Master-Slave Replication
Quick Navigation:
- Master-Slave Replication Definition
- Master-Slave Replication Explained Easy
- Master-Slave Replication Origin
- Master-Slave Replication Etymology
- Master-Slave Replication Usage Trends
- Master-Slave Replication Usage
- Master-Slave Replication Examples in Context
- Master-Slave Replication FAQ
- Master-Slave Replication Related Words
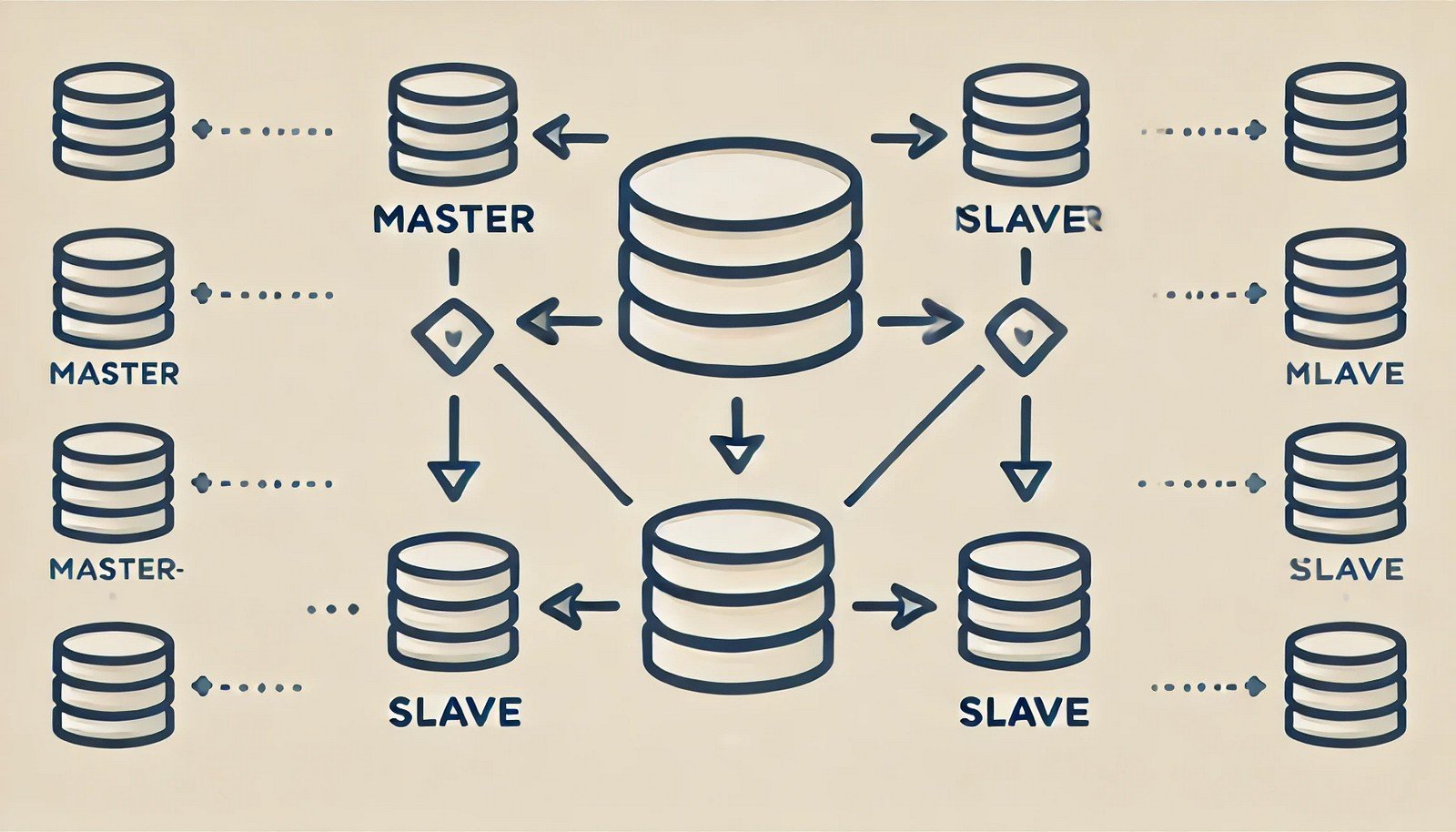
Master-Slave Replication Definition
Master-Slave Replication is a database architecture in which one database server (the master) handles all the write operations, while one or more secondary servers (the slaves) replicate the data from the master. The slaves act as read-only copies of the master, ensuring data redundancy, load balancing, and fault tolerance. This setup is widely used in distributed systems, ensuring high availability and failover capabilities in case the master fails.
Master-Slave Replication Explained Easy
Imagine a teacher writing on a whiteboard (the master), and a group of students copying everything into their notebooks (the slaves). The students can read from their notebooks, but they cannot change what the teacher writes. This way, if a student's notebook gets lost, they can get a copy from another student. Similarly, in databases, the master writes data, and the slaves copy it, ensuring that the information is always available.
Master-Slave Replication Origin
The concept of Master-Slave Replication dates back to early database management systems in the 1970s and 1980s. With the rise of distributed computing, this replication model became an essential strategy to enhance database scalability, backup mechanisms, and fault tolerance.
Master-Slave Replication Etymology
The term “master-slave” in computing originates from a hierarchical control system where one component (the master) dictates operations, while the others (the slaves) follow instructions without modifying the commands.
Master-Slave Replication Usage Trends
Master-Slave Replication has seen widespread adoption in high-traffic applications, such as web services, e-commerce platforms, and cloud databases. While traditional relational databases like MySQL and PostgreSQL support this model, newer distributed systems often replace it with multi-leader or leaderless architectures to enhance flexibility and fault tolerance. Additionally, the term "master-slave" has been increasingly replaced with "primary-replica" due to concerns about inclusive language.
Master-Slave Replication Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Database Replication
- Distributed Systems
- High Availability - Typical Collocations:
- "master-slave architecture"
- "replicated database system"
- "synchronous vs. asynchronous replication"
- "read scalability with master-slave"
Master-Slave Replication Examples in Context
- A MySQL database using master-slave replication ensures that the primary server handles write operations, while read queries are distributed across multiple replicas.
- In cloud computing, master-slave replication is employed to provide backup redundancy across different data centers.
- A large-scale e-commerce website implements master-slave replication to handle millions of transactions per second efficiently.
Master-Slave Replication FAQ
- What is master-slave replication?
It is a database replication technique where a primary (master) database manages all writes, while secondary (slave) databases replicate the data for redundancy and read operations. - How does master-slave replication improve database performance?
It offloads read queries to slave servers, reducing the load on the master and improving overall performance. - What are the challenges of master-slave replication?
Potential issues include replication lag, failover complexity, and data consistency challenges in asynchronous replication. - What is the difference between synchronous and asynchronous replication?
Synchronous replication ensures immediate data consistency across replicas, while asynchronous replication allows a delay between the master and slaves. - Can master-slave replication be used for high availability?
Yes, it is a common strategy to provide failover support in case the master database crashes. - What are some alternatives to master-slave replication?
Multi-master replication, leaderless replication, and sharding are alternative database architectures that offer different advantages. - Does master-slave replication work with NoSQL databases?
Yes, NoSQL databases like MongoDB and Redis implement replication strategies similar to master-slave replication. - Why is the term 'master-slave' being replaced?
Due to concerns about inclusivity, many organizations now use "primary-replica" or "leader-follower" instead of "master-slave." - How do you handle failover in master-slave replication?
Automated failover tools like MySQL Group Replication or PostgreSQL Patroni help switch to a new master if the current one fails. - Is master-slave replication suitable for real-time applications?
It depends on the replication method; synchronous replication supports real-time consistency, while asynchronous replication may have a delay.
Master-Slave Replication Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Database Management
- Distributed Systems
- High Availability
Did you know?
Master-Slave Replication played a crucial role in early internet-scale applications, enabling services like YouTube and Facebook to scale rapidly. Over time, many companies have moved toward multi-leader replication for greater flexibility and redundancy.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment