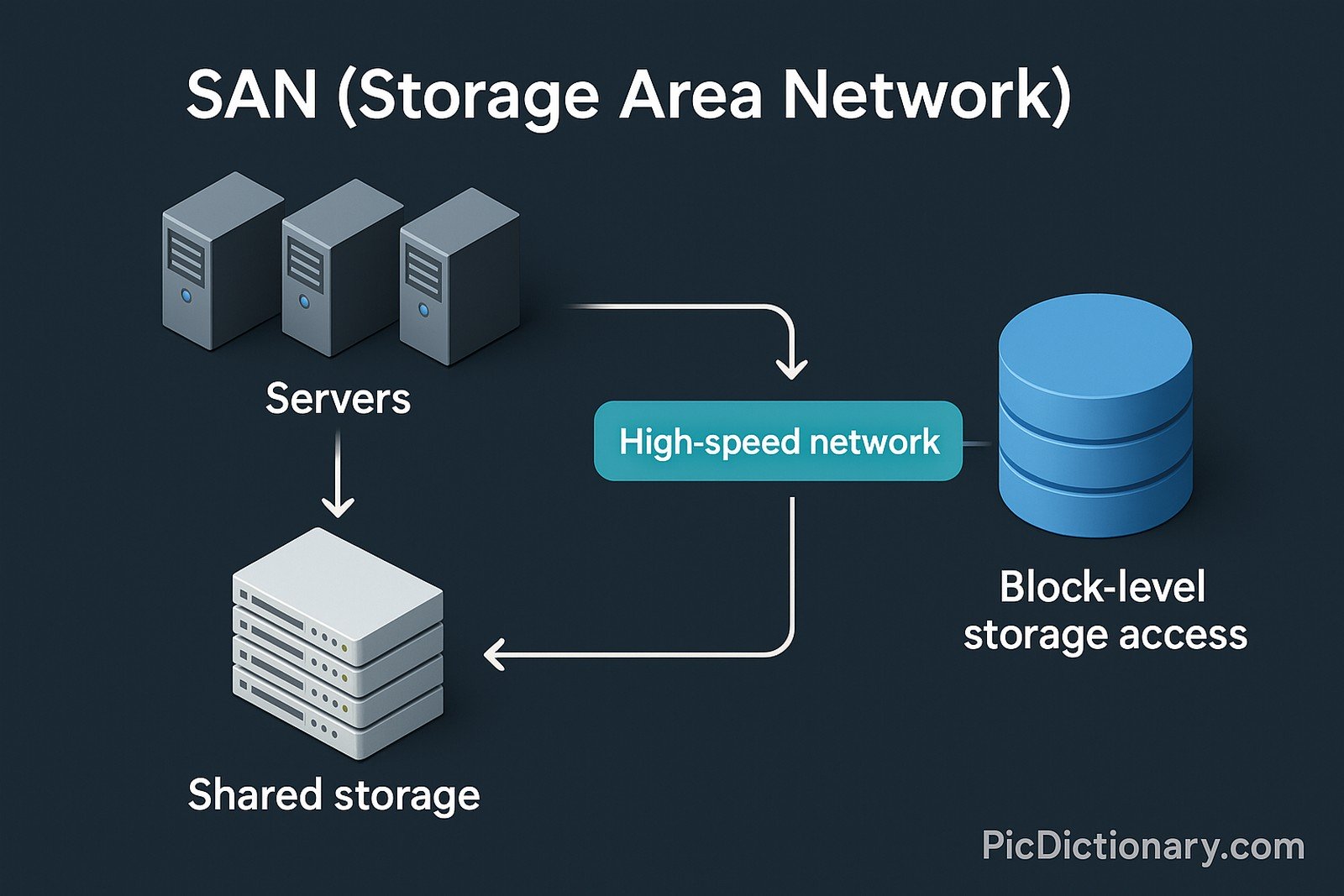
A SAN (Storage Area Network) is a specialized high-speed network that connects servers to a shared pool of storage devices. It enables block-level storage access, providing flexibility, scalability, and efficient data management. SANs are commonly used in enterprise environments where large volumes of data need to be accessed quickly and reliably. SAN architectures rely on technologies like Fibre Channel, iSCSI, and NVMe over Fabrics, allowing multiple servers to access storage devices as if they were locally attached. This separation of storage and servers enhances performance, disaster recovery, and storage utilization.
SAN Explained Easy
Imagine you have several computers that all need to use the same big toy box filled with building blocks. Instead of each computer having its own box, they all connect to one giant, super-fast toy box. Whenever they need a block, they grab it from this shared box quickly and easily. That giant toy box is like a SAN, helping different computers share storage without fighting over it.
SAN Origin
The idea of SAN emerged in the 1990s as organizations required faster access to large amounts of storage separate from their computing systems. Traditional direct-attached storage (DAS) couldn’t keep up with growing data demands. SAN provided a solution, offering scalable and centralized storage accessible over dedicated networks.
SAN Etymology
The term "SAN" was coined from the concept of creating a network that specifically serves storage needs, independent of server functions.
SAN Usage Trends
Over the past two decades, SAN has become a staple in enterprise data centers, especially where data availability and reliability are critical. With advancements in virtualization and cloud computing, SAN technologies have evolved to offer faster protocols, better redundancy, and hybrid setups. Organizations continue to adopt SAN for mission-critical applications and high-performance databases.
SAN Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Storage Networking
- Data Infrastructure
- Enterprise Storage - Typical Collocations:
- "SAN environment"
- "Fibre Channel SAN"
- "SAN storage array"
- "SAN switch configuration"
SAN Examples in Context
- A hospital uses a SAN to store and access medical imaging files from various machines and departments.
- Large financial institutions rely on SANs for high-speed, secure storage access for transaction processing.
- Cloud providers implement SAN to ensure scalability and performance for virtual machine storage backends.
SAN FAQ
- What is a SAN?
A SAN is a high-speed network connecting servers to storage devices, allowing block-level storage access. - How is SAN different from NAS?
SAN provides block-level access, like a local drive, while NAS offers file-level storage over traditional networks. - Why do enterprises use SAN?
Enterprises use SAN for scalability, performance, and reliability in handling large data workloads. - What protocols are commonly used in SANs?
Fibre Channel, iSCSI, and NVMe over Fabrics are commonly used protocols. - Can SANs support virtual environments?
Yes, SANs are widely used in virtual server and desktop environments for efficient storage allocation. - Are SANs expensive to set up?
While initial setup costs are high, SANs provide long-term value for large data environments. - How does SAN improve disaster recovery?
SAN enables replication and quick data recovery across different geographic locations. - Can SAN scale with growing data needs?
Yes, SAN architectures are designed to scale by adding more storage arrays and connections. - Is SAN only for large companies?
Primarily, but small and medium businesses also use entry-level SANs for critical applications. - How does SAN performance compare to traditional storage?
SAN provides significantly faster, more reliable, and redundant storage access compared to traditional DAS.
SAN Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Data Storage
- Networking
- Cloud Infrastructure
- Enterprise Computing
Did you know?
In 1999, the world’s first large-scale SAN was implemented by NASA to handle vast amounts of scientific data generated by space missions, revolutionizing how agencies manage and access high-speed storage for critical operations.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment