Persistent Memory
Quick Navigation:
- Persistent Memory Definition
- Persistent Memory Explained Easy
- Persistent Memory Origin
- Persistent Memory Etymology
- Persistent Memory Usage Trends
- Persistent Memory Usage
- Persistent Memory Examples in Context
- Persistent Memory FAQ
- Persistent Memory Related Words
Persistent Memory Definition
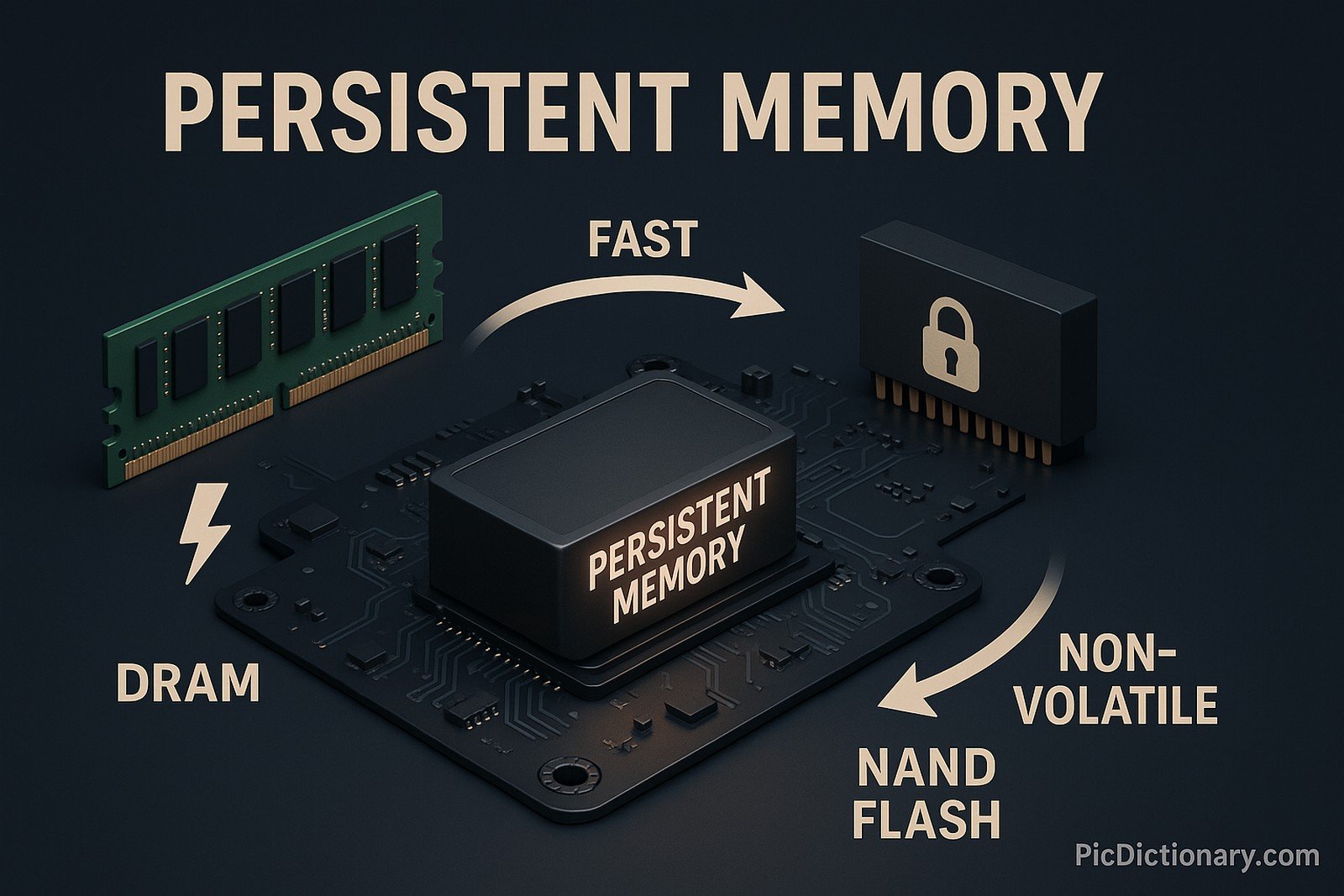
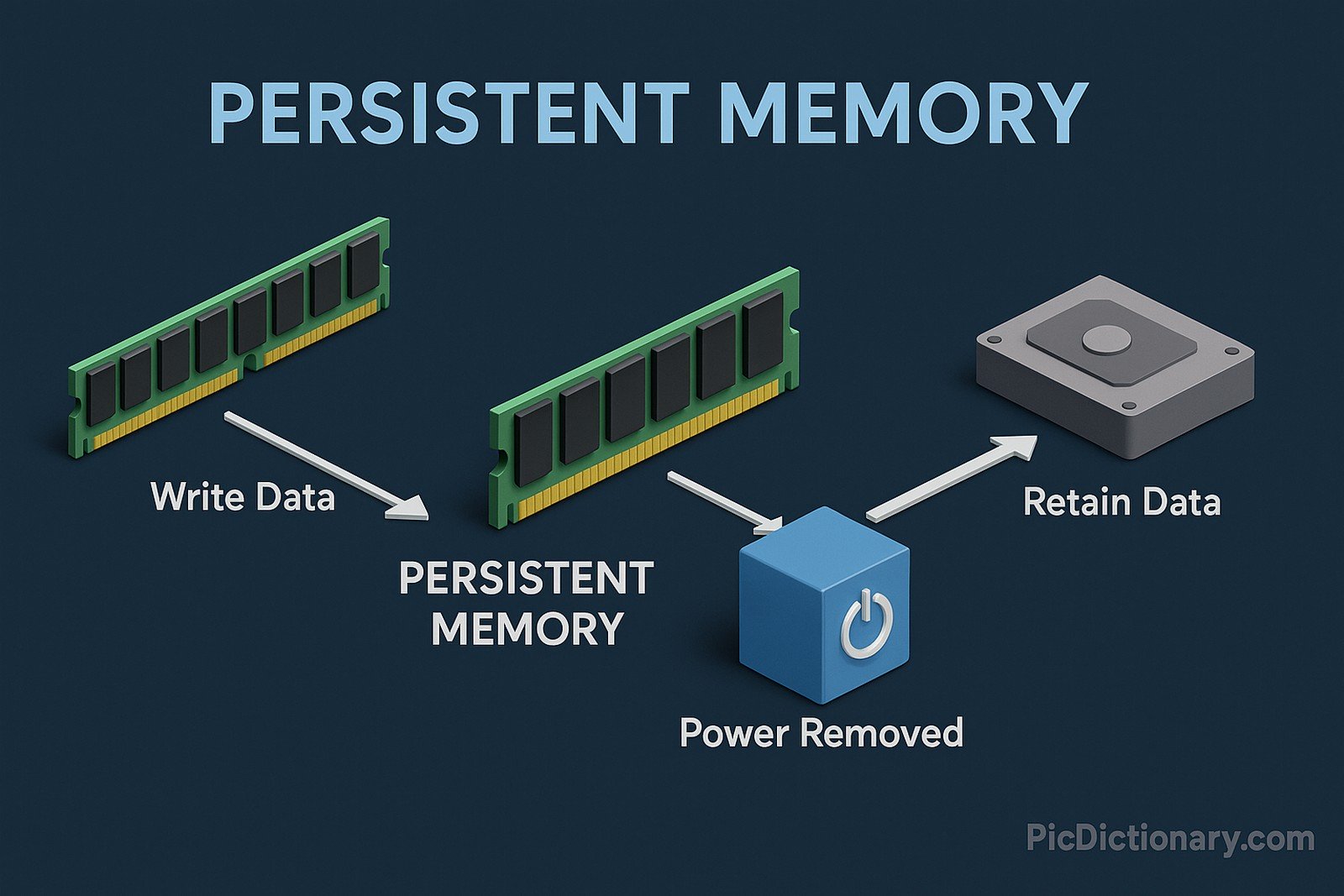
Persistent memory (PMEM) is a type of non-volatile memory that retains data even when the power is turned off. It bridges the gap between traditional RAM and storage devices by offering near-DRAM speeds with the persistence of SSDs. PMEM is commonly used in high-performance computing, databases, and in-memory analytics, allowing systems to store and access large datasets with reduced latency.
Persistent Memory Explained Easy
Imagine you have a notebook where you write down important things, but instead of losing everything when you close it, the notes stay forever! Persistent memory is like that for computers—it remembers data even after a shutdown, unlike regular RAM, which forgets everything.
Persistent Memory Origin
The concept of persistent memory has evolved over decades from research into faster storage solutions. It gained traction with the advent of non-volatile RAM (NVRAM) technologies and was further popularized by Intel Optane and similar developments in the early 21st century.
Persistent Memory Etymology
The term “persistent memory” comes from "persistence," meaning something that continues to exist, and "memory," referring to the data storage component of computers.
Persistent Memory Usage Trends
Persistent memory is increasingly used in data-intensive applications such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cloud computing. Enterprises use PMEM for accelerating databases like SAP HANA and improving performance in storage architectures. With the rising need for real-time processing, PMEM adoption is growing across industries.
Persistent Memory Usage
- Formal/Technical Tagging:
- Non-volatile memory
- High-performance computing
- Persistent storage - Typical Collocations:
- "persistent memory module"
- "NVRAM technology"
- "byte-addressable persistent memory"
- "low-latency persistent storage"
Persistent Memory Examples in Context
- A financial institution uses persistent memory to maintain transaction logs even after unexpected power failures.
- Cloud providers integrate PMEM for faster data retrieval and caching.
- High-performance computing clusters use persistent memory to speed up scientific simulations.
Persistent Memory FAQ
- What is persistent memory?
Persistent memory is a type of non-volatile memory that retains data even when the system is powered off, offering a balance between RAM speed and storage persistence. - How does persistent memory differ from RAM?
Unlike RAM, which loses data when powered off, persistent memory retains information even after shutdown, making it more like storage but with faster access speeds. - Is persistent memory the same as SSD?
No, persistent memory operates at near-RAM speeds and is byte-addressable, whereas SSDs rely on block storage, making PMEM significantly faster for certain applications. - What are common use cases for persistent memory?
Persistent memory is used in databases, caching, artificial intelligence, and real-time analytics where fast and durable data storage is needed. - What are the advantages of persistent memory?
It offers low latency, high-speed data access, and data retention without power, reducing reliance on slower storage devices. - What companies produce persistent memory technology?
Major contributors include Intel (Optane PMEM), Micron, and HPE, among others. - Can persistent memory replace traditional storage?
Not entirely—while PMEM enhances speed and reliability, traditional storage solutions like SSDs and HDDs still offer higher capacities for bulk data. - Does persistent memory require special software?
Yes, applications often need optimizations to fully leverage the benefits of PMEM, such as direct byte-addressable access. - Is persistent memory expensive?
Persistent memory is generally more expensive than DRAM or SSDs but provides significant performance gains, justifying the cost for enterprise applications. - How does persistent memory impact cloud computing?
Cloud services benefit from PMEM by reducing latency and improving storage efficiency, particularly for real-time applications and large-scale databases.
Persistent Memory Related Words
- Categories/Topics:
- Computer Storage
- High-Performance Computing
- Memory Technologies
Did you know?
Persistent memory can significantly reduce server restart times! Instead of reloading massive datasets from storage, applications can instantly access data retained in PMEM, saving hours in recovery time for mission-critical systems.
PicDictionary.com is an online dictionary in pictures. If you have questions or suggestions, please reach out to us on WhatsApp or Twitter.Authors | Arjun Vishnu | @ArjunAndVishnu

I am Vishnu. I like AI, Linux, Single Board Computers, and Cloud Computing. I create the web & video content, and I also write for popular websites.
My younger brother, Arjun handles image & video editing. Together, we run a YouTube Channel that's focused on reviewing gadgets and explaining technology.



Comments powered by CComment